Answers - Chemistry Courses: About
advertisement

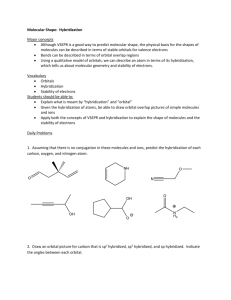
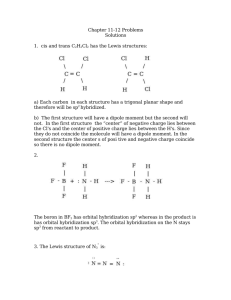
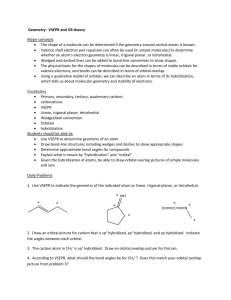
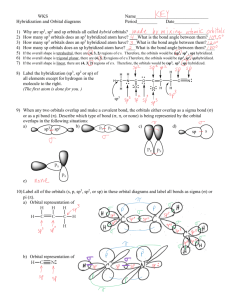
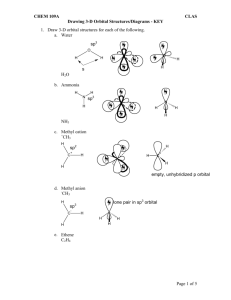
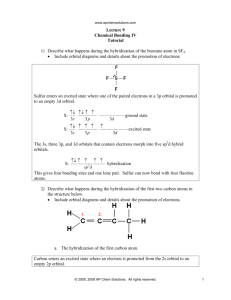
Molecular Shape: Hybridization Major concepts Although VSEPR is a good way to predict molecular shape, the physical basis for the shapes of molecules can be described in terms of stable orbitals for valence electrons Bonds can be described in terms of orbital overlap regions Using a qualitative model of orbitals, we can describe an atom in terms of its hybridization, which tells us about molecular geometry and stability of electrons. Vocabulary Orbitals Hybridization Stability of electrons Students should be able to: Explain what is meant by “hybridization” and “orbital” Given the hybridization of atoms, be able to draw orbital overlap pictures of simple molecules and ions Apply both the concepts of VSEPR and hybridization to explain the shape of molecules and the stability of electrons Daily Problems 1. Assuming that there is no conjugation in these molecules and ions, predict the hybridization of each carbon, oxygen, and nitrogen atom: 2. Draw an orbital picture for carbon that is sp3 hybridized, sp2 hybridized, and sp hybridized. Indicate the angles between each orbital. 3. The carbon atom in CH3+ is sp2 hybridized. Draw an orbital overlap picture for this ion. H H C H 4. According to VSEPR, what should the bond angles be for CH3+.? Does this match your orbital overlap picture from problem 3? In VSEPR, three areas of electron density means the geometry is trigonal planar and a bond angle of 120o. The picture in #3 is accurate. All the H-C-H have an angle of 120o, and the “empty” orbital is perpendicular. 5. The nitrogen atom in NH3 is sp3 hybridized. Draw an orbital overlap picture for this molecule. N H H H 6. According to VSEPR, what should the bond angles be for NH3.? Does this match your orbital overlap picture from problem 5? According to VSEPR, there are 4 areas of electron density, which means the geometry is tetrahedral with a bond angle of 109.5o. The picture in #5 is accurate with a H-N- H angle of ~109.5 o. Cumulative problems 7. Draw an orbital overlap picture for ethanal. 8. Draw an orbital overlap picture for ethene. H H C H C H 9. Indicate which of the following lone pairs is more stable, and explain with a physical justification. (Physical justifications include comparing resonance stabilized vs. non-resonance stabilized structures, comparing relative stability of orbitals (sp > sp2 > sp3), or electrons on a more vs. less electronegative atom.) sp more sp2 more stable stable more than sp3 than sp3 electroneg resonance stabilized resonance stabilized Extension problems 10. Which of these structures conveys more information? Explain. A B Compound A conveys connectivity. Compound B conveys both connectivity and shape/orientation in 3D. 11. Using models, explain one way in which these two compounds are the same, and one way in which they are different. Both show the same connectivity of atoms. They show different orientations in space (i.e. if the carbon atoms are all overlapped, the compound on the left would have the chlorine pointed away from you, while the compound on the right would have the chlorine atom pointed towards you).