1 - SP New Moodle
advertisement
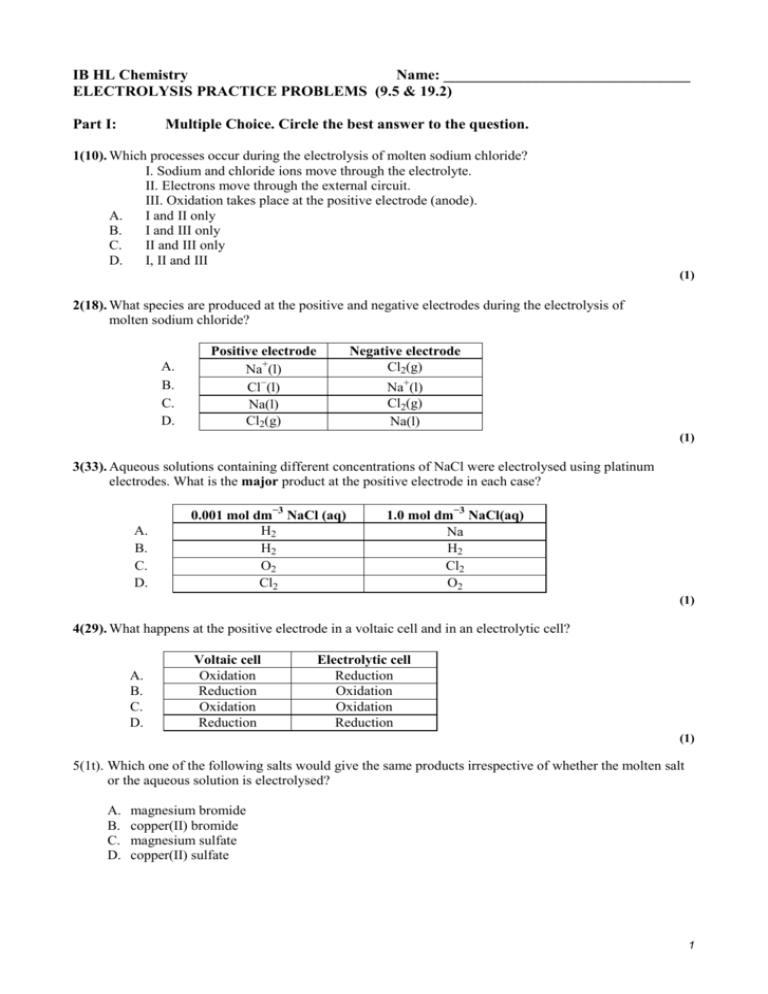
IB HL Chemistry Name: ________________________________ ELECTROLYSIS PRACTICE PROBLEMS (9.5 & 19.2) Part I: Multiple Choice. Circle the best answer to the question. 1(10). Which processes occur during the electrolysis of molten sodium chloride? I. Sodium and chloride ions move through the electrolyte. II. Electrons move through the external circuit. III. Oxidation takes place at the positive electrode (anode). A. I and II only B. I and III only C. II and III only D. I, II and III (1) 2(18). What species are produced at the positive and negative electrodes during the electrolysis of molten sodium chloride? A. B. C. D. Positive electrode Na+(l) Cl−(l) Na(l) Cl2(g) Negative electrode Cl2(g) Na+(l) Cl2(g) Na(l) (1) 3(33). Aqueous solutions containing different concentrations of NaCl were electrolysed using platinum electrodes. What is the major product at the positive electrode in each case? A. B. C. D. 0.001 mol dm−3 NaCl (aq) H2 H2 O2 Cl2 1.0 mol dm−3 NaCl(aq) Na H2 Cl2 O2 (1) 4(29). What happens at the positive electrode in a voltaic cell and in an electrolytic cell? A. B. C. D. Voltaic cell Oxidation Reduction Oxidation Reduction Electrolytic cell Reduction Oxidation Oxidation Reduction (1) 5(1t). Which one of the following salts would give the same products irrespective of whether the molten salt or the aqueous solution is electrolysed? A. B. C. D. magnesium bromide copper(II) bromide magnesium sulfate copper(II) sulfate 1 6(3t). When an aqueous solution of a metal salt is electrolyzed so that the metal is deposited on the cathode, which one of the following will not affect the increase in mass of the cathode, if the other variables are fixed? A B. C. D. the charge on the ion the molar mass of the metal the charge passed the potential difference applied 7(2t) An electric current is passed through two electrolysis cells in series. In the first, copper is deposited on the cathode from aqueous copper(II) sulfate. In the second, silver is deposited on the cathode from aqueous silver nitrate. After a certain length of time the mass of the copper cathode has increased by 1 g. Given that the relative atomic masses of silver and copper are 107.87 and 63.55 respectively, what will the increase in mass of the silver electrode be? A. B. C. D. (2 x 107.87) / 63.55 (2 x 63.55) / 107.87 107.87 / (2 x 63.55) 63.55 / (2 x 107.87) CHALLENGE ec1(5). Aqueous solutions of AgNO3, Cu(NO3)2 and Cr(NO3)3 are electrolyzed using the same quantity of electricity. How do the number of moles of metal formed compare? A. Ag = Cu = Cr B. Ag > Cu > Cr C. Ag < Cu < Cr D. Cu > Ag > Cr (1) ec2(40). Which pair of factors both affect the amount (in mol) of chlorine produced in the electrolysis of aqueous sodium chloride? A. current and temperature B. temperature and chloride ion concentration C. chloride ion concentration and length of time of electrolysis D. pressure and length of time of electrolysis (1) 2+ ec3(14). Metallic tin can be produced by the electrolysis of a molten salt containing Sn ions. Which change(s) would double the amount of tin produced? I. Doubling the current passed during electrolysis II. Doubling the time used for electrolysis III. Using Sn4+ions instead of Sn2+ions A. I only B. II only C. I and II only D. I, II and III (1) ο ο Ec4(23). Which combination of signs for E and ∆G correspond to a spontaneous electrochemical reaction? Eο ∆Gο A. + + B. + – C. – – D. – + (1) 2 Open Response – Answer the question completely. Be sure to notice the point value and respond accordingly. Part II: 1(6) (c) (i) State the name of a solution that would produce only hydrogen