Grade 5 Science Scope & Sequence
advertisement
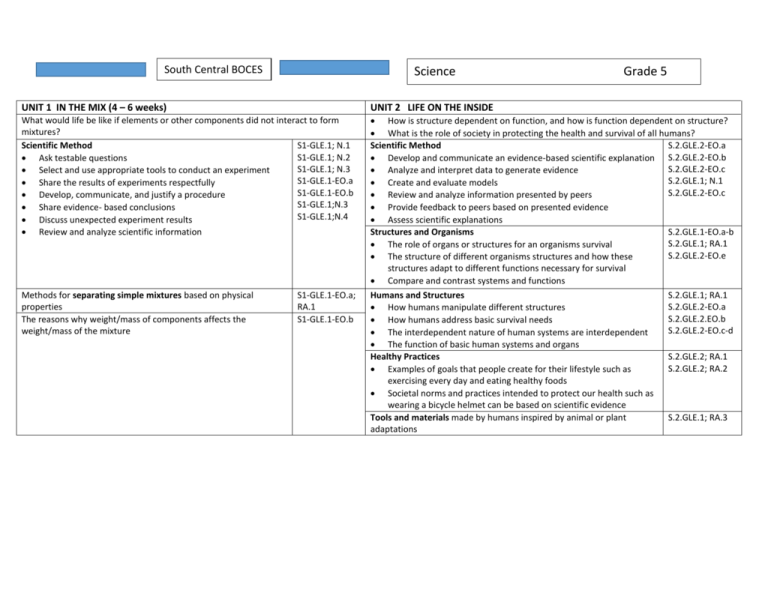
South Central BOCES Science Grade 5 UNIT 1 IN THE MIX (4 – 6 weeks) UNIT 2 LIFE ON THE INSIDE What would life be like if elements or other components did not interact to form mixtures? Scientific Method S1-GLE.1; N.1 S1-GLE.1; N.2 Ask testable questions S1-GLE.1; N.3 Select and use appropriate tools to conduct an experiment S1-GLE.1-EO.a Share the results of experiments respectfully S1-GLE.1-EO.b Develop, communicate, and justify a procedure S1-GLE.1;N.3 Share evidence- based conclusions S1-GLE.1;N.4 Discuss unexpected experiment results Review and analyze scientific information How is structure dependent on function, and how is function dependent on structure? What is the role of society in protecting the health and survival of all humans? Scientific Method S.2.GLE.2-EO.a Develop and communicate an evidence-based scientific explanation S.2.GLE.2-EO.b S.2.GLE.2-EO.c Analyze and interpret data to generate evidence S.2.GLE.1; N.1 Create and evaluate models S.2.GLE.2-EO.c Review and analyze information presented by peers Provide feedback to peers based on presented evidence Assess scientific explanations Structures and Organisms S.2.GLE.1-EO.a-b S.2.GLE.1; RA.1 The role of organs or structures for an organisms survival S.2.GLE.2-EO.e The structure of different organisms structures and how these structures adapt to different functions necessary for survival Compare and contrast systems and functions Humans and Structures S.2.GLE.1; RA.1 S.2.GLE.2-EO.a How humans manipulate different structures S.2.GLE.2.EO.b How humans address basic survival needs S.2.GLE.2-EO.c-d The interdependent nature of human systems are interdependent The function of basic human systems and organs Healthy Practices S.2.GLE.2; RA.1 S.2.GLE.2; RA.2 Examples of goals that people create for their lifestyle such as exercising every day and eating healthy foods Societal norms and practices intended to protect our health such as wearing a bicycle helmet can be based on scientific evidence Tools and materials made by humans inspired by animal or plant S.2.GLE.1; RA.3 adaptations Methods for separating simple mixtures based on physical properties The reasons why weight/mass of components affects the weight/mass of the mixture S1-GLE.1-EO.a; RA.1 S1-GLE.1-EO.b UNIT 3 RENEWABLE/NONRENEWABLE RESOURCES UNIT 4 AS THE EARTH CHANGES (4 – 6 weeks) What are the consequences to the earth of utilizing renewable and nonrenewable resources? Scientific Method S.2.GLE.2-EO.a S.2.GLE.2-EO.b Develop and communicate an evidence-based scientific S.2.GLE.2-EO.c explanation S.2.GLE.1; N.1 Analyze and interpret data to generate evidence S.2.GLE.2-EO.c Create and evaluate models S1-GLE.1-EO.a; Review and analyze information presented by peers IQ.3 Provide feedback to peers based on presented evidence How do changes on the Earth's surface impact humans? Assess scientific explanations Speak clearly and accurately to persuade an audience Renewable / Nonrenewable Resources Describe how natural resources provide energy List examples of nonrenewable resources provided by mining operations Discuss the limited nature of nonrenewable energy sources Describe the variety of renewable and nonrenewable resources the Earth and Sun provide Humans and Resources Discuss the reasons why towns are often built around resource extraction Discuss ways in which the distribution of resources is accomplished to meet human needs Explain the ways in which the environment affects humans and vice versa S.3-GLE.1 S.3-GLE.1;RA.1 S.3-GLE.1; N.2 S.3-GLE.1; RA.3 S.3-GLE.1; RA.2 S3-GLE.1-EO.b; N.1 Scientific Method Analyze and interpret data Develop and communicate an evidence based scientific explanation Ask testable questions Assess and provide feedback on a peer's scientific explanations S.3-GLE.2EO.a,b S.3-GLE.2-EO.b S.3-GLE.3-EO.a S.3-GLE.2; N.1 S.3-GLE.2-; N.3 Earth Changes Demonstrate how plate tectonics, erosion, deposition, solar influences, climate, and human activity change the earth's surface S.3-GLE.2-EO.a Describe the development of technology that led to tools and the establishment of measurement standards S.3-GLE.2; RA.3 Humans and Earth Changes The benefits and dangers to humans as Earth's surface constantly changes Examples of how communities compensate for the effects of our changing Earth Details of emergency plans that cities create in order to plan for earthquakes, flooding, volcanic eruptions, tornadoes, and other natural events S.3-GLE.2; RA.1 S.3-GLE.2; RA.2 S.3-GLE.2; RA.3 UNIT 5 WEATHER OR NOT (6 -8 weeks) How has accurate weather prediction allowed for the advancement of society? S.3-GLE.3-EO.a,b Scientific Method S.3-GLE.3-EO.a Analyze and interpret data S.3-GLE.3-; N.3 Develop and communicate an evidence based scientific S.3-GLE.3-EO.b explanation S.3-GLE.3; N.1 Assess and provide feedback on a peer's scientific explanations Gather, analyze, and interpret, data Use evidence to support scientific explanations S.3-GLE.3-EO.c Weather Basics S.3-GLE.3-EO.a Describe weather conditions S.3-GLE.3-EO.b Describe how weather is constantly changing S.3-GLE.3; RA.1 Demonstrate how air pressure, wind, temperature, and humidity affect daily weather conditions Describe the components of the water cycle and how they impact weather Weather Tools Use data collections tools to measure weather S.3-GLE.3-EO. c,d