Chemistry Vocabulary: Part 1
advertisement

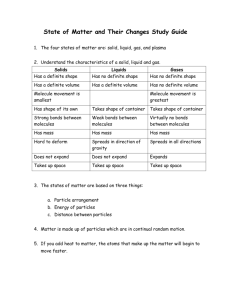
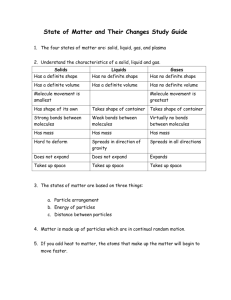
Anything that has mass and takes up space Made up of tiny particles called atoms Atoms: smallest particle of matter Smallest unit of an element that maintains the properties of that element Can not be broken down into anything smaller Scientists used to think they couldn’t be split, but we now know that was incorrect The physical forms of matter, which include solid, liquid, and gas The state of matter in which the volume and shape of a substance are fixed Definite shape Definite volume Particles are tightly packed Particles barely move They vibrate in place The state of matter that has a definite volume but not a definite shape No definite shape Definite volume Particles move fast enough to separate a little Allowing them to change shape Particles do not move fast enough to change volume Viscosity: a liquid’s resistance to flow High Viscosity: Slow Flow (Honey) Low Viscosity: Fast Flow (Water) Surface Tension: force that attracts the molecules at the surface of a liquid to form the drop The state of matter that does not have a definite shape or volume No definite shape No definite volume Particles move so fast that they completely separate from each other Allowing them to change shape and volume Change of a substance from one physical form to another Requires adding or removing energy so that particles can speed up or slow down Change of state when a solid becomes a liquid Particles must speed up Add energy/heat Endothermic Melting Point: Temperature at which a substance melts Water: 32°F or 0°C Change of state from a liquid to a solid Particles must slow down Remove energy/heat Exothermic Freezing Point: Temperature at which a substance freezes Water: 32°F or 0°C Change of a liquid to a gas (throughout an entire liquid) Particles (on bottom of liquid) must speed up Add energy/heat Endothermic Boiling Point: Temperature at which a substance boils Water: 212°F or 100°C At Sea Level: Boiling depends on Air Pressure **Won’t happen unless air pressure equals pressure in bubbles Change of a substance from a liquid to a gas (only on surface) Particles (on surface) must speed up Add energy/heat Endothermic Change of state from a gas to a liquid Particles must slow down Remove energy/heat Exothermic Change of state from a solid to a gas Example: Dry Ice Skips liquid stage Add energy/heat Endothermic