State of Matter and Their Changes Study Guide
advertisement

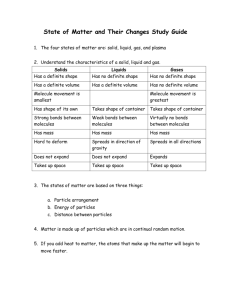
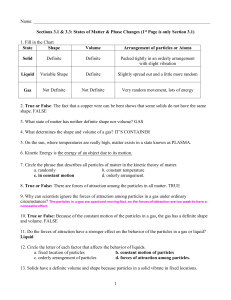
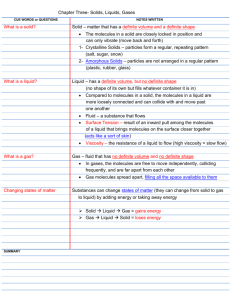
State of Matter and Their Changes Study Guide 1. The four states of matter are: solid, liquid, gas, and plasma 2. Understand the characteristics of a solid, liquid and gas. Solids Has a definite shape Liquids Has no definite shape Gases Has no definite shape Has a definite volume Has a definite volume Has no definite volume Molecule movement is smallest Molecule movement is greatest Has shape of its own Takes shape of container Takes shape of container Strong bonds between molecules Weak bonds between molecules Virtually no bonds between molecules Has mass Has mass Has mass Hard to deform Spreads in direction of gravity Spreads in all directions Does not expand Does not expand Expands Takes up space Takes up space Takes up space 3. The states of matter are based on three things: a. Particle arrangement b. Energy of particles c. Distance between particles 4. Matter is made up of particles which are in continual random motion. 5. If you add heat to matter, the atoms that make up the matter will begin to move faster. 6. If you remove heat from matter, the atoms that make up the matter will begin to move slower. Description of Phase Change Solid to Liquid Liquid to Solid Liquid to Gas Gas to Liquid Solid to Gas Term for Phase Change Melting Freezing Vaporization Condensation Sublimation Endothermic or Exothermic Endothermic Exothermic Endothermic Exothermic Endothermic 7. Know examples of phase changes. 8. Be able to define endothermic and exothermic energy changes. 9. Be able to identify if a substance is a solid, liquid, or a gas. 10. Matter is everything that has mass and volume. 11. The temperature at which a solid turns into a liquid is the melting point. 12. The temperature at which a liquid turns into a gas is the boiling point. 13. Viscosity is resistance of a liquid to flow. 14. Know what surface tension is and give an example. 15. Amorphous solids have no orderly arrangement of particles 16. Crystalline solids have an orderly arrangement of particles. 1. Matter is defined as anything that __Takes up space and has mass______. 2. Which of the following is NOT considered to be matter? air pens car Paper floor energy 3. Solids have a(n) ______definite_______ shape and a(n) __Definite___ volume. 4. Liquids have a(n) ____non-definite___ shape and a(n) _ Definite ___ volume. 5. Gases have a(n) __ non-definite ____ shape and a(n) _ non-definite __ volume. 6. In a _liquid__ the particles slide past each other. 7. In a _gas_ the particles are free to move from place to place. 8. In a _solid__ the particles vibrate. 9. A _gas__ expands the greatest amount when heated. 10. During _melting_ a solid changes to a liquid. 11. During _vaporization_ a liquid changes to a gas. 12. During _sublimation_ a solid changes to a gas. 13. During _deposition _ a gas changes to a solid 14. During _condensation_ a gas changes to a liquid. 15. During _freezing__ a liquid changes to a solid. 16. Using circles to represent particles, show how the particles are arranged in each of the following: