Science Sample Items
advertisement
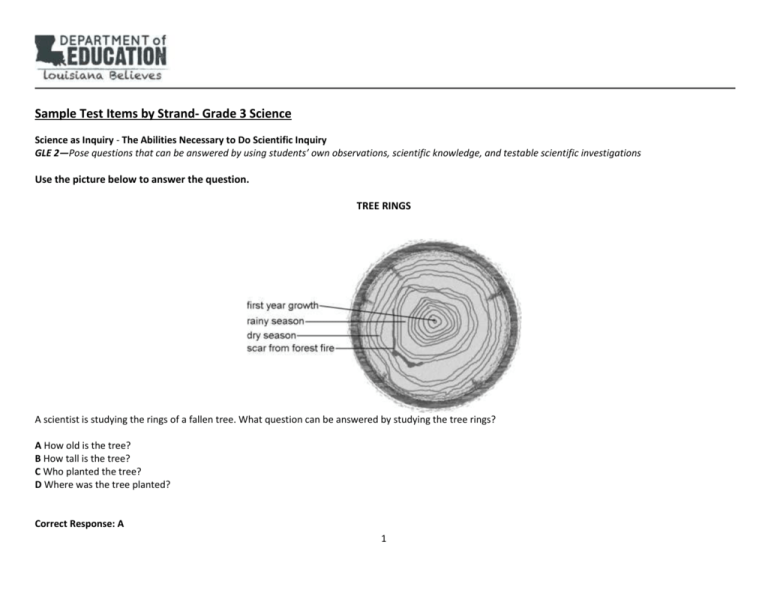
Sample Test Items by Strand- Grade 3 Science Science as Inquiry - The Abilities Necessary to Do Scientific Inquiry GLE 2—Pose questions that can be answered by using students’ own observations, scientific knowledge, and testable scientific investigations Use the picture below to answer the question. TREE RINGS A scientist is studying the rings of a fallen tree. What question can be answered by studying the tree rings? A How old is the tree? B How tall is the tree? C Who planted the tree? D Where was the tree planted? Correct Response: A 1 Science as Inquiry -The Abilities Necessary to Do Scientific Inquiry GLE 6—Use the five senses to describe observations Li walked into a room. She said, “I can tell that someone has perfume.” What sense did Li most likely use to know that there was perfume? A taste B sight C smell D hearing Correct Response: C 2 Science as Inquiry - The Abilities Necessary to Do Scientific Inquiry GLE 10—Combine information, data, and knowledge from one or more of the science content areas to reach a conclusion or make a prediction Use the data chart below to answer the question. SUN DATA FOR NEW ORLEANS Day Time the Sun Rises July 1 5:03 A.M. August 1 5:20 A.M. September 1 5:38 A.M. October 1 ? November 1 6:15 A.M. The chart shows the time that the sun rises on different days in New Orleans. What would most likely be the time that the sun rises on October 1 in New Orleans? A. 5:10 A.M. B. 5:35 A.M. C. 5:55 A.M. D. 6:20 A.M. Correct Response: C 3 Science as Inquiry - The Abilities Necessary to Do Scientific Inquiry GLE 12—Identify and use appropriate safety procedures and equipment when conducting investigations (e.g., gloves, goggles, hair ties) Which student needs to wear protective goggles the most? A. C. B. D. Correct Response: B 4 Science as Inquiry - Understanding Scientific Inquiry GLE 15—Recognize that a variety of tools can be used to examine objects at different degrees of magnification (e.g., hand lens, microscope) Kerri is studying cells that are much too small to see with her eyes alone. Which tool would be most helpful to Kerri? A. C. B. D. Correct Response: A 5 Science as Inquiry - Understanding Scientific Inquiry GLE 17—Explain and give examples of how scientific discoveries have affected society Which invention has been the most helpful in allowing people to communicate quickly with each other? A. C. B. D. Correct Response: C 6 Physical Science - Properties of Objects and Materials GLE 18—Compare and classify objects on properties determined through experimentation (e.g., ability to conduct electricity, tendency to float or sink in water) Use the data table below to answer the question. MATERIAL PROPERTIES Material Does it conduct Does it float electricity? in water? A Yes No B No Yes C No No D Yes Yes Kira is testing several materials to see whether they conduct electricity and float in water. Which material conducts electricity and floats in water? A. material A B. material B C. material C D. material D Correct Response: D 7 Physical Science - Properties of Objects and Materials GLE 22—Investigate and explain conditions under which matter changes physical states: heating, freezing, evaporating, condensing, boiling A scientist is studying a liquid. If she lowers the temperature of the liquid, which of the following will most likely occur? A. B. C. D. The liquid will boil. The liquid will melt. The liquid will freeze. The liquid will evaporate. Correct Response: C 8 Physical Science - Position and Motion of Objects GLE 24—Explain how the amount and direction of force exerted on an object (e.g., push, pull, friction, gravity) determine how much the object will move Use the diagram below to answer the question. The diagram shows two people moving an object. Bob is pushing the object, and Carol is pulling it. Use the arrows to help you figure out which dot the object will move toward. A. dot A B. dot B C. dot C D. dot D Correct Response: B 9 Physical Science - Position and Motion of Objects GLE 25—Observe and analyze motion and position of objects over time (e.g., shadows, apparent path of the Sun across the sky) Use the pictures below to answer the question. Insect Motion Picture 1 Picture 2 (one minute later) 10 Tina was measuring the speed of a moving insect. Picture 1 shows where the insect was when Tina started observing it. Picture 2 shows where the insect was after 1 minute. If the insect keeps moving at the same speed, which picture shows where it will most likely be after 1 more minute? A. B. C. D. Correct Response: B 11 Physical Science - Forms of Energy GLE 25—Use the words high/low to compare the pitch of sound and the words loud/soft to compare the volume (amplitude) of sound Which of these makes the loudest sound? A. B. C. D. Correct Response: A 12 Physical Science - Forms of Energy GLE 33—Identify simple machines and the tasks they make possible When would a ramp be most useful? A C B D Correct Response: A 13 Life Science - Characteristics of Organisms GLE 35—Compare structures (parts of the body) in a variety of animals (e.g., fish, mammals, reptiles, amphibians, birds, insects) Use the picture below to answer the question. Whale . Look where the arrow is pointing on the whale. What part of a bird is most similar