Cell Theory Guided Notes
advertisement

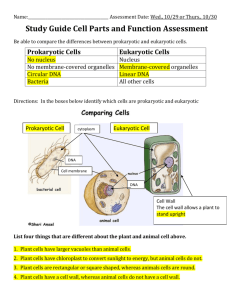
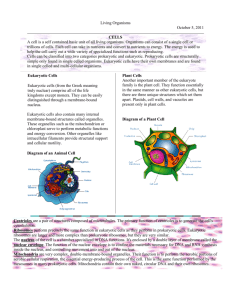
Name _________________________________ Date __________ Period __________ The Cell Theory: Types of Cells Notes KEY CONCEPT Cells are the ________________________________________________________________. The cell theory grew out of the work of _____________________________ and improvements in the ________________________. Many scientists contributed to the cell theory. a. ________________________ (1665) identified and named cells b. ________________________ (1674) observed living cells,; could see greater detail due to better lenses c. ________________________ (1838) notes that plants are made up of cells d. ________________________ (1839) concluded that all living things are made up of cells e. ________________________ (1855) proposed that all cells come from other cells The cell theory grew out of the work of many scientists and improvements in the microscope. _________________________________, specifically in ________________, enabled us to learn more about cells. The cell theory is a unifying concept of biology. Meaning __________________________________ __________________________________ is based on the cell theory. Early studies led to the development of the cell theory. The Cell theory has three principles. - All organisms are _________________________________________________________________. - All existing cells are produced by ____________________________________________________. - The cell is the ____________________________________________________________________. All cells share certain characteristics. a. Cells tend to be ________________________. b. All cells are enclosed by a ________________________. (aka plasma membrane) c. Have ________________________ (make proteins) d. All cells are filled with ________________________. e. Have ______________________________________________ - stored as DNA There are two cell types: ________________________ cells and ________________________ cells. 1. Eukaryotic cells a. Eukaryotic cells _______________________________________________. (This is where their DNA or genetic information is located) b. They have membrane- bound ________________________ (structures with a specific function in the cell.) c. Both prokaryotic cells and eukaryotic cells have _________________, ____________________, _____________________and a ________________________. d. Found in _______________, _______________, _______________ and _______________. e. Prokaryotic cells have a cell wall (________________________________________ surrounding the cell membrane which provides __________________________________________________________). Only some eukaryotic cells have a cell wall (some protists, plants, and animals) f. Eukaryotic cells are make up all ____________________________________ and can be found in some ____________________________________ (some members of kingdom Protista) 2. Prokaryotic cells a. Prokaryotic cells ________________________________________________. Their DNA (genetic information is in the cytoplasm) b. Prokaryotic cells ________________________ membrane-bound ________________________. (This is why prokaryotic cells are much smaller than eukaryotic cells. They have ___________________________________ and perform __________________________________.) c. Found in _________________________ Label the parts of the Prokaryotic and Eukaryotic Cell Prokaryotic and Eukaryotic Review Compare and contrast the Prokaryotic and Eukaryotic Cell by creating a venn diagram. Use the facts presented below to create your venn diagram. (Do this on a blank sheet of paper) Unicellular only Microscopic Some multicellular and some unicellular Bacteria Plants, animals protists and fungi Cell membrane aka plasma membrane Does not have organelles Nucleus Ribsomes (Nuclear DNA) DNA in a nucleus (Cytoplasmic DNA) DNA in cytoplasm Can not be seen with the naked eye Cytoplasm Has organelles Make up living things Reproduce Homeostasis Respond to environment Can die Make proteins No nucleus Flagella Cell wall Unicellular only Microscopic Some multicellular and some unicellular Plants, animals protists and fungi Cell membrane aka plasma membrane Does not have organelles Nucleus Bacteria Ribsomes Make up living things (Nuclear DNA) DNA in a nucleus (Cytoplasmic DNA) DNA in cytoplasm Can’t be seen with the naked eye Cytoplasm Has organelles Reproduce Homeostasis Respond to environment Can die Make proteins No nucleus Flagella Cell wall