B2 revision poster
advertisement

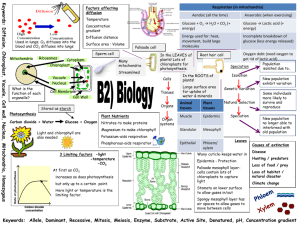
• Cell membrane • Nucleus • Cytoplasm • Mitochond ria for Animal cell Bacteria cell respiratio n • Ribosomes Allprotein these 3 for have Cell synthesis Walls Oxygen needed for respiration passes through cell membranes by diffusion. Remember it is a net movement from high to low concentrations. Plant & Algal cells (cellulose wall) Yeast cell Tissues form organs: e.g. stomach, which work together in organ systems, e.g. Cells work digestive together system in tissues: e.g. • glandular, • muscular, • epithelial tissues. Digestive system Specialised cells: e.g. Photosynthesis Stored as starch (insoluble) Carbon dioxide + Water Glucose + Oxygen Light and chlorophyll are also needed Three Limiting factors -light intensity -temperature -CO2 At first as CO2 increases so does photosynthesis sperm, nerve cell, glandular cell, epithelial cell Glucose used by plant for respiration and also to make • fat or oil for storage • cellulose, which strengthens the cell wall • proteins (also need nitrates). • stomach, • small intestine, • pancreas, • salivary glands, • liver (bile), • large intestine Distribu (faeces) tion of animals and plants is affected by physical factors e.g. • temp, • nutrient s, • light, • water, • oxygen Plant • carbon tissues: dioxide • but only up to a certain point • Here light or temperature is the limiting factor. • • epiderm al, mesoph yll, xylem, phloem Use quadrats: random sampling or belt transect. Sample size depends on • Validity ( big enough) • Reproduci bility (not too big) Results: look at mean, median, mode e.g. 1,2,3,6,6,12 Mean = 30/6 = 5 Mode = 6 Median = 4.5 1) 2) 3) Enzymes –biological catalysts that speed up reactions e.g. respiration in the mitochondria Proteins are long chains of amino acids folded to give a specific shape. e.g. muscle, hormones, antibodies, catalysts (enzymes). Enzymes have an optimum Enzymes are made from protein temperature and pH. Changes in pH/temp can denature the enzyme so its shape changes and the substrate can’t bind to the active site DNA: deoxyribose nucleic acid. Forms a code for making proteins from amino acids. DNA fingerprinting possible as a person’s DNA is unique ( except for id twins ). Stem cells: from embryos Embryo Mendel: or bone marrow. Can screenin discover differentiate to any kind g: to find ed of cell. Useful e.g paralysis alleles ‘inherite treated by making new for d nerve cells genetic factors” Uses of Enzymes Inheritance- Parents who are both carriers of the Cystic fibrosis allele (c). Parents Cc x Cc Gametes C or c x C or c C -Biological washing powders (P,L) -In baby foods (proteases) Enzymes and digestion Large molecules are broken down so they can be absorbed. Amylase ( a carbohydrase) breaks down starch into sugars in the mouth and small intestine. Starch - Carbohydrases to turn starch into sugar syrup -In slimming foods- fructose is made using isomerases. Fructose is sweeter than glucose so less is needed. Possible Outcomes C 75% healthy c 25% sufferers glucose Cystic Fibrosis Proteases breakdown proteins into amino acids in the stomach and small intestine. Lipases breakdown fats into fatty acids and glycerol in the small intestine. Caused by recessive allele (so two copies of allele are needed). A thick sticky mucus is produced affecting air passages and digestive systems Enzymes are made in the Polydactyly- extra fingers or toes. salivary glands (A), stomach Caused by dominant allele (so (P), pancreas (A,P,L), small only one allele is needed). intestine (A,P,L). • Stomach also makes acid (HCl). • Liver makes bile to 46 chromosomes in human body cell (23 pairs of which one pair is XX or XY). But only 23 chromosomes in gametes/sex cells Mitosis-(TWO) used for normal cell growth 1) Parent cell chromosomes make identical copies of themselves 2)They line up along the centre 3) They move apart 4)Two daughter cells form each with 46 identical chromosomes to the parent cell c CC Cc Cc cc diseases – ethics… by studying monohyb • Homozygous rid ( bb) or (BB), crosses • Heterozygous in peas. (Bb), • phenotype, ( what is seen/expressed e.g. brown eyes) • Genotype ( which alleles they Meiosis –(makes have e.g. BB) eggs in ovaries…..)used to make the sex cells (gametes) -the chromosomes are copied -cell divides twice to give 4 non-identical gamete cells (each with 23 chromosomes) Fossils may be formed in various ways: Aerobic respiration happens continuously in animals and plants Aerobic The energy may be used: ■ to build larger molecules from smaller ones Aerobic respiratio n happens in the mitochondr ia. ■ in animals, to enable muscles to contract ■ in mammals and birds, to maintain a steady body temperature in colder surroundings in plants: energy is used to build up sugars, nitrates and other nutrients into amino acids which are then built up into proteins. Muscles store glucose as glycogen, which can then be converted back to glucose for use during exercise. ■ from the hard parts of animals that do not decay easily ■ from parts that have not decayed because the conditions needed for decay are absent ■ when