B2 Key words and facts
advertisement

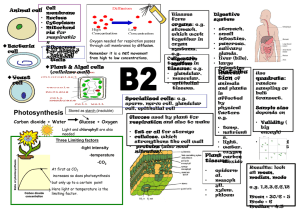
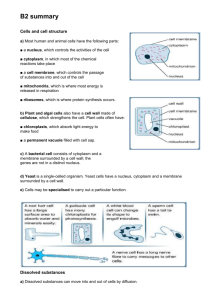
Keywords: Diffusion, Chloroplast, Vacuole, Cell wall, Nucleus, Mitochondria, Homozygous Factors affecting diffusion Respiration (in mitochondria) Aerobic (all the time) Temperature Used in lungs; O2 diffuses into the blood and CO2 diffuses into lungs Mitochondria Concentration gradient Glucose + O2 → H2O + CO2 (+ energy) Glucose → Lactic acid (+ energy) Diffusion distance Energy used for: heat, movement, build large molecules Incomplete breakdown of glucose (less energy released) Surface area : Volume Palisade cell Sperm cell Ribosomes Cytoplasm Chloroplast Many mitochondria Streamlined Vacuole Nucleus What is the function of each organelle? Tissues Organs Stored as starch Photosynthesis Plant Nutrients Glucose + Oxygen Light and chlorophyll are also needed In the LEAVES of plants! Lots of chloroplasts for photosynthesis. Cells Cell Membrane Cell Wall Carbon dioxide + Water Anaerobic (when exercising) Nitrates-to make proteins Magnesium-to make chlorophyll Organ systems Root hair cell 3 Limiting factors -light -temperature -CO2 At first as CO2 increases so does photosynthesis but only up to a certain point. Here light or temperature is the limiting factor. Population isolated due to… Speciation In the ROOTS of plants! Large surface area for uptake of water & minerals Animal tissues Plant tissues Muscle Epidermis Glandular Mesophyll Epithelial Phloem/ xylem Potassium-aids respiration Phosphorous-aids respiration Oxygen debt (need oxygen to get rid of lactic acid) Isolation New population exhibit variation Genetic Variation Natural Selection Speciation Leaves Waxy cuticle-keeps water in Epidermis - Protection Palisade mesophyll layercells contain lots of chloroplasts to capture light Stomata on lower surface to allow gases in/out Some individuals more likely to survive and reproduce New population no longer able to interbreed with old population Causes of extinction Disease Hunting / predators Loss of food / prey Loss of habitat / natural disaster Climate change Spongy mesophyll layer has air spaces to allow gases to move between cells Keywords: Allele, Dominant, Recessive, Mitosis, Meiosis, Enzyme, Substrate, Active Site, Denatured, pH, Concentration gradient 1) 2) 3) Enzymes –biological catalysts that speed up reactions yet remain unchanged e.g. respiration in the mitochondria 1) Enzyme and substrate 2)Substrate binds to active site 3) Substrate is broken down A cell nucleus contains 46 Chromosomes, which carry genes. Different versions of genes are called alleles. A chromosome is a DNA double helix Enzymes have an optimum temperature and pH. Changes in pH/temp can denature the enzyme so its shape changes and the substrate can’t bind to the active site Uses of Enzymes -Biological washing powders -In baby foods (proteases) -In slimming foods- fructose is made using isomerases. Fructose is sweeter than glucose so less is needed. Enzymes and digestion Large molecules are broken down so they can be absorbed. -Amylase breaks down starch into sugars in the mouth and small intestine. -Proteases breakdown proteins into amino acids in the stomach and small intestine. -Lipases breakdown fats into fatty acids and glycerol in the small intestine. - Enzymes in the stomach work best at acidic pH’s; enzymes in the small intestine work best at alkaline pH’s (bile neutralises acid from the stomach and provides these conditions). Starch 46=chromosomes in normal cell 23=chromosomes in sex cells glucose Stem cells: unspecialised; differentiate to form other cells (used for repair); from bone marrow or embryos A gene codes for specific sequence of amino acids, to make a specific protein Caused by recessive allele (so two copies of allele are needed). A thick sticky mucus is produced affecting air passages and digestive systems Polydactyly-Caused by dominant allele (so only one of allele are needed). Affects the number of digits. Treat illness Expensive Ethics of using embryo Early organisms = softbodied = few fossils Fossilisation = rapid burial, no oxygen, replacement of tissues, time, discovery… Parents Cc x Cc Gametes C or c x C or c (egg/sperm) Possible Outcomes C CC Cc c Cc cc Mitosis-used for normal cell growth 1) Parent cell 2) Chromosomes make identical copies of themselves 3) One cell division occurs 4)Two daughter cells form each with 46 identical chromosomes to the parent cell Physical factors affecting distribution of organsism: Temperature, Nutrients, Light, Water, CO2/O2 Proteins Made of amino acids Examples = enzymes, hormones, antibodies c C 25% sufferers Cystic Fibrosis Cons FOSSILS! Inheritance- Parents who are both carriers of the Cystic fibrosis allele (c). 75% Normal Pros Meiosis –used to make the sex cells (gametes) -the chromosomes are copied -two cell divisions to give four cells - Cells contain half original chromosome number

![Biology B2 revision sheet colour[1]](http://s3.studylib.net/store/data/006699123_1-118546e1cf2edc78c83e680e8a2fb59f-300x300.png)