B2_Revision_Sheets.ppt - New College Leicester
advertisement
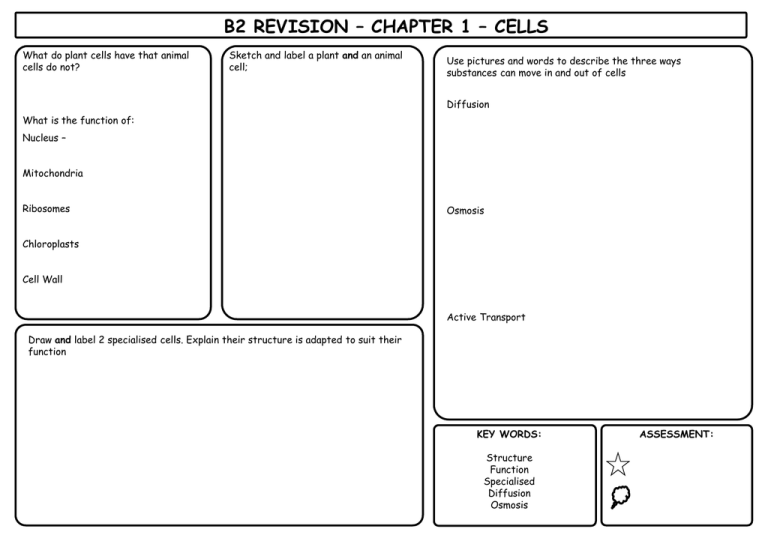
B2 REVISION – CHAPTER 1 – CELLS What do plant cells have that animal cells do not? Sketch and label a plant and an animal cell; Use pictures and words to describe the three ways substances can move in and out of cells Diffusion What is the function of: Nucleus – Mitochondria Ribosomes Osmosis Chloroplasts Cell Wall Active Transport Draw and label 2 specialised cells. Explain their structure is adapted to suit their function KEY WORDS: Structure Function Specialised Diffusion Osmosis ASSESSMENT: B2 REVISION – CHAPTER 2 – HOW PLANTS PRODUCE FOOD What is the equation for photosynthesis Why do plants need nitrates? Respiration Where in the plant does it occur? How are leaves adapted to perform photosynthesis? Explain how plants use glucose for the following: Why do plants need magnesium? Transport Explain how light, CO2 and temperature are limiting factors of photosynthesis Storage KEY WORDS: Respiration Photosynthesis Limiting Factor Nitrates Magnesium ASSESSMENT: B2 REVISION – CHAPTER 3 – ENERGY FLOWS What is the main source of energy for living things? What is biomass and how does it change along a food chain? What organisms break down matter? What conditions do they require? Explain how energy is lost in the following ways: Waste Why is the process of decay important? Movement Describe how energy losses can be reduced in food production Describe the different forms carbon can be found in, how it is used, and how it is cycled Maintaining Body Temperature KEY WORDS: Biomass Decay Decomposer Carbon cycle Energy ASSESSMENT: B2 REVISION – CHAPTER 4 – ENZYMES What are enzymes made from? What do enzymes do? What is the equation for aerobic respiration? Where in the cell does it occur? Why do we need respiration? What are the 3 groups of enzymes in digestion? What is their substrate and what do they break them down into? 1) 2) How do they work? (explain & draw the lock & key mechanism 3) Why is the stomach acidic? What effect does temperature have on enzyme activity What effect does pH have on enzyme activity Describe 3 industrial uses for enzymes What is bile, what does it do and how does it do it? KEY WORDS: Enzyme Lock and Key Denature Aerobic respiration Bile Carbohydrase/Protease/Lipase ASSESSMENT: B2 REVISION – CHAPTER 5 – HOMEOSTASIS What is homeostasis? Explain why the following are regulated: Waste products What part of the brain controls body temperature? How does the body control blood sugar levels? [Key Words: Insulin, Glucagon, Glycogen, Pancreas, Liver, Blood] Explain how the body: a) Keeps Cool [e.g. how does sweating help?] What is diabetes? CO2 What are the symptoms? b) Keeps warm Urea Water & ions How can it be treated? KEY WORDS: Homeostasis Thermoregulatory Centre Vasodilation/Vasoconstriction Insulin/Glucagon Glycogen Diabetes ASSESSMENT: B2 REVISION – CHAPTER 6 – INHERITANCE What is mitosis and why is it needed? What are stem cells? State 2 uses of stem cells: How many chromosomes in a) gamete and b) somatic cell? What is an allele? What is differentiation? What does a) dominant; and b) recessive mean? How does it differ in plants and animals? State 2 problems with stem cell research: What is meiosis? Chromosomes are made of long strands of what? What is Huntington’s Disease and what causes it? What is Cystic Fibrosis and what causes it? Small sections of this are called what? Why is it important? What do genes code for? On the back, cross 2 CF carriers and describe the offspring KEY WORDS: How does it help generate variation? What is DNA fingerprinting? Chromosome Mitosis / Meiosis Gene Allele DNA Stem Cells ASSESSMENT:






![Biology B2 revision sheet colour[1]](http://s3.studylib.net/store/data/006699123_1-118546e1cf2edc78c83e680e8a2fb59f-300x300.png)