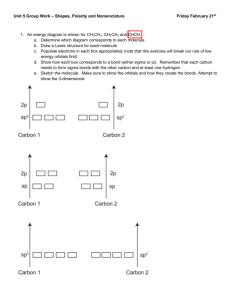
Hybridization In this process an atom adopts a different set of
advertisement
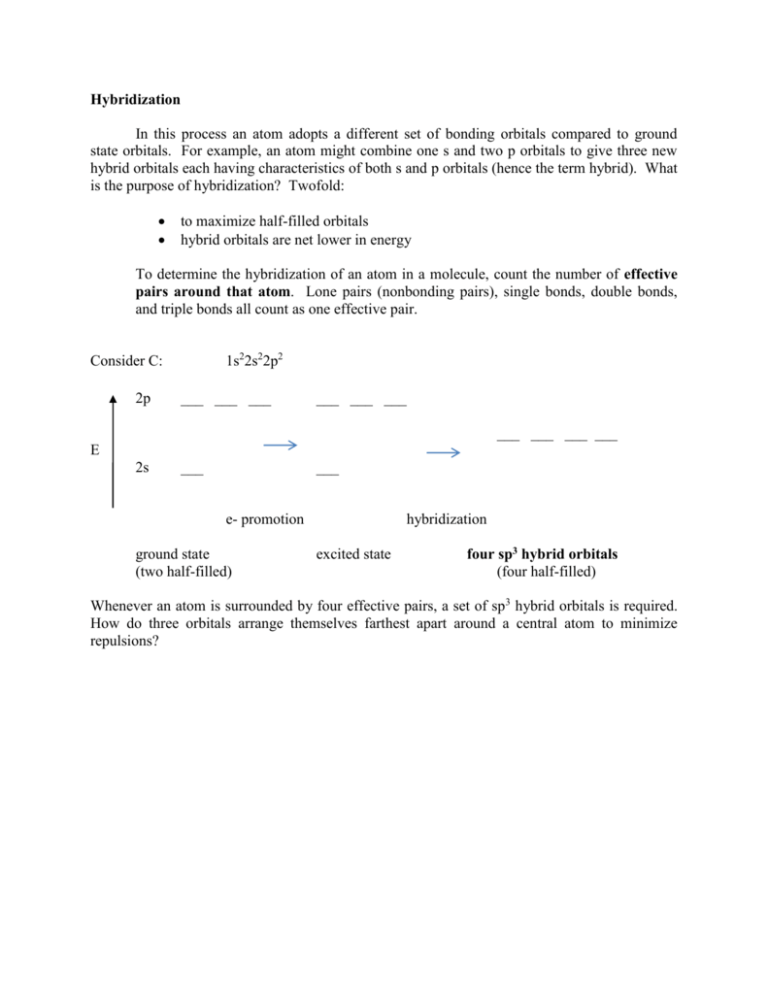
Hybridization In this process an atom adopts a different set of bonding orbitals compared to ground state orbitals. For example, an atom might combine one s and two p orbitals to give three new hybrid orbitals each having characteristics of both s and p orbitals (hence the term hybrid). What is the purpose of hybridization? Twofold: to maximize half-filled orbitals hybrid orbitals are net lower in energy To determine the hybridization of an atom in a molecule, count the number of effective pairs around that atom. Lone pairs (nonbonding pairs), single bonds, double bonds, and triple bonds all count as one effective pair. 1s22s22p2 Consider C: 2p ___ ___ ___ ___ ___ ___ ___ ___ ___ ___ E 2s ___ ___ e- promotion ground state (two half-filled) hybridization excited state four sp3 hybrid orbitals (four half-filled) Whenever an atom is surrounded by four effective pairs, a set of sp3 hybrid orbitals is required. How do three orbitals arrange themselves farthest apart around a central atom to minimize repulsions?