Mixed review
advertisement

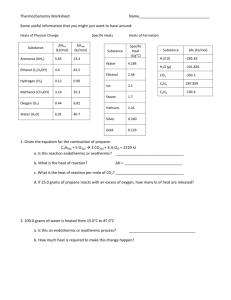
Thermochemistry Mixed Review 1. Define heat 2. Define energy a. Define enthaply 3. What does the law of conversation of energy state? 4. Compare and contrast exothermic and endothermic 5. What is a calorie? 6. Define heat capacity 7. Define specific heat (also include the equation) 8. What is the equation for the heat change in a chemical reaction? 9. What does “delta” or “∆”mean? 10. What is the main characteristic of a thermochemical equation? 11. Define heat of formation 12. How would you solve for the heat of reaction? 13. Convert each of the following quantities: a. 240 Joules to calories b. 1850 kilocalories to calories c. 4.25 kilocalories to Joules 14. How much heat is required to raise the temperature of 32.4 g of mercury from 20.0ºC to 98.0ºC? The specific heat of mercury is 0.13950 J/g x ºC. 15. Find the final temperature if 1932.7 J of energy is added to 27.5 g of water at 21.1ºC. 16. What is the specific heat of a substance if 250 cal are required to raise the temperature of 2.5 g from 10.0ºC to 22.5ºC? 17. Find the heat needed to melt 64.8 g of copper at its melting points. The heat of fusion of copper is 13.38 kJ/ mol. 18. Calculate the change in enthalpy (in kJ) for the following reactions: a. Given: ___SO2 (g) + ___O2 (g) ΔHofSO2 = -296.8 kJ/mole ΔHofSO3 = -395.7 kJ/mole b. ___Al (s) + ___Fe2O3 (s) Given: ___SO3 (g) Al2O3 (s) + ___ Fe (s) ΔHof Fe2O3 = -196 kcal/mole ΔHof Al2O3 = -399 kcal/mole 19. When ammonia reacts with oxygen gas, nitrogen dioxide and water vapor are produced. Thermochemistry Mixed Review __NH3(g) + __O2(g) __NO2(g) + __H2O(g) ΔHº = ? a. Balance the equation. b. Find the change in enthalpy (Hf) for the above equation using the standard heats of formation: ΔHºf NH3(g)= -46.19 kJ/mol ΔHºf NO2(g) = 33.85 kJ/mol ΔHºf H2O(g) = -241.8 kJ/mol 20. From the following data: ΔH = -890 kJ/mol ΔH = 44 kJ/mol at 298 K CH4 + 2O2 -> CO2 + 2H2O H2O(l) -> H2O(g) Calculate the enthalpy of the reaction for: CH4 + 2 O2(g) -> CO2(g) + 2 H2O(g) ΔH = ? 21. Calculate the standard enthalpy change, ΔHo, for the formation of 1 mol of strontium carbonate (the material that gives the red color in fireworks) from its elements. Sr (s) C(graphite ) 3 2 O2 (g) SrCO3 (s) The informatio n available is (1) Sr (s) 1 2 O2 (g) SrO (s) H - 592 kJ (2) SrO (s) CO2 (g) SrCO3 (s) H - 234 kJ (3) C(graphite ) O2 (g) CO2 (g) H - 394 kJ 22. The combination of coke and steam produces a mixture called coal gas, which can be used as a fuel or as a starting material for other reactions. If we assume coke can be represented by graphite, the equation for the production of coal gas is 2 C (s) 2 H2O (g) CH4 (g) CO2(g) Determine the standard enthalpy change for this reaction from the following standard enthalpies of reaction : (1) C(s) H2O (g) CO (g) H2 (g) H 131.3 kJ (2) CO (g) H2O (g) CO2 (g) H2 (g) (3) CH4 (g) H2O (g) 3 H2 (g) CO (g) H - 41.2 kJ H 206.1 kJ The next one is challenging! Thermochemistry Mixed Review 23. One reaction involved in the conversion of iron ore to the metal is FeO (s) CO (g) Fe (s) CO2 (g) Calculate the standard enthalpy change for this reaction from these reactions of iron oxides with CO : (1) 3 Fe2O3 (s) CO (g) 2 Fe3O4 (s) CO2 (g) (2) Fe2O3 (s) 3 CO (g) 2 Fe (s) 3 CO2 (g) H - 47 kJ H - 25 kJ (3) Fe3O4 (s) CO (g) 3 FeO (s) CO2 (g) H 19 kJ