TOPIC: Properties of Matter Do Now: A sample of CO2(s) and a
advertisement

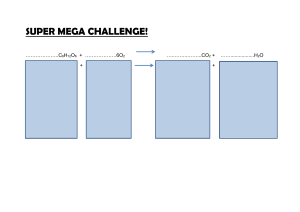
NEW UNIT: UNIT 3 fold next section in your notes TOPIC: Properties of Matter Do Now: Anything that has 1) Define Matter: mass and occupies space 2)Fill in page 2 in packet Properties – used to characterize matter Physical –how they look Chemical – how they react with others Physical Properties • Describe the appearance and form of matter Words: • color, texture, luster, odor, solid, liquid, gas Measurements: • a number and a unit • A sample of CO2(s) and a sample of CO2(g) different in their 1) chemical composition 2) empirical formula 3) molecular structure 4) physical properties Other physical properties include Density, boiling point (BP), and melting point (MP) (where can you find the density of Al? Fe?) Solubility in water (g/ml) (how well it dissolves in water) Intensive Properties: sample size DOES NOT matter Other physical properties like volume and mass depend on sample size Extensive Properties: sample size matters Chemical Properties • Describe how matter behaves in presence of other matter • Describe how matter changes into another kind of matter – Flammable – Corrosive – Ability to neutralize acids or bases Physical or Chemical? • • • • Reddish brown - physical Forms new substances with HNO3 - chemical MP = 1085C - physical Density = 8.92 g/cm3 - physical • Reacts to form green copper carbonate • Shiny - physical • Malleable - physical • BP = 2570C - physical - chemical Matter goes through changes Changes Physical – identity remains the same Chemical – identity of matter changes Physical Change • The form or appearance of sample may change but identity remains same – Cutting, crushing, grinding, tearing • Dissolving is physical change • Think of sugar in water • still have sugar – you just spread it out with water molecules in between • C6H12O6(s) C6H12O6(aq) Aq = dissolved in water • Phase changes are physical changes • No new substance is created (chemical formula stays the same) • Ex: • ice melting: H2O(s) H2O(l) • water boiling: H2O (l) H2O(g) Chemical Change • chemical change - identity of matter is changed • new substance with unique properties is formed • The chemical formula changes • Ex: 2H2O(l) 2H2(g) + O2(g) Burning • Common name for oxidation reaction • Burning means reacting with oxygen • Burning is chemical change, because original substance is changed into new kinds of matter Ex: COMBUSTION CH4(g) + 2O2(g) CO2(g) + 2H2O(g) Evidence of Chemical a Chemical Change • Bubbles (formation of a gas) • Color change • Heat • Light • new substance form (if 2 liquids mix and solid is formed, we call this a precipitate(ppt))