Periodic Trends Question 1: Understanding the basis of the trends a
advertisement
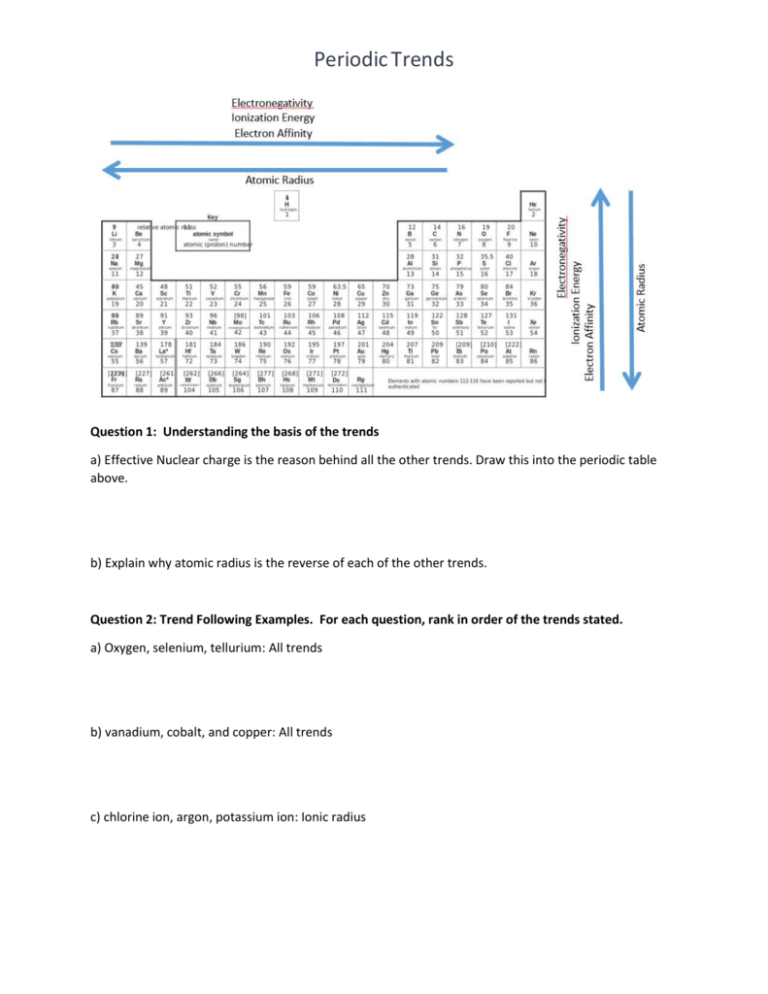
Periodic Trends Question 1: Understanding the basis of the trends a) Effective Nuclear charge is the reason behind all the other trends. Draw this into the periodic table above. b) Explain why atomic radius is the reverse of each of the other trends. Question 2: Trend Following Examples. For each question, rank in order of the trends stated. a) Oxygen, selenium, tellurium: All trends b) vanadium, cobalt, and copper: All trends c) chlorine ion, argon, potassium ion: Ionic radius Periodic Trends Question 3: Exceptions to the rule Ionization energy and electron affinity have several examples of exceptions. This includes exceptions within the p-block that you are responsible for knowing. Atomic radius and electronegativity do not have as many exceptions, and none are notable enough that you must know. a) State the p-block exceptions for ionization energy and electron affinity. b) Explain why ionization energy and electron affinity have these exceptions, while atomic radius and electronegativity do not. Question 4: If time or for at home studying with friends. On a separate piece of paper write down three atoms or ions. a) Write the electron configurations for each. b) For each one rank in order of each trend: (note: it is possible that they can give you ones that may be impossible to rank, if you think this is the case, rank what you can, and explain why you can’t rank the ones you can’t) Effective nuclear charge: Electron affinity: Ionization Energy: Radius: c) Discuss your results with the people you traded with, and discuss theirs with you. Periodic Trends Challenge Question: Energies for orbitals can be determined theoretically as we saw when discussing the Schrodinger equation. When you move onto lab, you will see how these can be determined using computer software which utilizes these theoretical calculations. Photoemission spectroscopy be can be used to determine the value of these orbitals experimentally for comparison with the theoretical calculations. This works of the principles of the photoelectric effect, the experiment that Einstein used to show the wave particle duality of light. Remember that in the photo electric effect, energy is provided in the form of photons. If these photons have a high enough energy, they will eject electrons, whose kinetic energy and velocity are dependent on the energy of the photons and the energy with which they are held onto the metal (work function, or binding energy). A PES measures the velocity of electrons by passing them through a region of magnetic field which deflects their path. By changing the filed strength the path of the electrons are altered and the velocity measurement is obtained. From here kinetic energy of the electrons and therefore the energy level of the orbital can be both be calculated. The following peaks were observed in the PES spectra for an element. Identify the element and electron configuration. Note: Use appendix 2 or the internet to compare the values of the binding energy found with values of ionization energies listed. 21 MJ/mol, 2.4 MJ/mol and 0.80 MJ/mol