PERIODIC PROPERTIES
advertisement

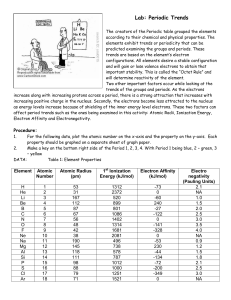
PERIODIC PROPERTIES DESCRİPTİON For the following data, plot the atomic number on the x- axis and the proporty on the yaxis.Each property should be graphed on a separate sheet of graph paper. ELEMENT ATOMIC NUMBER ATOMİC RADIUS (pm) H He Li Be B C N O F Ne Na Mg Al Si P S Cl Ar 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 53 31 167 112 87 67 56 48 42 38 190 145 118 111 98 88 79 71 FIRST IONIZATION ENERGY (kj/mol) 1312 2372 520 899 801 1086 1402 1314 1681 2081 496 738 578 787 1012 1000 1251 1521 ELECTRON AFFINITY (kj/mol) Analysis of the Data 1. Based on your graphs, what is the trend for atomic radius Across a period? Atomic radius decreases across a period. Down a family? Atomic radius increases down a family. 2. Based on your graphs, what is the trend for ionization energy Across a period? -73 0 -60 240 -27 -122 0 -141 -328 0 -53 230 -44 -134 -72 -200 -349 0 ELECTRON AFFINITY (Pauling Units) 2.1 N.A 1.0 1.5 2.0 2.5 3.0 3.5 4.0 N.A 0.9 1.2 1.5 1.8 2.1 2.5 3.0 N.A Ionization energy increases across a period,exceptions are 2A more than 3A and 4A more than 5A. 1A<3A<2A<5A<4A<6A<7A Down a family? Ionization energy decreases down a family. 3. Based on your graphs, what is the trend for electron affinity Across a period? Electron affinity increases across a period. Down a family? Electron affinity decreases down a family and noble gas do not have electron affinity. 4. Based on your graphs, what is the trend for electro negativity Across a period? Electronegativity increases across a period. Down a family? Electronegativity decreases down a family. 5. What can you infer about the relationship between ionization energy and reactivity of metals? Metals should be smaller in order to occur reactivity and metals that are more reactive have less ionization energy than are less reactive. 6. What can you infer about the relationship between electron affinity and reactivity of nonmetals? Reactivity of nonmetals is based on electron affinity. Most electron affinity one is the most reactive.