Ultimate Thermochemistry Worksheet
advertisement
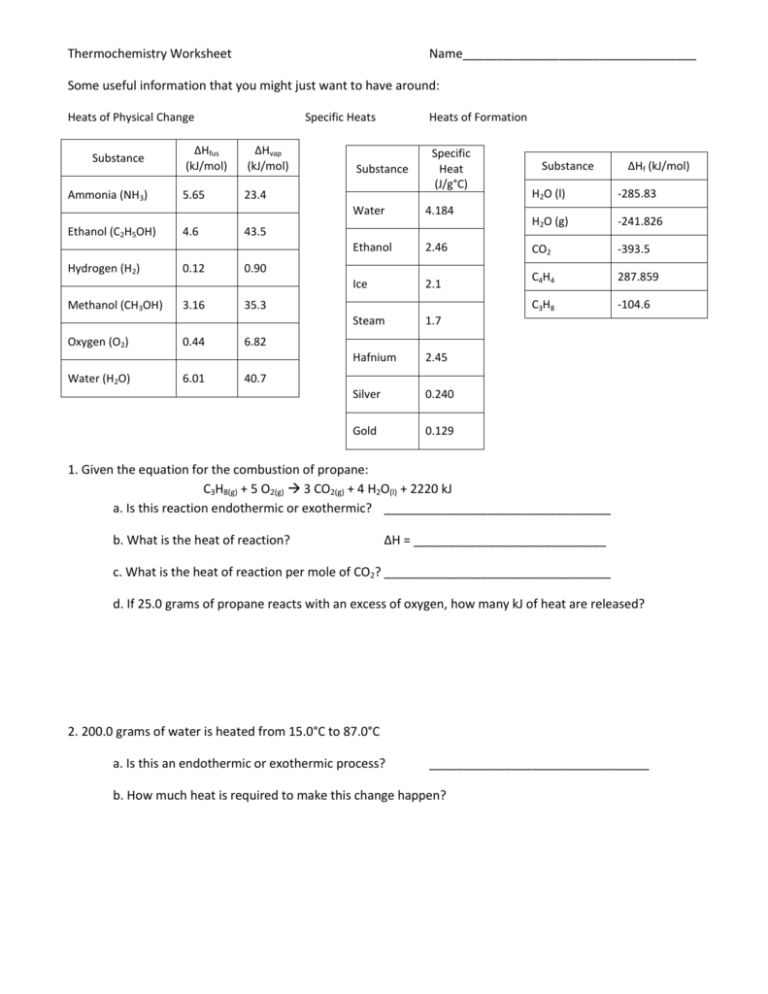
Thermochemistry Worksheet Name__________________________________ Some useful information that you might just want to have around: Heats of Physical Change Substance Ammonia (NH3) Ethanol (C2H5OH) Hydrogen (H2) Methanol (CH3OH) Oxygen (O2) Water (H2O) Specific Heats ΔHfus (kJ/mol) ΔHvap (kJ/mol) 5.65 23.4 4.6 0.12 3.16 0.44 6.01 Heats of Formation Substance Specific Heat (J/g°C) Substance ΔHf (kJ/mol) H2O (l) -285.83 H2O (g) -241.826 2.46 CO2 -393.5 Ice 2.1 C4H4 287.859 C3H8 -104.6 Steam 1.7 Hafnium 2.45 Silver 0.240 Gold 0.129 Water 4.184 Ethanol 43.5 0.90 35.3 6.82 40.7 1. Given the equation for the combustion of propane: C3H8(g) + 5 O2(g) 3 CO2(g) + 4 H2O(l) + 2220 kJ a. Is this reaction endothermic or exothermic? _________________________________ b. What is the heat of reaction? ∆H = ____________________________ c. What is the heat of reaction per mole of CO2? _________________________________ d. If 25.0 grams of propane reacts with an excess of oxygen, how many kJ of heat are released? 2. 200.0 grams of water is heated from 15.0°C to 87.0°C a. Is this an endothermic or exothermic process? ________________________________ b. How much heat is required to make this change happen? 3. A piece of silver is cooled releasing 450 kJ of heat. It changes temperature from 125.0°C to 10°C. What is the mass of this piece of silver? 4. When 15.3 g of sodium nitrate, NaNO3,was dissolved in 250 mL water in a calorimeter, the temperature fell from 25.00oC to 21.56oC. What is the enthalpy change when one mole of NaNO3 dissolves? 5. Calculate the enthalpy change for the reaction given below, using thermodynamic tables above C2H4(g) + O2(g) → H2O(g) + CO2(g) (not balanced) 6. When 1.14 g of S is burned to give SO2, 10.3 kJ is released. From this information write the balanced equation, inserting the ΔH value (per mole) on the proper side of the equation. 7. A piece of hot hafnium weighing 15.6 g at a temperature of 160.0°C is dropped into 125 g of ethanol that has an initial temperature of 20.0°C. What is the final temperature that is reached, assuming no heat loss to surroundings? 8. A 2.05 g solid is heated to 74.21°C and immersed in 26.05 g H2O in a constant-pressure calorimeter. The initial temperature of the water is 27.20°C and csolid = 0.519 J/g K. What is the change in temperature for the water and the solid? 9. Hydrazine (N2H4) reacts with chlorine gas according to the following equation. N2H4 (l) + 2 Cl2 (g) 4 HCl (g) + N2 (g) ∆H = - 420.0 kJ Calculate the change in enthalpy for this reaction under each of the following conditions. a. 25.4 g hydrazine reacts with excess chlorine b. 1.45 mol HCl (g) is generated 10. Sodium hydroxide and hydrochloric acid react in a 1:1 ratio. If 20.0 g of solid NaOH are added to 1000 mL of a solution containing 0.500 moles of HCl, the temperature of the solution rises 6.9oC. Assuming that the total solution mass is 1000 g and the specific heat of the solution is 4.184 J/goC, calculate the heat released by this reaction. Then calculate ΔHrxn (i.e., the heat released per mole of NaOH). 11. Using the ∆H°f values in the table, determine the standard heats of reaction for the combustion of propane (C3H8) gas. 12. Given the following reactions: S(s) + O2(g) → SO2(g) ΔH = -297 kJ/mol SO2(g) + ½ O2(g) → SO3(g) ΔH = -141 kJ/mol calculate the ΔH for the reaction: S(s) + 3/2O2(g) → SO3(g) 13. "Water gas" is an industrial fuel composed of a mixture of carbon monoxide and hydrogen gases. When this fuel is burned, carbon dioxide and water result. From the information given below, write a balanced equation and determine the enthalpy of this reaction: CO(g) + ½ O2(g) → CO2(g) + 282.8 kJ H2(g) + ½ O2(g) → H2O(g) + 241.8 kJ 14. To produce the original "water gas" mixture, carbon (in a combustible form known as coke) is reacted with steam: 131.4 kJ + H2O(g) + C(s) → CO(g) + H2(g) From this information and the equations in the previous problem, calculate the enthalpy for the combustion of carbon to form carbon dioxide. 15. Given the following two reactions and corresponding enthalpy changes, CO2 (g) + SiO (g) SiO2 (s) + CO (g) ∆H = - 520.9 kJ 8 CO2 (g) + Si3N4 (s) 3 SiO2 (s) + 2 N2O (g) + 8 CO (g) ∆H = + 461.05 kJ Compute the change in enthalpy for the following reaction. 5CO2 (g) + Si3N4 (s) 3 SiO (g) + 2 N2O (g) + 5 CO (g) 16. How much energy is involved in taking 25.0 g of ice at -18.7°C, melting it, heating the liquid, and eventually boiling it all away?