and oxygen when electrolyzed using platinum electrodes. …………………………………………………………………………………… (ii) (1) Draw a diagram of apparatus that would allow the gases produced in the reaction in (c) (i) to be collected separately. Annotate your diagram to show the polarity of each electrode and the names and relative volumes of each gas. (3) ……………………………………………………………………………………… ……………………………………………………………………………………… ……………………………………………………………………………………… ……………………………………………………………………………………… ……………………………………………………………………………………… ……………………………………………………………………………………… ……………………………………………………………………………………… ……………………………………………………………………………………… 2(7). – + A X Y CuSO 4 (aq) Two copper strips X and Y are placed in an aqueous solution of copper(II) sulfate and electrolyzed for a certain time. X was then dried and weighed. (i) State and explain what would happen to the mass of X. (3) …………………………………………………………………………………… ……………………………………………………………………………………. …………………………………………………………………………………… (ii) State two ways in which the change in the mass of X could be increased. (2) …………………………………………………………………………………… …………………………………………………………………………………… 3 15. (a) When a concentrated aqueous solution of sodium chloride is electrolyzed using inert electrodes, a different gas is produced at each electrode. (i) Write equations for the oxidation and reduction half-reactions. (2) Oxidation half-reaction:........................................................................................... Reduction half-reaction:........................................................................................... (ii) Explain why sodium is not formed during the electrolysis of aqueous NaCl solution. (1) ........................................................................................................................... ........................................................................................................................... (b) Deduce the products formed during the electrolysis of an aqueous solution of sodium fluoride. Write an equation for the reaction at the positive electrode (the anode) and give your reasoning. (4) ...................................................................................................................................... ...................................................................................................................................... ...................................................................................................................................... ...................................................................................................................................... ...................................................................................................................................... ...................................................................................................................................... ...................................................................................................................................... 21. (i) Solid sodium chloride does not conduct electricity but molten sodium chloride does. Explain this difference, and outline what happens in an electrolytic cell during the electrolysis of molten sodium chloride using carbon electrodes. (4) …………………………………………………………………………………………… …………………………………………………………………………………………… …………………………………………………………………………………………… …………………………………………………………………………………………… …………………………………………………………………………………………… …………………………………………………………………………………………… …………………………………………………………………………………………… (ii) State the products formed and give equations showing the reactions at each