to this part of the whale? A. C. 14 B. D. Correct Response: C 15 Life Science - Characteristics of Organisms GLE 36—Compare structures (e.g., roots, leaves, stems, flowers, seeds) and their functions in a variety of plants Use the pictures below to answer the question. Tree Trunk Flower What part of the flower is most similar in use to the tree trunk? A. part A B. part B C. part C D. part D Correct Response: A 16 Life Science - Characteristics of Organisms GLE 37—Describe how plant structures enable the plant to meet its basic needs Use the picture below to answer the question. POTATO PLANT Which part of the potato plant absorbs the most water? A. B. C. D. part A part B part C part D Correct Response: D 17 Life Science - Characteristics of Organisms GLE 38—Classify groups of organisms based on common characteristics Use the three pictures of related animals below to answer the question. Related Animals Which animal is most closely related to the animals in the pictures above? A. C. 18 B. D. Correct Response: A 19 Life Science - Characteristics of Organisms GLE 40—Explain how the organs of the digestive system function Use the diagram below to answer the question. DIGESTIVE SYSTEM Which part of the digestive system gets nutrients from food? A. B. C. D. part A part B part C part D Correct Response: D 20 Life Science - Characteristics of Organisms GLE 41—Describe how the components of the skeletal system function Which body part belongs to the skeletal system? A. C. jawbone B. brain D. heart stomach Correct Response: A 21 Earth and Space Science - Properties of Earth Materials GLE 45—Recognize and describe that rock is composed of different combinations of minerals Which object is composed mostly of minerals? A. B. rock C. tree branch D. plastic fork grasshopper Correct Response: A 22 Earth and Space Science - Properties of Earth Materials GLE 47—Describe the difference between weather and climate Susan lives in a city where the days are usually very warm. However, yesterday was very cold. Which statement is true about the city yesterday? A. B. C. D. The city had cold weather and climate. The city had warm weather and climate. The city had warm weather but a cold climate. The city had cold weather but a warm climate. Correct Response: D Earth and Space Science - Properties of Earth Materials GLE 48—Identify examples of the processes of a water cycle (e.g., evaporation, condensation, precipitation, collection of runoff) Which statement is an example of precipitation? A. B. C. D. Water from a river enters the ocean. Water from a cloud falls to the ground. Water in a puddle soaks into the ground. Water in a cup is heated and enters the air. Correct Response: B 23 Earth and Space Science - Properties of Earth Materials GLE 50—Compare and group common rocks according to their characteristics (i.e., igneous, metamorphic, sedimentary) Ricky finds a rock that has tiny seashells in it. Which statement is most likely true about the rock? A. B. C. D. The rock was formed in outer space. The rock was formed in an ocean, lake, or river. The rock was formed by a volcano that erupted. The rock was formed by materials that were under heat and pressure. Correct Response: B Earth and Space Science - Objects in the Sky GLE 55—Explain the results of the rotation and revolution of Earth (e.g., day and night, year) How long does it take Earth to spin around on its axis one time? A. a day B. a week C. a month D. a year Correct Response: A 24 Earth and Space Science - Objects in the Sky GLE 56—Compare shadow direction and length at different times of day and year Use the pictures below to answer the question. Flagpole Shadows The pictures show a flagpole and its shadow at two different times during the day. Which statement is most likely true? A. B. C. D. A occurred earlier in the day than B. A occurred later in the day than B. A occurred closer to noon than B. A occurred closer to midnight than B. Correct Response: C 25 Science and the Environment GLE 57—Describe the interrelationships of living (biotic) and nonliving (abiotic) components within various ecosystems (e.g., terrarium, swamp, backyard) Which of these living things depends most on good soil to grow? A. C. B D. Correct Response: D 26 Science and the Environment GLE 58—Describe how humans have had negative and positive effects on organisms and their environments Which human activity most affects the environment? A. B. C. D. rowing a boat driving in a car hiking on a trail talking on the phone Correct Response: B 27 Science and the Environment GLE 59—Classify manufactured products according to the natural resources from which they are made (e.g., copper wire from copper ore, plastic from petroleum) Which object is made from material that comes from oil? A. C. plastic spoon B. glass vase D. copper pot wooden chair Correct Response: A 28 Science and the Environment GLE 60—Explain how renewable and nonrenewable resources can be replenished or depleted Which energy source cannot be used up by humans? A. B. C. D. oil coal natural gas solar power Correct Response: D Science and the Environment GLE 61—Explain how selected animals once classified as endangered have recovered How can humans best help an endangered species avoid extinction? A. B. C. D. They can feed the animals. They can put the animals in