Chapter 3
advertisement

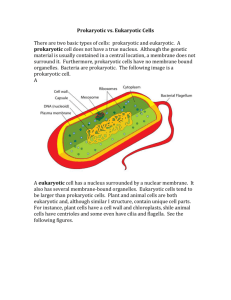
Chapter 3 Cells: Agriculture’s Building Blocks Introduction • Most important was the invention of the microscope in the 1600s. • Robert Hook termed the tiny spaces “cells” • Cells vary greatly in size and shape – – – – Largest is ostrich egg Smallest is bacteria Round, square, long, thin plate Amoebas change shape constantly • All of agriculture is built around cells. – Plants and animals grow from cells – Reproduction begins with cells – One-celled bacteria digest food in certain animals Types of Cells • Prokaryotic Cells Types of Cells • Eukaryotic Cells Cell Components • Cell wall – cellulose provides rigidity for the walls of the cell and provides some support for the entire plant – Lumber and paper are manufactured from the cellulose – Pectin is found in softer plant tissues such as leaves ad fruit. • Pectin gives jelly its thick consistency Cell Membrane • Inside the cell wall is the cell membrane • Semi permeable which means that it allows only certain material to pass through • Diffusion –molecules in a solution pass through the membrane from a region of higher concentration to a region of lower concentration • Osmosis – diffusion of water • Homeostasis- the ability of an organism to remain stable when conditions around it change • Turgid – when cells are filled with the proper amount of water, cells are filled out and taut • In a drought plants are limp and wilted, but as soon as water is made available, they return to their normal healthy apperance The Nucleus • Eukaryotic cells have a nucleus • Prokaryotic cells do not have a true nucleus • Composed primarily of nucleic acids, protein, and enzymes and serves as the control center for all of the activities of the cell Cytoplasm • Is a thick, clear fluid that surrounds the nucleus and it contains all of the material needed by the cell to conduct life processes. • Mitochondria – break down food nutrients and supply the cell with energy • Vacuoles are organelles that serve as storage compartments for the cell • Microtubules act as the bones of the cell • Microfilaments are fine fiberlike structures composed of protein • Ribosomes are the sites where protein molecules are assembled. • Golgi apparatus remove water from proteins and prepare them for export from the cell • Endoplasmic reticulum is a large webbing or network of double membranes that transport material within the cell • Lysosomes are the digestive units of the cell Plastids • Plant cells have organelles called plastids that are present in animal cells. Three types of plastids exist: chloroplasts, leucoplasts and chromoplasts. Cell Reproduction • Eukaryotic cells divide by a process called mitosis. • Activity on mitosis