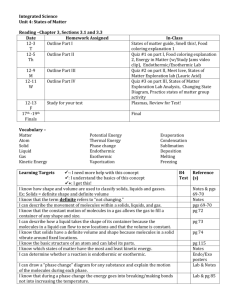
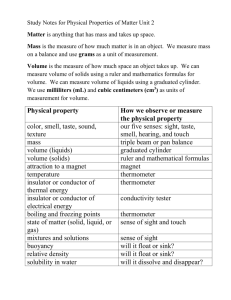
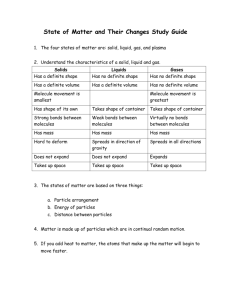
Chapter 3- solids, liquids, and gas
advertisement
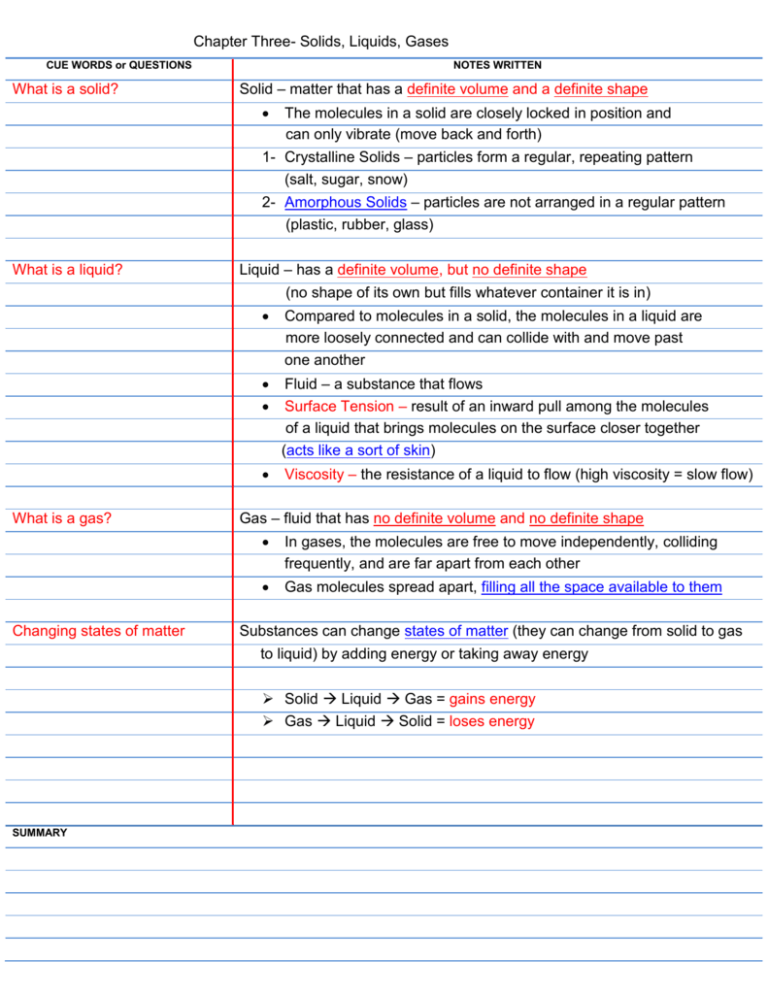
Chapter Three- Solids, Liquids, Gases CUE WORDS or QUESTIONS What is a solid? NOTES WRITTEN Solid – matter that has a definite volume and a definite shape The molecules in a solid are closely locked in position and can only vibrate (move back and forth) 1- Crystalline Solids – particles form a regular, repeating pattern (salt, sugar, snow) 2- Amorphous Solids – particles are not arranged in a regular pattern (plastic, rubber, glass) What is a liquid? Liquid – has a definite volume, but no definite shape (no shape of its own but fills whatever container it is in) Compared to molecules in a solid, the molecules in a liquid are more loosely connected and can collide with and move past one another What is a gas? Changing states of matter Fluid – a substance that flows Surface Tension – result of an inward pull among the molecules of a liquid that brings molecules on the surface closer together (acts like a sort of skin) Viscosity – the resistance of a liquid to flow (high viscosity = slow flow) Gas – fluid that has no definite volume and no definite shape In gases, the molecules are free to move independently, colliding frequently, and are far apart from each other Gas molecules spread apart, filling all the space available to them Substances can change states of matter (they can change from solid to gas to liquid) by adding energy or taking away energy Solid Liquid Gas = gains energy Gas Liquid Solid = loses energy SUMMARY CUE WORDS or QUESTIONS Melting- NOTES WRITTEN Melting – change in state from a solid to a liquid Thermal energy (heat) is gained Melting point – the temp at which the substance begins to melt When a substance melts, the particles in the solid vibrate so fast that they break apart and become free from their fixed positions Freezing- Freezing – change of state from a liquid to a solid Thermal energy (heat) is lost When a substance freezes, the particles in the liquid move so slowly they begin to take on fixed positions Vaporizing- Vaporization – change from a liquid to a gas Takes place when the particles in a liquid gain enough energy to move independently, forming a gas Two kinds – Boiling and Evaporation 1- Boiling – when a liquid changes to a gas on the surface and below the surface 2- Evaporation – vaporization that takes place only on the surface of a liquid Liquid gains thermal energy Boiling point – temperature at which a liquid boils Condensing- Condensation – change in state from a gas to a liquid During condensation, the particles in a gas lose enough thermal energy to form a liquid Sublimating- Sublimation – occurs when the surface particles of a solid gain enough energy that they form a gas SUMMARY X