Circulatory Unit Guide Notes
advertisement
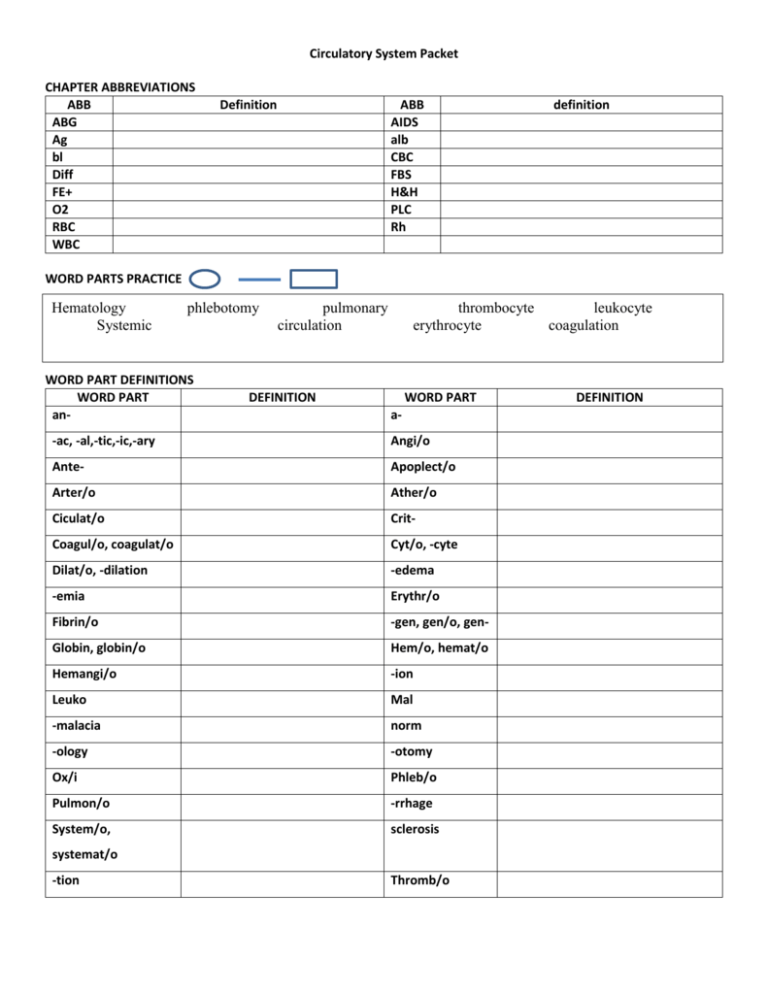
Circulatory System Packet CHAPTER ABBREVIATIONS ABB ABG Ag bl Diff FE+ O2 RBC WBC Definition ABB AIDS alb CBC FBS H&H PLC Rh definition WORD PARTS PRACTICE Hematology Systemic phlebotomy WORD PART DEFINITIONS WORD PART an- pulmonary circulation thrombocyte leukocyte erythrocyte coagulation DEFINITION WORD PART a- -ac, -al,-tic,-ic,-ary Angi/o Ante- Apoplect/o Arter/o Ather/o Ciculat/o Crit- Coagul/o, coagulat/o Cyt/o, -cyte Dilat/o, -dilation -edema -emia Erythr/o Fibrin/o -gen, gen/o, gen- Globin, globin/o Hem/o, hemat/o Hemangi/o -ion Leuko Mal -malacia norm -ology -otomy Ox/i Phleb/o Pulmon/o -rrhage System/o, sclerosis systemat/o -tion Thromb/o DEFINITION CIRCULATORY VOCAB Term Anemia Antibody Coagulation Coronary circulation Erythrocyte Hematocrit Hemoglobin Immunity Inflammation Definition Below normal number of RBC Molecule that interacts with specific antigen Security against a particular disease Localized protective response to injury or destruction of tissue resulting in pain, heat, redness, swelling and LOF Leukocyte Phlebotomy Plasma: Pulmonary circulation Systemic Circulation Thrombocyte Using pages185-186 List and define 3 types of circulation: 1. 2. 3. What is the main difference between Pulmonary and Systemic circulation? Blood functions: In your own words from your W.A. list the functions of blood **the body contains about 5 liters of blood. It makes up about 8% of the body’s weight!** Key terms: - antigen: - antibodies: antibodies bond with antigens = A person’s blood type is inherited Each person inherits 2 genes, one from each parent that control the production of antigens. - Dominant genes o o o EX: - Recessive genes o o o EX: Blood type is determined by antigens on the surface of the RBC Four Blood Types: A: B: AB: O: Immune system has a tolerance against its own antigens. EX: Antigen A does not affect Type A Blood. So the person will not form anti – A antibodies. (remember antibodies lock onto antigens to destroy them) The person with Type B blood will make antibodies against the A antigen Antigens on RBC’s Blood Type A B AB O Antibodies in Plasma Complete the table showing which blood can be safely transfused from the donor to recipient. DONOR RECIPIENT Blood Type A B AB O A B Transfusions - if Type A gets matched with Type B then - if this test is not done Type O blood o because it lacks Type AB blood - universal recipients because they lack AB O Rh Factor antigen - found - Rh - : - Rh+ : - about 85% of Americans are Rh + - if Rh + blood is giving to Rh – then the body thinks it is an invading pathogen and starts form antibodies for the lock and key Rh Factor Health Concern - when an Rh- mother delivers an Rh+ baby, some of the baby’s blood may contact the blood of the mother. - If the mother has another Rh+ pregnancy the antibodies will attack the baby’s blood causing erythroblastosis fetalis. Disorder Etiology S/S TX LYMPHATIC SYSTEM The Lymphatic & Immune Systems Outline (pg. 234) What structures do the lymphatic & immune systems share? 1. 2. 3. What is the function of both systems? What systems are the lymphatic & immune systems similar to & why? What is the function of lymph? What does lymph contain? Does it contain RBC or platelets? What are the smallest parts of the lymphatic system? What is the fluid in the spaces between tissues called? What are lymph nodes & what is their function? What are lymphocytes? What is the function of the lymph vessels?











