extra info- blood types
advertisement
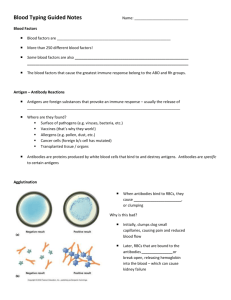
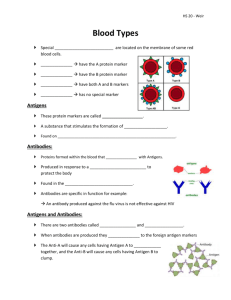
Human Blood GroupsMultiple Alleles AND CoDominance OK… Humans and many other primates Recall: There are three different alleles for human blood type (multiple alleles): Alleles Blood Type IA IB A i O B •“A” indicates the presence of 1 type of antigen (protein that can “activate” your immune system) and “B” represents a different antigen on the surface of a red blood cell •“O” has no antigen on the surface of the RBC Allele from Parent 1 A Allele from Genotype of Blood types Parent 2 offspring of offspring (Phenotype) A AA A A O AO A B B BB B B O BO B A B AB AB O O OO O Antibodies • A “foreign” antigen will trigger your immune system to create antibodies. • Since antibodies are proteins, they have a specific shape & will attach onto the antigen for which they were made. • There are bacteria in the atmosphere that have a very similar shape to our “A” and “B” antigens & we are exposed to them as soon as we are born. • Therefore, each person can have antibodies against an antigen they didn’t inherit. • These antibodies are floating around in our blood with our RBC’s. • Type A blood (has A antigens on cell surface) has Anti-B antibodies – Antibodies are named for what they attack – Anti-B antibodies attack and will clump up (agglutinate) in the presence of B-antigen • Type B blood (has B antigens on cell surface) has A-antibodies • Type AB blood doesn’t have any antibodies • Type O blood has Anti-A and Anti-B antibodies Rh Factor • The Rh factor genetic information is also inherited from our parents, but it is inherited independently of the ABO blood type alleles (a separate gene). •There are 2 different alleles for the Rh factor known as Rh+ and Rh-. •Normal dominant/recessive inheritance •Positive (+) allele is dominant to negative (-) allele •Rh +: you have the protein Rh-: you don’t Mother Father Child Rh- Rh+ Rh+ Rh- Rh- Rh- The “Rh Issue”… Mom = Rh- Baby #1 = Rh+