BIOS 1010 Unit 2 Review
advertisement

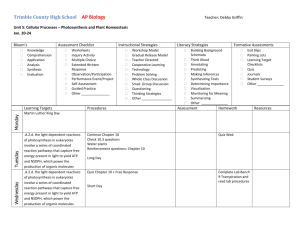
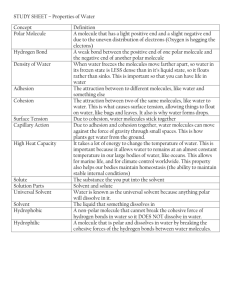
BIOS 1010 Unit 2 Review You should be able to speak these answers out loud (or write them) without looking at your notes. Drawing pictures may also help for some questions. Never just read to study. Your brain then relies on having the answer in front of you. This does not allow you to answer short answer questions. Chapter 2 What are atoms? What 3 particles are atoms composed of? What kind of charge does each one have? What is an element? What does the atomic number and atomic mass of an element stand for? What is a radioactive isotope? What are electron shells? What part of an atom determines its chemical properties (energy capacity, interactions)? Define the three major types of chemical bonds and be able to give an example of each. What is a free radical? What are the unique characteristics of water? What makes a solution neutral, basic, or acidic? What numbers represent these solutions? What is a buffer? Chapter 3 What is the difference between organic and inorganic molecules? How are monomers joined to make polymers? How are polymers broken down to make monomers? What are the major organic molecules? For each major organic molecule, know the classes, their functions, characteristics and examples. What is the most abundant organic molecule on Earth? What are the four levels of complexity for proteins? What determines the structure of proteins? Why is the structure of a protein important? What is it called when a protein loses its function and what causes it to happen? Chapter 6 Define energy. What two types of energy are there? What do they mean? What are the laws of thermodynamics? What are the two types of chemical reactions? What do they mean? Define activation energy. What are the three major energy-carrier molecules? What is a coupled reaction? What are the three important properties of enzymes? How do enzymes work to catalyze a chemical reaction? How do metabolic pathways work? How are metabolic pathways controlled? How do drugs, poisons, and environmental conditions effect enzymes? Chapter 7 Define photosynthesis. Why is a leaf structured the way it is? Know the parts of a leaf and their function. What is the chemical equation for photosynthesis? What are the two main pathways of photosynthesis? Where do they take place? What do chloroplasts have to capture photons? What is the main molecule that captures photons in a green plant? What are the events of the light reactions? What are the major end products of the light reactions? What happens during the Calvin cycle? How are CAM plants different from the common C3 plants? Why aren’t all plants C3 plants (why do we find CAM and C4 plants)? Chapter 8 Why is photosynthesis important? What is the chemical equation for cellular respiration? What energy production pathway do all organisms that don’t photosynthesis use? Glycolysis is a chemical reaction. What is the reactant? What are the products? Where does the activation energy come from? What determines the fate of the pyruvate molecules after Glycolysis? Where does aerobic respiration take place? What happens during the matrix reactions? What are the end products of the Kreb’s cycle/Citric acid cycle? What happens during the membrane reactions? How much total ATP is produced from aerobic respiration? What other sources can be used if needed to produce energy? Why is anaerobic fermentation necessary? How many ATP are produced from anaerobic fermentation?