Lab Exam 2 Review Sheet
advertisement

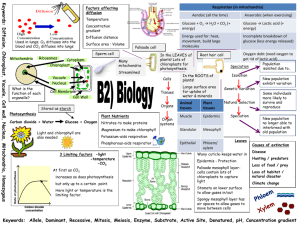
BIO 101 Lab Dr. Jean Anastasia Lab Exam 2 Review Sheet Lab 7 Osmosis Know that osmosis is the diffusion of water across a semi-permeable membrane know the difference among hypotonic, isotonic, and hypertonic environments (be able to identify which is which) know how a water will move (in or out of the cell) and what will happen to the cell in each of the three environments be able to identify an Elodea leaf under a microscope and know if it has been put in a hypotonic or hypertonic environment by looking at the cells know the function of the large central vacuole in plant cells Lab 8 Enzymes know that enzymes are proteins know that enzymes are catalysts which speed up the rate of chemical reactions know that enzymes are fast and are specific (only work for one type of reaction) know that enzymes have ideal temperatures for activity and that too high temperatures are worse than too low temperatures know that high temperatures can denature an enzymes which is not reversible know that pH measures how acidic or basic a solution is. pH below 7 are acidic, pH of 7 is neutral, pH above 7 is basic know that enzymes have an ideal pH for activity and that too high pH or too low pH can lower activity know that the enzymes that we worked with was catalase and that it catalyzed the reaction to turn hydrogen peroxide into water and oxygen know that we measured enzyme activity of catalase by measuring the size of the bubble of oxygen produced in a test tube Lab 9 Photosynthesis and Respiration know that photosynthesis uses light energy, water and carbon dioxide to produce carbohydrates know where in the plant cell that photosynthesis takes place= chloroplast know the structures of the chloroplast: thylakoid membrane, grana, stroma know that cellular respiration is a metabolic pathway that lets cells resynthesize ATP. The pathway starts with glucose and oxygen as the reactants and produces carbon dioxide, water and energy know where in a cell respiration takes place= mitochondria know that when CO2 (carbon dioxide) is released into water it produces an acid and lowers the pH know that when CO2 is used up and the levels lowers in a solution, the solution becomes more basic and the pH increases know that Bromothymol Blue (BTB) is a pH indicator. It is green when neutral, turns yellow when the solution is acidic and turns blue when the solution is basic. be able to predict what will happen to BTB when a plant is placed in it in the light and in the dark know that yeast use glucose as their main substrate for respiration but are able to use other substrates, especially fructose (since it occurs in the natural habitat or fruits) BIO 101 Lab Dr. Jean Anastasia know that yeast's cellular respiration proceeds most efficiently at 37oC and much slower at high or low temperatures know how we measured respiration in the lab- using a small test tube inverted into a larger one and measuring the bubble of CO2 produced Lab 10 Reproduction know the definitions and differences between asexual reproduction and sexual reproduction and the advantages of each know the parts of the flower shown on page 124 and be able to identify them on a picture of a flower know which parts of the flower are part of the male parts (Stamen) and which are part of the female part (pistil) know that sperm are found inside the pollen grains which are produced in the anthers and that eggs are found inside the ovules which are inside the ovary know the parts of the human reproductive system shown on pages 126 and know their functions (filled in Tables 10-2 and 10-3) Lab 11 Genetics Know that people have two copies of every gene and that different versions of a gene are called alleles Know that each person inherits one allele from their mother and one allele from their father Know the definitons of the following terms: allele, dominant allele, recessive allele, homozygous and heterozygous, phenotype, genotype Know how to represent the genotype of using letters . For example, for a trait for Blue flowers represented by “B”(BB= homozygous dominant, Bb = heterozygous, bb= homozygous recessive) Understand the rules of simple Mendelian Inheritance and be able to use a Punnet square to figure out the expected ratios of offspring in the F1 and F2 generations if given the genotypes of the parent (P1) Know how to use pedigree analysis to study the inheritance of traits in humans. Know how to read a pedigree and use it to determine the dominance of traits and likely genotypes of individuals Lab 12 Natural Selection Know the definitions of evolution, natural selection, adaptation and fitness Understand that natural selection is one cause of evolution Know that for natural selection to occur, phenotypes of inividuals must vary, the variation must be heritable (genetically based) and that the variation must result in differential reproductive success (differential fitness) For the three types of selection (directional, stabilizing and disruptive), know which phenotypes of favored and which are selected against Understand that natural selection leads to adaptation Understand why peppered moths evolved darker color after the industrial revolution Be able to predict what will happen to the black allele (CB) after selection in a black habitat, a white habitat, or a grey habitat

![Biology B2 revision sheet colour[1]](http://s3.studylib.net/store/data/006699123_1-118546e1cf2edc78c83e680e8a2fb59f-300x300.png)