Cell Parts & Functions Study Guide: Prokaryotic vs. Eukaryotic
advertisement
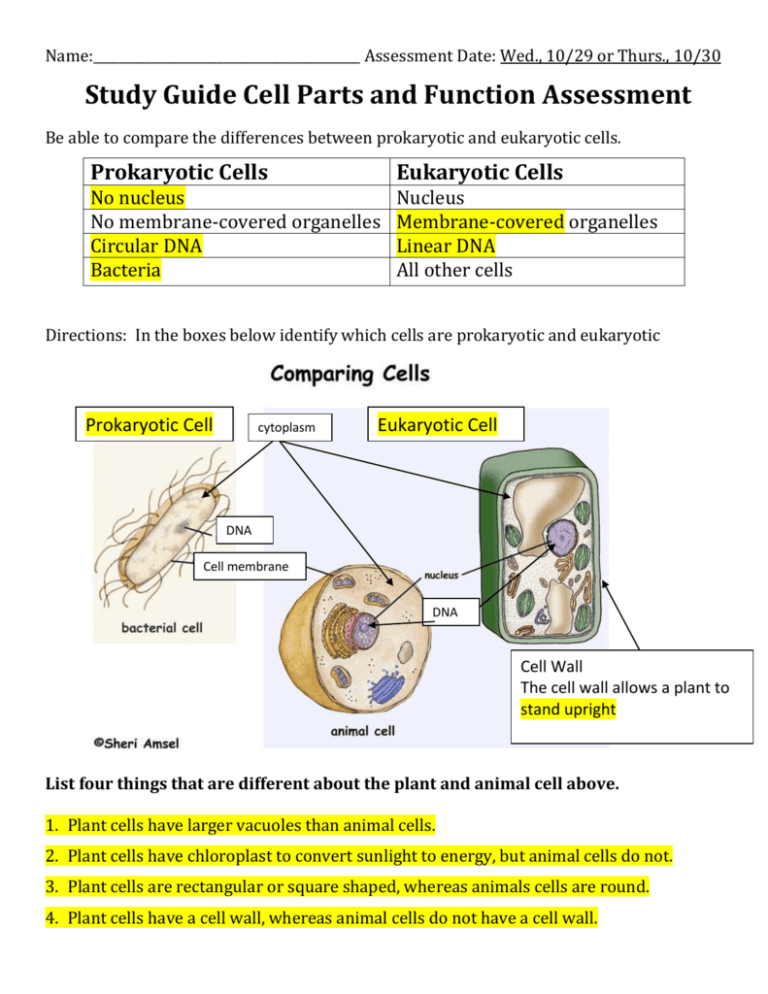
Name:_________________________________________ Assessment Date: Wed., 10/29 or Thurs., 10/30 Study Guide Cell Parts and Function Assessment Be able to compare the differences between prokaryotic and eukaryotic cells. Prokaryotic Cells Eukaryotic Cells No nucleus No membrane-covered organelles Circular DNA Bacteria Nucleus Membrane-covered organelles Linear DNA All other cells Directions: In the boxes below identify which cells are prokaryotic and eukaryotic Prokaryotic Cell cytoplasm Eukaryotic Cell DNA Cell membrane DNA Cell Wall The cell wall allows a plant to stand upright List four things that are different about the plant and animal cell above. 1. Plant cells have larger vacuoles than animal cells. 2. Plant cells have chloroplast to convert sunlight to energy, but animal cells do not. 3. Plant cells are rectangular or square shaped, whereas animals cells are round. 4. Plant cells have a cell wall, whereas animal cells do not have a cell wall. List the four things all cells have in common. 1. Small in size 2. Have cell membrane (allows nutrients in and wastes out) 3. Have DNA (hereditary material- manual on how to grow) 4. Have cytoplasm CIRCLE: Human have (prokaryotic/eukaryotic) and are (unicellular/multicellular). Know following organelles and the function of each: organelles: specialized structures which carry out the cell’s life processes cell membrane: a phospholipid layer that surrounds a cell’s surface and acts like a barrier between the inside and outside of the cell. Allows nutrients in and waste products out cell wall: a structure made from cellulose that surrounds the cell membrane of plant and bacteria cells and provides strength and support to the cell Animal cells do not have a cell wall. nucleus: the most visible organelle when looking through a microscope In a eukaryotic cell the DNA is found in the nucleus. Control center of the cell or brain of cell. nucleolus: stores the materials that will be used later to make ribosomes in the cytoplasm DNA: heredity material found in the nucleus of cell of eukaryotic cells, and in the cytoplasm of prokaryotic cells. cytoplasm: jelly-like fluid inside of the cell mitochondria: breaks down food molecules to make ATP (energy) bean-shaped organelle chloroplast: found in plant and algae cells -make food using the energy from the sun endoplasmic reticulum: transports material from the nucleus to other parts of the cell, often covered with ribosomes. lysosomes: digests food particles, waste and old cell parts and transports them out of the cell in vesicles Two examples of lysosomes at work would be -breaking down the webbing between our fingers as we develop -breaking down a frog’s tail as it goes through metamorphosis ribosome: the only organelle in eukaryotic cells that is not covered by a membrane the smallest most abundant organelle (lots of them!) makes proteins vacuole: stores food, water and other materials much larger in a plant cell pigment in vacuoles is what gives some plants their color makes vegetables crispy if they are full of water Be able to identify and label all of the following organelles in a cell cell membrane cell wall chloroplast DNA endoplasmic reticulum nucleus ribosomes vacuole(s) cytoplasm nucleolus mitochondria











