Matter Unit Study Guide Answers
advertisement

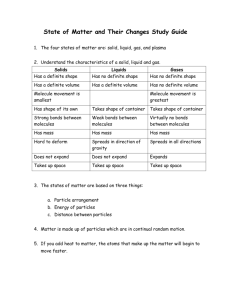
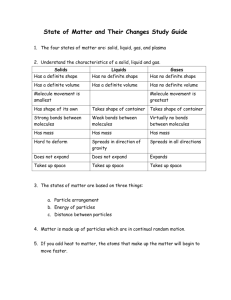
REVIEW ON MATTER List 3 Examples of Matter: 1. Solids- definite shape and volume 2. Liquids- definite volume, no definite shape 3. Gases – No definite shape, no definite volume Physical Changes vs. Chemical Changes Physical: Matter physically changes- keeps its identity 1. freezing water. Cutting paper 2. Crushing an aluminum can, mixing oil and vinegar Chemical: Matter chemically changes- does not keep its identity 1. baking soda reacting with water or vinegar 2. soured milk, rust, cooking or burning REVIEW CONTINUED Define each of the following Mass: the amount of matter that something is made of Volume: the amount of space that something contains or occupies Weight: a measure of the gravitational force put on an object What is the formula to calculate density? D = m/v What are the properties of: Solid: particles arranged in an orderly way, vibrating back and forth Liquid: particles are spread out more than a solid and slide past each other. Gas: particles move rapidly overcoming mostly all of their attraction to each other. What is Boyles Law? Give an Example Increase pressure, decrease volume at a constant temperature Example: Balloon being squeezed, rolling up a filled zip- lock bag What is Charles Law? Can you give an Example? Increase temperature, increase volume at a constant pressure Example: Hot air balloon. Define the following: Describe each one Freezing- Change of state from a liquid to a solid, exothermic change Example: Water turning to ice Melting- Change of state from a solid to a liquid, endothermic change Example: Ice melting to water. Evaporation - vaporization that occurs at the surface of a liquid below its boiling point. Example: liquid turning to water vapor, endothermic change Condensation- Change of state from a gas to a liquid. Exothermic change. Example- Water drops forming on the outside of ice water What is an Element? Is a pure substance that can not be separated or broken down into simpler substances by physical or chemical means. Properties of elements: melting point, boiling point, density. 2 examples of elements: 1. gold 2. silver 3 categories of elements 1. metals 2. non-metals 3. metalloids Define: Compound- a pure substance composed of two or more elements that are chemically combined. 2 Examples: 1. water – H2O 2. carbon dioxide - CO2 Define: Solubility- ability to dissolve into another substance. Example- salt dissolving into water Solvent – the substance in which a solute is dissolved to form a solution. Example- Salt water, water is the solvent Solution – a mixture that appears to be a single substance but is composed of particles of two or more substances that are distributed evenly amongst each other. PRACTICE QUESTIONS 1. Gravity effects weight. The gravitational force is higher with large masses. 2. They do not have the same weight but do have the same volume because they are the same size but the bowling ball has more matter. 3. Condensation because the water vapor from the air has condensed and turned back into a liquid onto the grass. 4. Balloon would shrink because decrease temperature, decrease volume which proves Charles’s Law 5. As water heats up, the particles gain energy and move away from each other turning into a gas. Particles that evaporated have more energy than particles in the pot. Water is the universal solvent. 6.