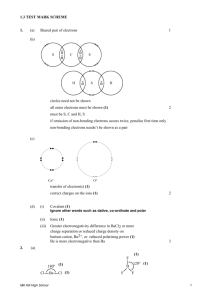
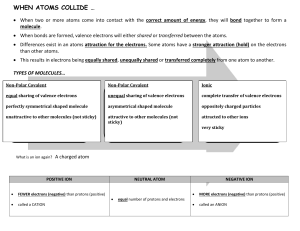
A force that holds two atoms together. Ionic, covalent and polar
advertisement

1. A force that holds two atoms together. Ionic, covalent and polar covalent. 2. Elements (electron donors and acceptors) of different electronegativity react with each other. NaCl 3. Covalent bonds consist of atoms equally sharing electrons (similar electronegitivities – H2, N2, etc.); polar covalent bonds share electrons but do so unequally – the element with greater electronegativity pulls more electrons. 4. The ability of an atom to attract shared electrons toward itself. 5. The centers of positive and negative charge do not coincide. 6. Ionic bond properties: hard, brittle, high boiling point, etc. All a result of orderly packing of ions to increase – and + attraction. 7. A. [Ne] 3s1, Na+1, [Ne] B. [Kr] 5s2 4d10 5p5, I-1, [Xe] C. [Ar] 4s2, Ca+2, [Ar] 8. BaCl2, NaFl, K2O 9. Isoelectric with noble gas. Bonding and lone pairs = 8 10. The 2 electrons that fill the valance shell of He 11. The full valance shell of 8 required by the representative elements 12. Bonding pairs are shared electrons between atoms while lone pairs are electrons entirely held by an atom. 13. Refer to book 14. 4 electrons shared. 6 electrons shared 15. Average of multiple Lewis structures where electrons are delocalized. 16. Not to be concerned with