Eukaryotic Cells
advertisement

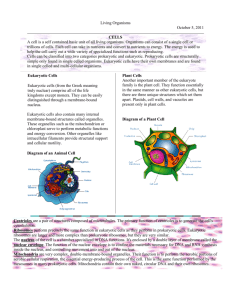
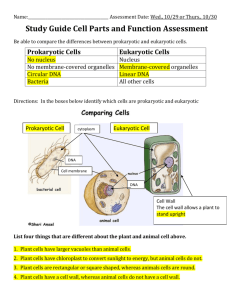
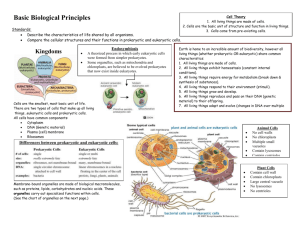
Cell Theory & Types Study Guide There were many different scientists that had an influence in the discovery of cells. Below, you will find a list of scientists involved and their contributions to the scientific community. 1. Robert Hooke- British scientist, who in 1665, built a microscope and looked at cork from a plant. He described the cork as looking like hundreds of boxes, and named these boxes “cells” which means “little boxes”. 2. Anton van Leeuwenhoek- Dutch merchant, in 1673, built a microscope to look at pond scum. He saw many small creatures swimming around and named them “animalcules” which means “little animals”. He also was the first person to see bacteria. 3. Matthias Schleiden- German scientist, in 1838, made the observation and conclusion that all plant parts are made of cells. He came to this conclusion after looking at thousands of plant slides and reading about other scientists’ research. 4. Theodor Schwann- German scientist, in 1839, stated that all animal tissues are made of cells. He concluded this after studying numerous animals under the microscope. He also wrote the first two parts of the cell theory: a. ALL ORGANISMS ARE COMPOSED OF ONE OR MORE CELLS. b. THE CELL IS THE BASIC UNIT OF LIFE IN ALL LIVING THINGS. 5. Rudolf Virchow- German scientist, in 1858, saw that cells could not develop from anything except other cells. He then wrote the third part of the cell theory: a. ALL CELLS COME FROM EXISTING CELLS. CELL THEORY 1. ALL ORGANISMS ARE COMPOSED OF ONE OR MORE CELLS. (Schwann) 2. THE CELL IS THE BASIC UNIT OF LIFE IN ALL LIVING THINGS. (Schwann) 3. ALL CELLS COME FROM CELLS. (Virchow) Prokaryotic Cell 1. No complex organelles 2. Circular DNA 3. No nucleus Only unicellular Most have a cell wall Reproduce asexually by binary fission Thought to have been the first cells Much smaller than eukaryotic cells Has DNA, ribosomes, cell membrane, and cytoplasm Eukaryotic Cell 1. Has a lot of organelles 2. Linear DNA 3. Has a nucleus Can be unicellular or multicellular Only plants and some fungi have cell walls Reproduce mainly sexual, some asexually Thought to have evolved from prokaryotes Much larger than prokaryotic cells Has DNA, ribosomes, cell membrane, cytoplasm (as well as other organelles) Organisms that are made up of the two types of cells Prokaryotic Cells: Archaebacteria Eubacteria Eukaryotic Cells: Animals Plants Fungi Protists Similarities and Differences Between Prokaryotic and Eukaryotic Cells Similarities Both types have DNA, cytoplasm, cell membranes, and ribosomes. They also have all seven living characteristics in common (grow and develop, DNA, respond to stimuli, reproduce, excrete, use energy, and they are cells of course) Differences Prokaryotic No membrane-covered organelles No Nucleus Circular DNA Much smaller than eukaryotic cells Theory is that they are much older than eukaryotic cells Has three general shapes- spheres, spirals, or rod shaped Eukaryotic Bunches of membrane-covered organelles Has a nucleus Linear DNA Larger than prokaryotic Theory is that they evolved from prokaryotic cells Animal- usually round shaped Plant- usually rectangular shaped