parts of the organism are replaced by other materials as they decay ■Extinction as preserved traces of organisms, eg footprints, may be caused by: burrows andto rootlet traces. ■ changes the environment Speciation over geological time ■ new predators ■ new diseases ■ new, more successful, competitors ■ a single catastrophic event, eg massive volcanic eruptions or collisions with asteroids ■ through the cyclical nature of speciation. glucose + oxygen ➞ carbon dioxide + water During exercise: (+ energy) Anaero bic the heart rate increases ■ the rate and depth of breathing increases. These changes increase the blood flow to the muscles and so • increase the supply of sugar and oxygen • increase the rate of removal of carbon As the breakdown of glucose is incomplete, much less energy is released than during aerobic respiration. New species form because of ■ geographical isolation ■ genetic variation ■ natural If selection muscles are subjected to long ■ speciation periods of vigorous activity they become fatigued, i.e. they stop contracting One cause of muscle fatigue is the build-up efficiently. of lactic acid in the muscles. Blood flowing through the muscles removes exercise if the ,lactic acid. During insufficient oxygen is reaching the muscles they use anaerobic respiration to obtain energy. Anaerobic Anaerobic respiration results respiration is the incomplete in an oxygen debt breakdown of that has to be glucose and repaid in order to produces oxidise lactic acid lactic acid. to carbon dioxide lactic + oxygen carbon andacid water. dioxide + water 1. name 4 cells with a cell walll. 2. What is found in a plant cell walll? 3. What is the function of mitochondria? 4. Where does protein synthesis take place? 5. Which cell does not contain a nucleus? 6. Is a yeast cell more like an animal, bacteria or plant cell – explain your answer. 7. A cell X has a cell wall, nucleus , no chloroplasts and a permanent vacuole – what type of cell do you think it is? 8. How do cells get oxygen? 9. Why would oxygen move into a cell? 10. Name 3 tyoes of tissue in a stomach 11. What do plants store in the vacuole? 12. Why do plants store glucose as starch? 13. Give the word equation for photosynthesis 14. What are 3 limiting factors for photosynthesis? 15. What else is needed for photosynthesis? 16. Give 3 substances a plant can make from glucose 17. What else does a plant use glucose for? 18. What is needed for plants to make proteins? How do they get it? 19. Name 3 types of plant tissue 20. Name 4 parts of the digestive system that contain glandular tissue. 21. What is the mesophyll tissue’s function? 22. What does the phloem transport? 23. How could we estimate the number of plants in a field? 24. Describe how to do a belt transect 25. What factors need to be considered when deciding how many quadrats to place? 26. What is the mean, mode and median of 12,13,10,9,5,9,12,4,5,9,5,9,10,9 1. Where in a cell are enzymes made? 2. Give 4 types of proteins made in cells 3. What is a biological catalyst? 4. Why do high temps denature enzymes? 5. Name 3 types of digestive enzymes 6. What type is amylase? 7. Give 3 types of enzyme made in the pancreas 8. Give 3 digestive organs where amylase is produced 9. What type of acid is made in the stomach 10. What is the purpose of bile? 11. Where is it made and stored? 12.What are fats broken down in to? 13.Why must starch, fats and protein be digested? 14.What is the optimum temp for human digestive enzymes? 15.What is the optimum pH for stomach protease? 16.What would be the optimum pH for pancreatic proteases? 17. Which 2 types of enzymes are in biological detergents? 18. Which enzyme is used to make baby food? 19.Which enzyme would be used to turn starch into sugar syrup? 20.Why are isomerases used in slimming foods? 21.What is DNA? 22.What are alleles? 23.What is a recessive allele? 24.What is a dominant allele? 25.What is a chromosome? 26.How many are in a human body cell? 27.How many in a human sperm cell? 28.What does homozygous mean? 29.What is a genotype? 30.Describe cystic fibrosis symptoms 31.What are the chances of inheriting 1. Where does aerobic respiration take place? 2. Give the word equation 3. Give 3 ways in which the energy is used in animal cells 4. Give one use of energy in plants 5. When do plants respire? 6. Name 2 substances needed by muscles for aerobic respiration 7. Why must our heart rate increase when we exercise? ( 3 reasons) 8. What happens to our breathing during exercise? Why? 9. Where and how do we store glucose? 10.What happens if we cannot take in enough oxygen during exercise? 11. What is made in anaerobic respiration? 12.What is a problem with build up of lactic acid? 13.How can we remove lactic acid from the muscles? 14.Why is it important to warm down after exercise? 15.Why do we continue to breathe heavily after exercise has finished? 16.What does lactic acid get broken down in to ? Give the word equation. 17.Why do we need to eat more in winter? 18.How would you make

![Biology B2 revision sheet colour[1]](http://s3.studylib.net/store/data/006699123_1-118546e1cf2edc78c83e680e8a2fb59f-300x300.png)