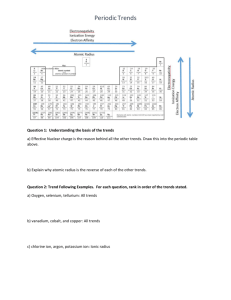
Periodic Table Review
advertisement

Level 3 Review for Periodic Table Test Directions: Answer the questions using a separate sheet of paper. Questions in bold are required. Other questions are optional, but recommended. Remember that even if you are not required to answer a question, you are still held responsible for knowing how to answer it on the test. 1. Write the noble gas configurations for the following elements a. b. c. d. e. f. g. h. i. j. k. Si: [Ne] 3s23p2 Sb: [Kr] 5s24d105p3 Re: [Xe] 6s24f145d5 Cu: [Ar] 4s13d10 Cd: [Kr] 5s24d10 Br: [Ar] 4s23d104p5 Kr: [Ar] 4s23d104p6 K: [Ar] 4s1 Y: [Kr] 5s24d1 S: [Ne] 3s23p4 Mo: [Kr] 5s14d5 2. Identify the following elements based in their electron configurations a. b. c. d. e. f. g. h. i. j. k. l. m. Se Br Kr Fr Ds Po Mn Sn Sb Xe K Rh Al 3. How many periods are on the periodic table? How are they numbered? 7, numbered 1-7 4. How many groups are on the periodic table? How are they numbered? 18, numbered 1-18 5. Of Cesium (Cs), Hafnium (Hf), and Gold (Au), which element has the smallest atomic radius? Explain your answer in terms of atomic structure. Gold has the smallest radius because it has the greatest effective nuclear charge (most protons in the nucleus). 6. Arrange the following elements in order of decreasing electronegativities: C, O, Li, Na, Rb, and F. F, O, C, Li, Na, Rb 7. Arrange the following atoms in order of decreasing first ionization energies: Li, O, C, K, Ne, and F. Ne, F, O, C, Li K 8. Which element is most electronegative among C, N, O, Br, and S? Which group does it belong to? O, group 16 9. The two ions K+ and Ca2+ each have 18 electrons surrounding the nucleus. Which would you expect to have the smaller radius? Why? Ca2+ because it has a greater effective nuclear charge (more protons) 10. Describe the state of matter (solid, liquid, or gas), reactivity, conductivity, and ionization energy of each of the following elements: a. Fluorine (F) Gas, very reactive, not a conductor, high ionization energy b. Xenon (Xe) Gas, very unreactive, not a conductor, high ionization energy c. Sodium (Na) Solid, very reactive, conductor, low ionization energy From the textbook: Page 151 #27- see notes, 31 (c) , 32 see notes, 48 see notes, 50 see notes Page 122 #6 same number of occupied energy levels, 7 same number of valence electrons Page 131 #1 noble gases- full valence shells, 3 see notes, 7 see notes Page 141 #3 see notes, 8 more electron shells, 10 decreases down a group, increases across a period, 13 gets smaller because electron repulsion decreases, and in come cases atom loses an electron shell Page 155 #3 a, 5 a, 7 c, 8 c, 9 a, 10 b, 11 d