States of Matter Worksheet: Physical Science Activities
advertisement

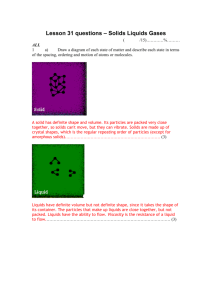
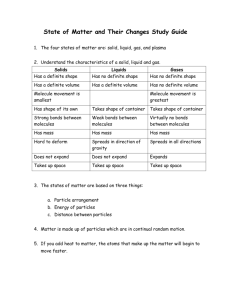
Physical Science Unit 1: Introduction to Physical Science Is you desk moving? Monday: Objectives: Activity: Video: Tuesday: Objectives: Activity: Wednesday Objectives: Discussion: Activity: Thursday: Objectives: Activity: HW: Define matter and describe its major properties Compare the properties of the four states of matter in terms of the arrangement and movement of particles. Give specific examples of the states of matter Matter/Non matter T chart Phases of matter- Unites Streaming Define matter and describe its major properties Compare the properties of the four states of matter in terms of the arrangement and movement of particles. Give specific examples of the states of matter States of Matter Webquest Define matter and describe its major properties Compare the properties of the four states of matter in terms of the arrangement and movement of particles. Give specific examples of the states of matter States of matter, Particle arrangement Venn Diagram or foldable Compare the properties of the four states of matter in terms of the arrangement and movement of particles. Building models of the states of matter States of matter review WS Study for Celebration Friday: Objectives: Activity: HW: Demonstrate an understanding of the states of matter through a Celebration. Smart Board Review TBA Physical Science Classification of Matter Phases of Matter Video Questions 1. List the four states of matter. 2. What are two characteristics of solids? 3. What are two characteristics of liquids? 4. What is viscosity? 5. What are two characteristics of gases? 6. What does Boyle’s Law state? 7. What does Charles’ Law state? 8. What is the 4th state of matter? 9. Describe matter in the plasma state. 10. What common household item contains plasma? 11. ________________ contains more energy than solids. 12. ________________ contains more energy than liquids. 13. Taking away or adding _________________ causes a phase change to occur. 14. __________ ___________: matter changing its state or phase. 15. _______________ : changing from a solid to a liquid. 16. __________ ___________: temperature at which a solid changes to a liquid. 17. What is the melting point of ice? 18. _______________: process of a liquid changing to a gas. 19. _______________: process of a liquid changing to a gas at its boiling point. 20. What is the boiling point of water? 21. _______________: vaporization that occurs at the surface of liquid. 22. _______________: process of a gas changing to a liquid. 23. _______________: process of a liquid changing to a solid. 24. ___________ ____________: temperature at which a liquid becomes a solid. 25. What is the freezing point of water? 26. _____________ : process of a solid changing to a gas without becoming a liquid. 27. Give an example of #26. Name: ________________ Date: ________________ Period: ________________ Physical Science Honors Classification of matter States of Matter Web quest 1. Use the following website to fill in the table below. http://www.abpischools.org.uk/page/modules/solids-liquids-gases/slg2.cfm?coSiteNavigation_allTopic=1 Shape Describe molecule movement Solid Liquid Gas 2. Click on the following link to fill in the table below. http://www.iknowthat.com/ScienceIllustrations/matter/science_desk.swf Volume Solid Liquid Gas 3. Use the following link to help draw a picture showing the particle arrangements of each state. http://www.harcourtschool.com/activity/states_of_matter/index.html Solid Liquid Gas 4. There are actually five states of matter. What are the five states of matter? Unit II: Composition and Classification of Matter States of Matter Complete the table by placing a check mark “” in the correct column. Characteristics of Phases of Matter Has a definite shape and a definite volume Has no definite shape, but has definite volume Has no definite shape and no definite volume Particles close together, but flow freely Particles closely packed and do not change position Particles expand to fill available space Exits naturally only in stars Will take the shape of any container Most occur as crystals Most common form of matter in universe Solids Liquids Gases Plasma