electrode. (4) …………………………………………………………………………………………… …………………………………………………………………………………………… …………………………………………………………………………………………… …………………………………………………………………………………………… (iii) State what practical use is made of this process. (1) …………………………………………………………………………………………… …………………………………………………………………………………………… 4 34 (d) Both zinc and tin are used to coat iron to prevent it from rusting. Once the surface is scratched, oxygen and water containing dissolved ions come into contact with the iron and the coating metal. (i) State and explain whether zinc or tin would be more effective in preventing iron from rusting under these conditions. …………………………………………………………………………………… …………………………………………………………………………………… …………………………………………………………………………………… …………………………………………………………………………………… (2) (ii) Electroplating may be used to coat one metal with another metal. Identify the three factors affecting the amount of metal discharged during electroplating. …………………………………………………………………………………… …………………………………………………………………………………… …………………………………………………………………………………… (3) (iii) Explain why electrolysis of aqueous zinc sulfate is not used for coating with zinc metal. …………………………………………………………………………………… …………………………………………………………………………………… …………………………………………………………………………………… …………………………………………………………………………………… (2) 5 IB HL Chemistry REDOX QUIZ (9.5 & 19.2) Part I: FORM D Name: ________________________________ Date: _____________________ Pd:_________ Multiple Choice. 1 (10). D [1] 2 (18). D [1] 3 (33). C [1] 4 (29). B [1] 5 (1t). B [1] 6 (3t). D [1] 7 (2t) A [1] Part II: CHALLENGE ec1 (5). B [1] ec2 (40). C [1] ec3 (14). C [1] ec4 (23). B [1] Open Response 1(6) (c) (i) (aqueous) sodium hydroxide / dilute sulfuric acid / sodium sulfate; Accept correct formulas. Any combination of K+ / Na+ / H+ and NO – / SO 3 2– 4 1 . Halides not acceptable. (“water” is not a solution) (ii) hydrogen / H 2 oxygen / O 2 Or similar suitable diagram. gas collection method; names of gases correct way round at electrodes; 2:1 volume ratio correct way round; 3 – 2(7). (i) (ii) 3(15). (a) mass increases; copper deposited; because X is negative and attracts Cu2+ ions / reduction occurs at X / Cu2+ + 2e– Cu; increase time; increase current; (i) (ii) (b) + oxidation half-reaction: 2Cl− → Cl2 + 2e–; reduction half-reaction: 2H2O + 2e− → H2 + 2OH– / 2H+ + 2e– → H2 Award [1] only if equations are interchanged. States not required. Na has high Eοred /Na+ not readily reduced (in comparison to H2O) / if formed, Na would (immediately) react with water to form Na+ H(g) and O2(g) / accept names; 2H2O → O2 + 4H+ + 4e− / 4OH−→ 2H2O + O2 + 4e−; water is oxidized (instead of the halide); since EοOX for F2 is very negative / Eοred for F2 is very high; Accept answer based on oxidizing / reducing strengths. 3 2 2 1 4 6 4(21). (i) (ii) (iii) 5(34) (d) sodium chloride crystals consist of ions in a rigid lattice / ions can not move about; when melted the ions are free to move or ions move when a voltage is applied; in electrolysis positive sodium ions or Na+ ions move to the negative electrode or cathode; and negative chloride ions or Cl− move to the positive electrode or anode; sodium formed at cathode or negative electrode; Na+ + e Na; chlorine formed at anode or positive electrode; 2Cl– → Cl2 + 2e; 1st and 3rd marks can be scored in (c) (i). manufacture of sodium and chlorine / one stated use of chlorine or sodium; 4 1 (i) zinc; zinc is more readily oxidised than iron and so protects it by reacting preferentially / OWTTE or tin is less readily oxidised than iron and so iron reacts preferentially / OWTTE; (ii) (iii) (2) 4 2 charge on the ion discharged; size / magnitude of the current; time / duration of the electrolysis; 3 positive ions / cations in solution = H+(aq), Zn2+(aq); H+(aq) discharged preferentially; 2 7