a zoo. They can protect the animal’s habitat. They can take the animal to new habitats. Correct Response: C 29 Science and the Environment GLE 62—Identify animals in Louisiana that have recovered and that are no longer considered endangered American alligators used to be an endangered species, but they are not endangered anymore. Which of the following is the best reason why there are more American alligators in Louisiana today than there were 50 years ago? A. American alligators have learned to live in new places. B. American alligators are bigger now than they were 50 years ago. C. American alligators are now protected from hunting by humans. D. American alligators have much more habitat than they did 50 years ago. Correct Response: C 30 Task C.J. grows some small plants. He does three experiments to learn more about how plants grow. His experiments are described below. Use the information to answer questions 1 through 3. C.J.’s Plant Experiments Experiment 1—Covered Plants C.J. grows four small plants in the same conditions. Then he completely covers two plants with aluminum foil for a week. He continues to water all of the plants the same. Next C.J. removes the foil. The plants that were covered are yellow and look like they might be dying. The plants that were not covered are still green and healthy. Experiment 2—Removing Flowers C.J. takes two similar plants and cuts the flowers off of one. He gives both plants the same amount of light and water. The pictures show how each plant grows. 31 Experiment 3—Cutting Stems and Removing Leaves 32 C.J. has six healthy plants that are the same size. He cuts the stem at the base of two of the plants, and sets the cut plants on the soil. He removes all the leaves from two other plants. He does not make any changes to the last two plants. He continues to give all six plants the same amount of light and water. Study the information in C.J.’s Plant Experiments before answering the question. 1. Which statement explains why the covered plants most likely turned yellow in experiment 1? A. The foil stopped the plants’ leaves from getting nutrients from the stem, so they began to die. B. The foil stopped the plants’ leaves from getting water from the air, so they dried up. C. The foil kept light from reaching the plants’ leaves, so they could not make their own food. D. The foil stained the plants’ leaves a yellow color, so they no longer looked green. 2. In experiment 2, the plant with the flowers removed grew new flowers. Flowers are needed for the plant to A. absorb carbon dioxide from the air. B. pull nutrients out of the soil. C. attract animals to eat the fruits. D. grow seeds and reproduce. 33 The following question requires you to write an extended response that combines information from the source with your knowledge of science. To earn full credit you should: Read the question and then study the information in C J.’s Plant Experiments. Answer all parts of the question and support your ideas with examples, data, facts, or details. Write a response that is long enough to fully address the topic. This may require more than one paragraph. Responses with fewer than 25 words will not be scored. 3. Predict what will happen to the six plants in experiment 3. Explain your predictions by describing how plant parts are important to a plant. 34 Exemplary Response 1. C 2. D 3. The plants cut at the stem have lost their roots. Without roots, the plants cannot draw water and nutrients from the soil, so the leaves, stem, and flowers will wilt and die. Depending on the plant, the roots might be able to live and grow new leaves. But without the leaves, it is possible that the roots will not be able to get enough food and they will die too. The plants with all the leaves removed may be able to grow new leaves. They may have enough food saved in the roots and stems to grow new leaves, and the new leaves could produce food for the plants to keep growing. But they will not be able to grow as fast or be as healthy as the plants that were not changed. The plants that were not cut at all will grow the fastest and be the healthiest. They have leaves to make food and roots to bring water and nutrients to the leaves through the stems. They should be able to grow flowers and seeds so they can reproduce. Rubric (Question #3) Score 2 1 0 The student’s response demonstrates an in-depth understanding of the roles of roots, stems, and leaves in plant survival and growth. The student completes all key components of the task accurately and communicates ideas effectively. The student’s response is supported by relevant evidence in the form of data and/or examples. Where appropriate, the student uses a higher level of reasoning skills that may include applications, procedures, etc. The response contains no errors. The student’s response demonstrates a limited understanding of major concepts of the roles of roots, stems, and leaves in plant survival and growth (gaps in conceptual understanding). The student completes some parts of the task successfully. The student’s response is not sufficiently supported by relevant evidence. The response contains errors. The response attempts to address the prompt, but is mostly or entirely incorrect or contains some correct work that is irrelevant to the skill or concept being measured. 35