Human Blood Circulation
advertisement

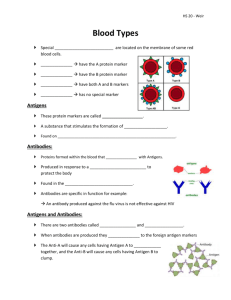
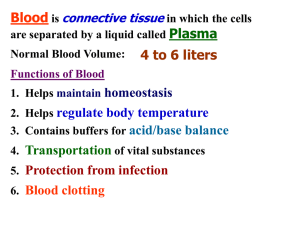
Human Blood Circulation Human circulation facts: 1. About 70 ml of blood with each contraction of heart 2. Human heart has the pericardium (around), the epicardium (outer), myocardium (middle layer of muscle responsible for the majority of the pumping), endocardium (inner) 3. Average resting pulse rate is 60 per second. What is yours? 4. Heartbeat is controlled by the SA node (sinoatrial node) located in the upper corner of the right atrium. Basically it contracts, causing ions to rush to muscles cells around it causing them to contract as well. The impulse is passed to the ventricle by the AV node. When a person has a pace maker, it is the SA Node that is replaced. 5. Blood flow – Right Atrium collects, right ventricle sends to the pulmonary circuit to the lungs. Oxygenated blood returns to the Left Atrium and pumped to the body by the Left Ventricle. 6. Capillaries are very thin arteries used to transfer nutrients and gasses to and from the circulatory system. In the lungs, oxygen will enter the circulatory system through the capillaries by diffusion, while the carbon dioxide will leave through diffusion. 7. Some of this blood entering the capillaries can be lost, around about 1 % of it. This blood enters the lymphatic system by travelling through the interstitial fluid in the body Eventually this blood enters the lymphatic which are structured like veins with valves preventing backflow. This is how White Blood Cells are carried through the body to make an immune response. 8. Blood pressure is representing by two numbers, the systolic over the diastolic. Systolic represents the maximum amount of pressure represented by the heart, the diastolic represents blood flow at a constant level. 120 over 80 is considered to be average, healthy. 9. Hypertension is having high blood pressure. Often the result of a high systolic numbers because the arteries can harden, for many reasons, causing them to be less elastic, raising the pressure. 10.Heart Attack – generally caused by a lack of blood flow to an area of the heart caused by the blockage or damage to a coronary artery. 11.Stroke – blood is blocked in the arteries of the brain by a clot, causing death to the cells around it. Blood Typing Humans use the A-B-O blood typing. If different types of blood are mixed, meaning type A and type B, antibodies in the plasma will cause the blood to be incompatible and clot. Can cause large problems if one is given a blood transfusion of the wrong blood, or an organ is donated. Blood Group Antigen on RBC Antibody in Plasma A A Anti B B B Anti A AB A,B none O none Anti A , Anti B Rh factors – sometimes found on the surface of RBC If Rh +, Rh antigen is on the RBC. If Rh-, there is no antigen on the cell. Antibodies may develop if Rh+ is transferred to Rh-, as can happen if there is an Rh- other an Rh+ baby. After the first pregnancy, an Rh- mother may produce antibodies to fight Rh+ blood. In the 2nd pregnancy, the antibodies slip from the mother to the baby and attack the fetal blood. As a solution, within 72 hours of the first child’s birth, the mother is given Rh antibodies to level the fetal blood still in her so that the body does not produce antibodies.