File

Hybridization
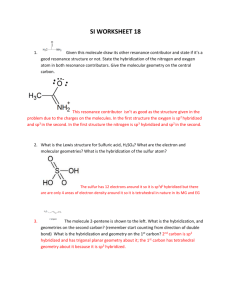
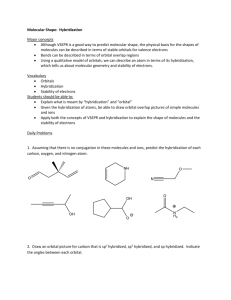
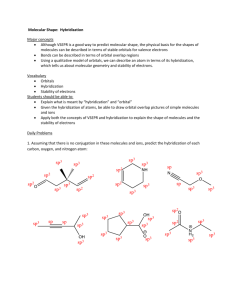
1. Ethene can be hydrogenated in the presence of a nickel catalyst to give ethane.
State the change in the type of hybridization that occurs on the carbon atoms during this process and state how the number of σ and π bonds changes from ethene to ethane.
_____________________________________________________________________________________
_____________________________________________________________________________________
_____________________________________________________________________________________
_____________________________________________________________________________________
_____________________________________________________________________________________
2. Consider the carbon atom marked with an arrow in the structure of the indicator phenolphthalein.
Phenolphthalein, which has the structure on the left in acid solution, is colourless but in alkali solution it has the structure on the right and is pink. Explain in terms of hybridization what happens to the labelled carbon atom as the pH changes from acid to alkali.
_____________________________________________________________________________________
_____________________________________________________________________________________
3. Hydrazine, N
2
H
4
, can be synthesised by reacting ammonia with hydrogen peroxide:
2NH
3
+ H
2
O
2
→ H
2
N-NH
2
+ 2H
2
O
It can react with propanone, (CH
3
)
2
C=O, by a condensation reaction to form a compound called a hydrazone which has the formula (CH
3
)
2
C=N-NH
2
. State the type of hybridization that occurs on the nitrogen atoms in ammonia, hydrazine and the hydrazone.
_____________________________________________________________________________________
_____________________________________________________________________________________
_____________________________________________________________________________________
4. Hydrogen cyanide, HCN, reacts with bromoethane to give a nitrile, C2H5CN, which can then be hydrolysed to form propanoic acid, C2H5COOH. Identify the type of hybridization shown by the carbon atom in hydrogen cyanide and state what happens to it as the carbon atom becomes part of first the nitrile then the carboxylic acid.
_____________________________________________________________________________________
_____________________________________________________________________________________
____________________________________________________________________________________
5. Deduce the type of hybridization shown by beryllium in beryllium dichloride, BeCl
2
.
_____________________________________________________________________________________
_____________________________________________________________________________________
_____________________________________________________________________________________
Answers
1. In ethene both carbon atoms are sp 2 hybridized whereas in ethane they are both sp 3 hybridized.
Ethene contains five σ bonds and one π bond. In ethane there are seven σ bonds and no π bonds.
2. The hybridization changes from sp 3 to sp 2 . (This allows for much greater conjugation in the cation and hence explains why phenolphthalein is coloured in alkaline solution.)
3. The nitrogen atom in ammonia is sp 3 hybridized. Both nitrogen atoms in hydrazine are also sp 3 hybridized. In the hydrazone the nitrogen atom bonded to carbon is sp 2 hybridized and the remaining nitrogen atom in the –NH
2
group is sp 3 hybridized.
4. The carbon atom in HCN is sp hybridized. It is also sp hybridized in the nitrile but is sp 2 hybridized in the carboxylic acid.
5. Beryllium is sp hybridized in beryllium dichloride, BeCl
2
.