WHEN ATOMS COLLIDE*
advertisement
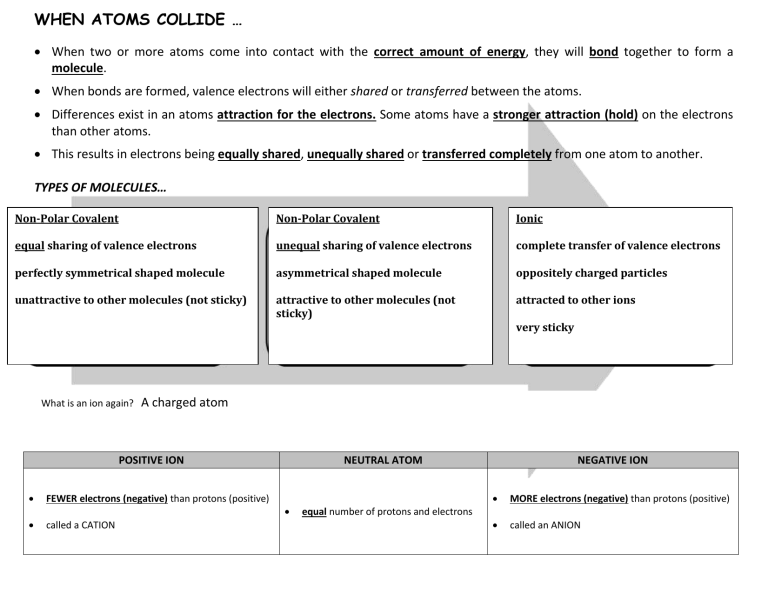
WHEN ATOMS COLLIDE … When two or more atoms come into contact with the correct amount of energy, they will bond together to form a molecule. When bonds are formed, valence electrons will either shared or transferred between the atoms. Differences exist in an atoms attraction for the electrons. Some atoms have a stronger attraction (hold) on the electrons than other atoms. This results in electrons being equally shared, unequally shared or transferred completely from one atom to another. TYPES OF MOLECULES… Non-Polar Covalent Non-Polar Covalent Ionic equal sharing of valence electrons unequal sharing of valence electrons complete transfer of valence electrons perfectly symmetrical shaped molecule asymmetrical shaped molecule oppositely charged particles unattractive to other molecules (not sticky) attractive to other molecules (not sticky) attracted to other ions very sticky What is an ion again? A charged atom POSITIVE ION FEWER electrons (negative) than protons (positive) called a CATION NEUTRAL ATOM equal number of protons and electrons NEGATIVE ION MORE electrons (negative) than protons (positive) called an ANION WHY DOES BONDING MATTER? Depending on the type of bonding taking place, the observed physical properties will change. Here are a few examples: low melting point low solubility high melting point high solubility MOLECULE LEWIS STRUCTURE H2O CO2 NaCl NH3 Ca(OH)2 BONDING TYPE PROPERTIES & MOLECULAR SHAPE polar covalent polar due to unequal sharing of electrons bent shape (asymmetrical) medium melting point soluble in water may look like a crystal when solid non-polar covalent non-polar due to equal sharing of electrons linear shape (symmetrical) very low melting point low solubility in water looks like a powder when solid ionic ionic due to oppositely charged ions very high melting point high solubility in water looks like a crystal when solid polar covalent polar due unequal sharing of electrons asymmetrical shape (like a pyramid) medium melting point soluble in water may look like a crystal when solid ionic ionic due to oppositely charged ions very high melting point high water solubility looks like a crystal when solid




