Thermochemistry - Madison Public Schools
advertisement

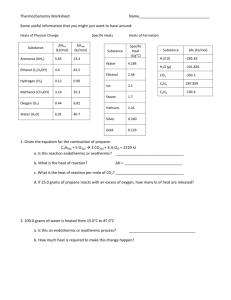
Reaction Energy and Reaction Kinetics Thermochemistry Thermochemistry Objectives: 1. Define heat and temperature. 2. Perform specific heat calculations. Temperature and Heat Temperature – measure of the average kinetic energy of the particles of a substance. What are the units? oC, K Heat – the flow of energy from one substance to another. What are the units? Joules, calories, Calories, kJ, kcal 1 cal = 4.184 J Specific Heat Specific Heat (C): the amount of energy needed to raise the temperature of 1 gram of a substance by 1 degree celcius For water: C = 4.184 J/goC C = 1 cal/g0C Specific Heat q m C T q = heat (joule or cal) m= mass (grams) C = specific heat (J/g*C) or (cal/g*C) ΔT= change in temperature (oC) Specific Heat Problems 1. Determine the specific heat of a material if a 35 g sample absorbed 48 J as it was heated from 293K to 313K. 2. If 980 kJ of energy are added to 6.2 L of water at 18oC, what will the final temperature be? Heat of Reaction Enthalpy (H) – heat content of a system Enthalpy change (ΔH) – amount of energy absorbed or lost by a system during a process at constant pressure. ΔH = Hproducts- Hreactants Heat of Reaction Heat of Reaction Combustion of propane C3H8 (g) + 5 O2(g) 3 CO2 (g) + 4 H2O(g) + 2043 kJ ΔH = -2043 kJ (exothermic) Formation of synthesis gas C(s) + H2O(g) +113kJ CO(g) + H2(g) ΔH = +113 kJ (endothermic) Sample Problems 1. How much heat will be released when 6.44 g of sulfur reacts with excess O2 according to the following equation? 2 S + 3 O2 2 SO3 ΔH = -791.4 kJ 2. How much heat is transferred when 9.22 g of glucose (C6H12O6) in your body reacts with O2 according to the following equation? C6H12O6 (s) + 6 O2(g) 6 CO2 (g) + 6 H2O(l) ΔH= -2803 kJ Heat of Formation Molar Heat of Formation (∆Hf0 ) – energy change that occurs when 1 mole of a compound forms from the combination of its elements. H2 (g) + 1/2 O2 (g) H2O(l) C(s) + O2 (g) CO2 (g) ∆Hf0 = -285.8 kJ/mol ∆Hf0 = -393.5 kJ/mol Stability and Heat of Formation Al2O3 (s) -1676.0 kJ/mol CaCO3(s) -1206.92 kJ/mol NO(g) 90.29 kJ/mol O3(g) 142.7 kJ/mol • Stability goes with a high negative heat of formation. Heat of Combustion Heat of Combustion (∆Hc0) –energy released with the combustion of one mole of a substance. C3H8(g) + 5 O2(g) 3 CO2(g) + 4 H2O(l) ∆Hc0 = -2219.2 kJ/mol