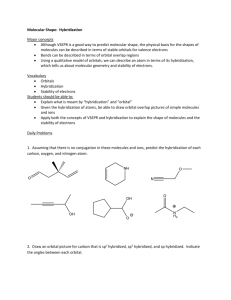
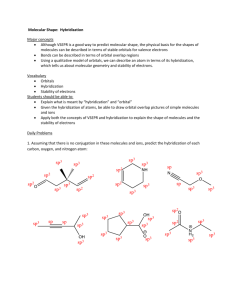
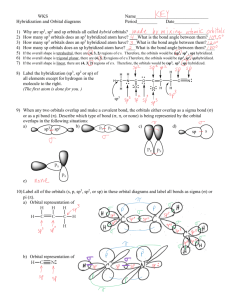
Discussion: Ch 1
advertisement
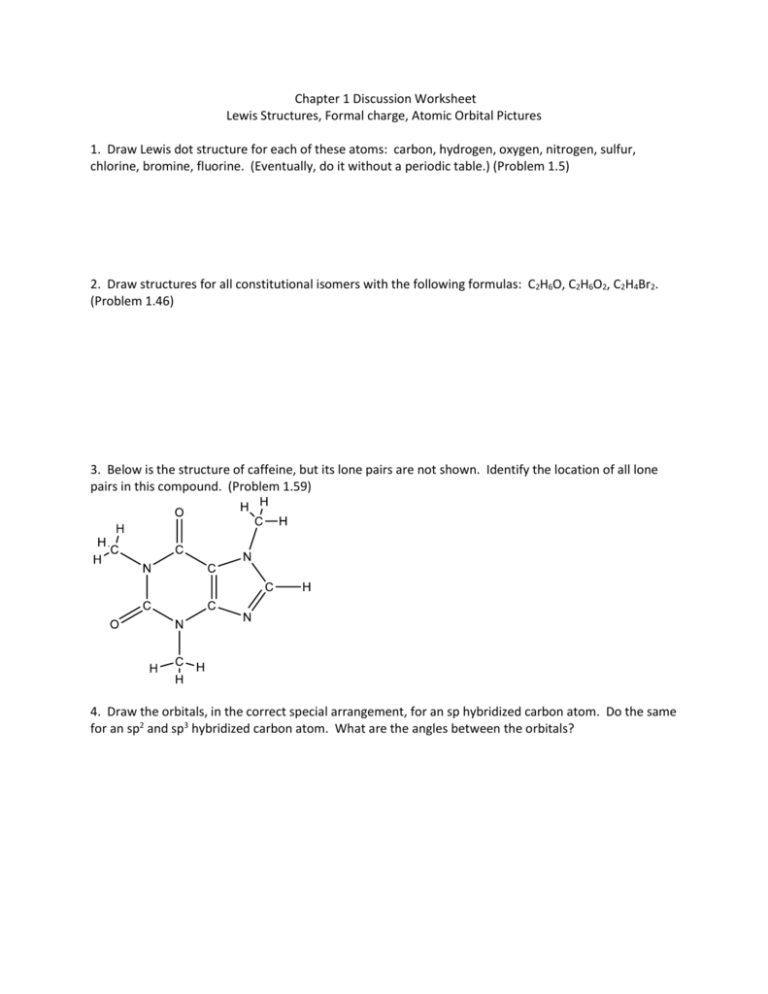
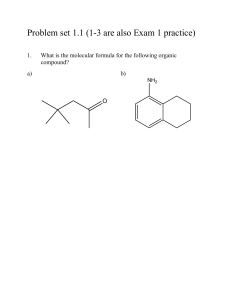
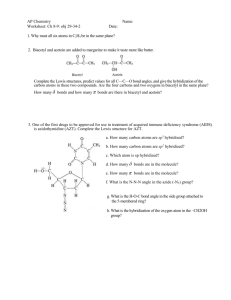
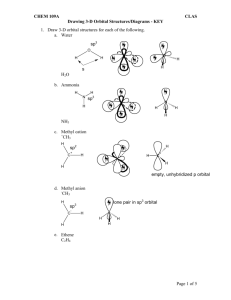
Chapter 1 Discussion Worksheet Lewis Structures, Formal charge, Atomic Orbital Pictures 1. Draw Lewis dot structure for each of these atoms: carbon, hydrogen, oxygen, nitrogen, sulfur, chlorine, bromine, fluorine. (Eventually, do it without a periodic table.) (Problem 1.5) 2. Draw structures for all constitutional isomers with the following formulas: C2H6O, C2H6O2, C2H4Br2. (Problem 1.46) 3. Below is the structure of caffeine, but its lone pairs are not shown. Identify the location of all lone pairs in this compound. (Problem 1.59) 4. Draw the orbitals, in the correct special arrangement, for an sp hybridized carbon atom. Do the same for an sp2 and sp3 hybridized carbon atom. What are the angles between the orbitals? 5. Below are two CH3 molecules, one with a lone pair, one with no lone pair. Both are ions. Give a formal charge to each. The carbon with no lone pair is sp2 hybridized. The carbon with a lone pair is sp3 hybridized. Draw an orbital overlap picture of both ions. How are they different? Why are the hybridizations different? (Based on problem 1.27) 6. Draw Lewis structures for CH3CH3 and CH2=CH2. Identify the sigma bonds and pi bonds in each molecule. Given that the molecule with no pi bonds has sp3 hybridized carbons and the molecule with a pi bond has sp2 hybridized carbons, draw orbital overlap pictures for both molecules. Use these pictures to explain why sigma bonds experience free rotation at room temperature, but pi bonds do not. (Problem 1.21) 7. Label any atoms with formal charges on the Lewis structures. What pattern do you see? Draw orbital overlap pictures for these molecules. How are they similar? (All the carbon, nitrogen, and oxygen atoms in these molecules are sp2 hybridized, and the indicated lone pair is in a p orbital.) 8. Bonds between carbon and oxygen are more polar than bonds between sulfur and oxygen. Nevertheless, sulfur dioxide (SO2) exhibits a dipole moment while carbon dioxide (CO2) does not. Explain. (Problem 1.31) 9. There are two different conmpunds with molecular formula C2H6O. One of these isomers has a much higher boilig point than the other. Explain why. (Problem 1.60)