Enthalpy and Hess`s Law

Enthalpy and Hess’s Law
Supplemental Instruction
Iowa State University
Leader: Lilli Howard
Course: Chem 177 (BC)
Instructor: Dr. Irmi
Date: 10/14/13
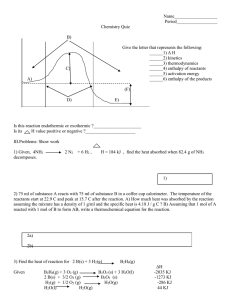
1.
The __________________ _____________ for a substance is its most stable form at the given temperature and pressure.
2.
Fudge is about 2% protein, 11% fat, and 81% carbohydrates. The average “fuel value” of these are as follows: protein = 17 kJ/g fat = 38 kJ/g carb = 17 kJ/g. a.
What is the “fuel value” of 10 g of fudge? How many Calories does 10 g contain?
3.
Calculate the enthalpy change for the reaction: C(s) + ½ O
2
(g)
CO(g)
The following information is given: a.
C(s) + O
2
(g)
CO
2
(g) b.
CO(g) + ½ O
2
(g)
CO
2
(g)
ΔH = -393.5 kJ
ΔH = -283.0 kJ
4.
Calculate the enthalpy change for the reaction: C
2
H
4
(g) + H
2
(g)
C
2
H
6
(l)
The following information is given: a.
C
2
H
4
(g) + 3 O2(g)
2CO
2
(g) + 2 H
2
O(l) b.
2 H
2
(g) + O
2
(g)
2 H
2
O(l) c.
2 C
2
H
6
(l) + 7 O
2
(g)
4 CO
2
(g) + 6 H
2
O(l)
5.
Write the reaction associated with the standard enthalpy of formation for each of the following: a.
AgCl(s) b.
NH
3
(g) c.
Na
2
CO
3
(s)
1060 Hixson-Lied Student Success Center
515-294-6624
sistaff@iastate.edu
http://www.si.iastate.edu
6.
Calculate the standard enthalpy change for the reaction:
CH
2
N
2
(s) + O
2
(g)
CO(g) + H
2
O(l) + N
2
(g)
The following information is given: a.
CO(g) = -110.5 kJ/mol b.
CH2N2(s) = +62.4 kJ/mol c.
H2O(l) = -285.8 kJ/mol
7.
A small coffee cup calorimeter contains 110 g of water at 22.0 °C. A 100 g sample of lead is heated to 90.0°C and then placed in the water. The contents of the calorimeter come to a temperature of 23.9°C. What is the specific heat of lead?