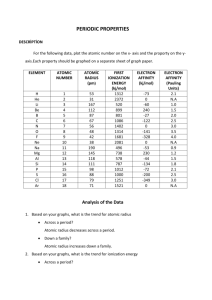
Chemistry Fall Final Study Guide What is chemistry the study of
advertisement

Chemistry Fall Final Study Guide 1) 2) 3) 4) 5) 6) 7) 8) 9) 10) 11) 12) 13) 14) 15) 16) 17) 18) 19) 20) 21) 22) 23) 24) 25) 26) 27) 28) 29) 30) 31) 32) 33) 34) 35) 36) 37) 38) What is chemistry the study of? The branches of chemistry and what they study. The branches of chemistry and what they study. The branches of chemistry and what they study. The branches of chemistry and what they study. Example of chemical v physical property Example of chemical v physical change Example of heterogeneous v homogeneous mixtures Example of chemical v physical change List the two properties of matter Define products Describe solid, liquid and gas in terms of their volume and shape. Period verses family Define an atom List the stages of scientific method Identify the mixture as homogeneous or heterogeneous Identify the mixture as homogeneous or heterogeneous Identify the mixture as homogeneous or heterogeneous Identify the mixture as homogeneous or heterogeneous Explain the law of conservation of mass Mass number verses Atomic number Mass number verses Atomic number Given the atomic symbol, identify the number of protons, neutrons and electrons. Find the # of electrons in an atom Explain proton v. neutron v. electron How is the periodic table arranged? Find the atomic number of an atom Location of proton v. neutron v. electron Given the atomic symbol, identify the number of protons, neutrons and electrons. Identify the correct atomic symbol given the mass # and identity of the atom. Estimate the average atomic mass given the % abundance. Find the average atomic mass from the periodic table. Hund v Pauli v Aurbau v Heisenburg Ground v excited state Frequency v wavelength (know the definition for both) What happens when an electron falls from its excited to ground state? Hund v Pauli v Aurbau v Heisenburg Symbol for the speed of light. 39) 40) 41) 42) 43) 44) 45) 46) 47) 48) 49) 50) 51) 52) 53) 54) 55) 56) 57) 58) 59) 60) 61) 62) 63) 64) 65) 66) 67) 68) 69) 70) 71) 72) 73) 74) Solve for wavelength from frequency (given the equation and value for c) Shape of the S orbital Hund v Pauli v Aurbau v Heisenburg What noble gas will be used in the noble gas notation of… Se, Sr, Fr What noble gas notation is achieved by the ion formed from Se, Sr, Fr Hund v Pauli v Aurbau v Heisenburg Identify the correct electron configuration Identify the correct noble gas notation Find the group based on the noble gas notation Pick the: most/ least electronegative, highest/ lowest ionization energy or electron affinity, smallest/ largest BASE ON THE TREND Pick the: most/ least electronegative, highest/ lowest ionization energy or electron affinity, smallest/ largest BASE ON THE TREND Explain Mendeleev’s periodic table Pick the: most/ least electronegative, highest/ lowest ionization energy or electron affinity, smallest/ largest BASE ON THE TREND Explain the trend of ionization energy, atomic radius, electronegativity and electron affinity What is the goal when atoms from ions? How do metals or nonmetals form ions? What type do they form? How do metals or nonmetals form ions? What type do they form? Predict the ion formed by… Se, Sr, Fr Pick the: most/ least electronegative, highest/ lowest ionization energy or electron affinity, smallest/ largest BASE ON THE TREND Explain the trend of ionization energy, atomic radius, electronegativity and electron affinity List all you know about group 17 Moseley Pick the: most/ least electronegative, highest/ lowest ionization energy or electron affinity, smallest/ largest BASE ON THE TREND List all you know about group 18 Groups v periods Representative elements Explain the trend of ionization energy, atomic radius, electronegativity and electron affinity Cation v anion Explain the size of a cation v anion v neutral atom Pick the: most/ least electronegative, highest/ lowest ionization energy or electron affinity, smallest/ largest BASE ON THE TREND List and describe the 4 types of bonds. List and describe the 4 types of bonds. List and describe the 4 types of bonds. Which atoms from multiple bonds List and describe the 4 types of bonds. Identify as polar covalent, nonpolar covalent, or ionic based on EN 75) 76) 77) 78) 79) 80) 81) 82) 83) 84) 85) 86) Identify as polar covalent, nonpolar covalent, or ionic based on EN Single v double v triple bonds (describe them, which is shortest?) Identify a characteristic of molecular compounds Single v double v triple bonds (describe them, which is shortest?) Single v double v triple bonds (describe them, which is shortest?) Role of valence electrons Draw a Lewis structure then count the number of lone pairs. Formula unit v crystal lattice List and describe the 4 types of bonds. List and describe the 3 types of INTERMOLECULAR FORCES Give the correct formula when given the ions Name a molecule.