Life Science: Cells Test Review - Middle School
advertisement

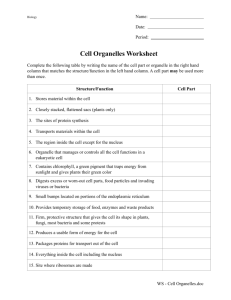
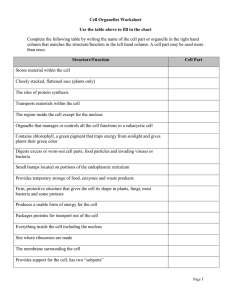
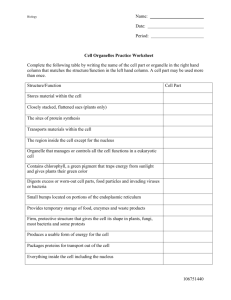
Life Science Unit 3 – Cells – Test Review 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. 6. 7. 8. 9. 10. 11. 12. 13. 14. 15. 16. 17. 18. 19. 20. 21. 22. 23. 24. 25. 26. 27. 28. 29. What kind of cells contain a nucleus? What is the function of the nucleus? Which type of molecule is DNA? After a protein is made, which order of organelles does it follow to exit the cell? What are the three parts of the cell theory? Which organelles would you find in plant cells, but not in animal cells? Which organelle contains the cell’s genetic material? Organs working together to perform a specific function are called? What is the main function of the cell wall? What structure is not found in prokaryotic cells? Which organelle makes proteins using instructions that come from the nucleus? What is a group of cells that perform a similar function? Sodium (Na) and chlorine (Cl) atoms bond to make table salt (NaCl). What is the best description of table salt? Which kind of organism does not have a cell wall? What are small membrane sacs that specialize in moving products into, out of, and within a cell called? Name the levels of organization of a multicellular organism from the simplest to the most complex. Why are carbohydrates important to cell processes? What is a cell that has no nucleus and no mitochondria, but does have a cell membrane and a cell wall? What organelle received proteins and lipids from the endoplasmic reticulum, modifies the molecules made in the endoplasmic reticulum to their specific function, and releases molecules in vesicles? Which structure immediately identifies as cell as a eukaryotic cell? What is the mitochondria used for? What is the smallest unit of all things? Which molecule is made of amino acids? What are lipids used for? What makes up the framework of the cell membrane? Describe the cell membrane’s structure. Is a plant cell a prokaryotic or a eukaryotic cell? Describe the vacuole found in plant cells. What organelle does the nuclear envelope surround? Be able to label these structures on a cell: cell membrane, cell wall, cytoplasm, nucleus, mitochondria, central vacuole, and ribosomes.