Cell Structure Concept Map: Biology Basics for Grade 10
advertisement

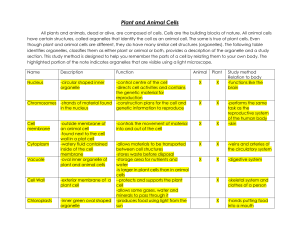
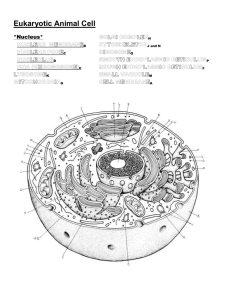
Unit 1B Concept Map Course Essential Question Unit 1b - Biology Basics of Life - Cell Structure Grade Level: 10 Cells have organized structures and systems necessary to support chemical reactions needed to maintain the living condition. Subject: Biology Unit Essential Question How is structure related to function at the cellular levels of organization? PA Standards/Anchors/(Assessment Anchor/Eligible Content) BIO.A.1.2.1 BIO.A.1.2.2 Lesson Essential Questions: 1. What is the cell theory? 2. What are the structural and functional differences of the internal structures of prokaryotic and eukaryotic cells? 3. What are the functions of each of the organelles in the cell? 4. How do organelles work together to carry out the characteristics of life? 5. What are the structural and functional differences between animal and plant cells? Concepts 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. 6. Cells are the basic unit of structure and function for all living things. Cells occur in two basic forms: Prokaryotes (Bacteria and Archaea) and Eukaryotes (all other cells). A cell’s interior is separated or compartmentalized from the environment by a phospholipid bilayer plasma membrane. The cytoplasm contains a collection of connected, internal membranous sacs that divide the cytoplasm into functional and structural compartments or organelles. Each organelle has a specific and necessary function. Chemical reactions and processes necessary for life are carried out in cytoplasm or organelles within a eukaryotic cell’s protoplasm. Structure is related to function at the cellular and organelle levels of biological organization. -----------------------------------------------------------------Skills 1. Analyze cellular structures and their functions in prokaryotic and eukaryotic cells 2. Describe and interpret relationships Vocabulary 1. Cell membrane 2. Nucleus 3. Cytoplasm 4. Organelle 5. Vacuole 6. Lysosome 7. Cytoskeleton 8. Centriole 9. Ribosome 10. Endoplasmic reticulum (smooth and rough) 11. Golgi apparatus 12. Mitochondrion 13. Cell wall 14. Lipid Bilayer 15. Selectively permeable 16. Microtubules 17. Microfilaments 18. Protein 19. Chloroplast 20. Flagella 21. Cilia between structure and function at various levels of biological organization (ex: organelles, cells, tissues, organs, organ systems, and multicellular organisms) 3. Predict the changes to function for anomalies in structure. Formative Assessments Summative Assessments 1. Ticket out the 1. Quizzes door 2. Unit Tests 2. Think-pair-share 3. Cell model 3. Thumbs up – 4. Labs microscope/stereoscope Thumbs down 5. Projects (cell 4. Concept Map membrane model, 5. Sentence starter cell in a bag) prompts 6. CDT biology 6. Collins writing 7. Compare cell to a 7. Venn diagram factory 8. Compare contrast 9. 3-2-1 10. Frayer diagrams 11. KWL 12. Whiteboard responses Resources Biology textbook Powerpoints (from textbook) Biology websites: -biologyjunction.com -biologycorner.com -biology.com