Biology B2 revision sheet colour[1]
advertisement
![Biology B2 revision sheet colour[1]](http://s3.studylib.net/store/data/006699123_1-118546e1cf2edc78c83e680e8a2fb59f-768x994.png)
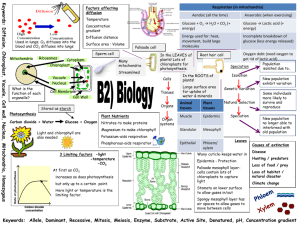
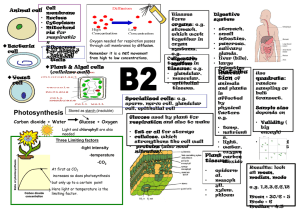
Specialised Cells – Adapted for a specific job eg sperm, red blood cells, neurones Nucleus Cell Membrane Cytoplasm Ribosomes Mitochondria Cell Wall Vacuole Chloroplast Nucleus – controls cell activity and carries genetic information Cell Membrane–controls movement in/out of cell Cytoplasm – where reactions take place Ribosomes – where protein syntheses occur Mitochondria – where most respiration and energy release occurs Chloroplast – contain chlorophyll to trap sun energy for photosynthesis Vacuole – storage of cell sap DIFFUSION – passive movement of molecules from area of high concentration High Low to low concentration across a semipermeable membrane Eg movement of oxygen from lungs to blood The greater the difference in concentration, the faster diffusion occurs Plant Cell C Chemical Reactions – occur in Cytoplasm – controlled by ENZYMES = Biological Catalyst (speed up chemical reactions eg respiration, protein synthesis, photosynthesis) - Long chain of amino acids folded into specific shape and denatured above 42°C and work best at specific pH - Digestive enzymes –Protease (stomach, pancreas, small intestine) convert proteins to amino acids -Lipase (pancreas, small intestine) convert fats to fatty acids and glycerol -Carbohydrase eg amylase (saliva) convert starch to sugars Stomach produces HCl to make Industrial uses – Baby foods contains proteases to ‘pre-digest’ food stomach acidic for enzymes. - Isomerases convert glucose to fructose which is sweeter so smaller amounts needed Liver then makes bile to so used in slimming products neutralise acid so enzymes in - Carbohydrases used to convert starch to sugar syrup small intestine can work - Proteases and Lipases in biological detergents to break down dirt Animal Cell Photosynthesis -Limited by temp, CO2, and light sunlight Carbon + Water Dioxide Glucose + Oxygen chlorophyll Storage as Starch Energy Losses in Food Chains Sun Plant For respiration Energy is lost at each stage due to Rabbit Fox So farmers can keep costs to minimum by controlling environment of farm animals eg keep warm, restrict movement etc respiration, heat, movement and waste Inheritance Homeostasis faeces, urine, gas 83kJ Respiration Wood/fossil fuels Die / Decompose Microbes in warm, O2 rich conditions, break down material Testes / Ovaries – produce gametes with half chromosomes (by meiosis) which fuse and then divide by mitosis to form embryo Sperm and Embryo Eagle Foxes Rabbits Grass 8Kg 13Kg 15Kg 20Kg Pyramid of Biomass – material and energy lost at each stage Membrane Body cell – contain 23 pairs of chromosome (1 of each pair from each parent)– each chromosomes contains genes = 1 or more genes code for a characteristic. Different forms of the same gene = Alleles Photosynthesis Respiration Semi-Permeable Blood sugar level – monitored by pancreas - too much sugar? Pancreas releases INSULIN – converts glucose to glycogen - if body cannot produce insulin/enough insulin = Diabetes CO2 Combustion Low Concentration To maintain a constant internal environment Eg. Removal of wastes – CO2 (via lungs) and urea (via kidneys) Eg. Maintaining temperature, blood sugar levels, water and ions Temperature– monitored by thermoregulatory centre of brain, and skin receptors-too hot? – Vasodilation (blood capillaries widen) and sweating – evaporation of sweat requires heat - too cold? – Vasodilation (blood capillaries constrict) and shivering – muscle contractions require energy and release some heat respiration 13kJ eat 100kJ tissues 4kJ Cycling of Materials eg Carbon Cycle Special type of diffusion = OSMOSIS = the movement of water molecules from a dilute solution to a more concentrated solution Eg movement of water into/out of cells Biology B2 -Need minerals for Need minerals for healthy growth healthy growth Nitrogen –to make amino acids to form proteins for growth – deficiency = stunted growth Nitrogen – for growth Magnesium –for chlorophyll – deficiency = yellow plant High Concentration These cells are called STEM CELLS and can be made to differentiate into many different types of cells (only possible from stem cells and bone marrow cells) and can be used in treatment of certain conditions Bb x Bb Dominant allele – only 1 needed for gene to be expressed (B=brown eyes, b=blue) Recessive allele – both genes needed for expression B b Inherited disease Cystic Fibrosis – caused by recessive allele – both alleles B BB Bb needed for disease expression. If 1 allele present = Brown Brown carrier Huntingtons Disease – caused by dominant allele – only 1 b Bb bb allele for the Brown Blue disease is needed for the child to express the disease