Covalent Bonding HL revision notes

Covalent Bonding: Key concepts ( HL only)
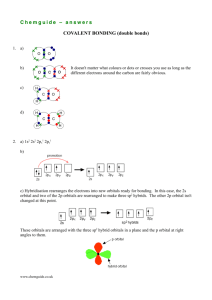
When covalent bonds form, the atomic orbitals overlap forming two types of molecular orbitals
When two atomic orbitals overlap along the bond axis (head on), a sigma bond is formed
This bond involves s-atomic orbitals, p(x)-atomic orbitals and the combination s and p(x) orbitals
All single bonds are sigma bonds
When two p-atomic orbitals overlap sideways , a pi bond is formed
The second (in a double bond) and third bond (in a triple bond) between two atoms are pi bonds
The electrons involved in pi-bonds are sometimes able to spread between different bonding positions. This is called delocalization of electrons.
The delocalization of electrons gives stability to the structure
You can represent this idea using resonance structures .
Benzene displays a special ring structure due to the delocalization of the electrons.
The formation of covalent bonds often starts with the excitation (gaining energy) of the atom.
Atoms are able to form stronger covalent bonds using hybrid orbitals
Hybrid orbitals form when atomic orbitals mix to produce orbitals of intermediate energy
The idea of hybridization is used to explain why methane (CH4) has 4 identical C-H bonds.
The shape of hybrid orbitals is found on www.heinemann.co.uk/hotlinks
The idea of hybridization can also be used to explain the shape of molecules