Chem 1B-Experiment 14 Report sheet
advertisement

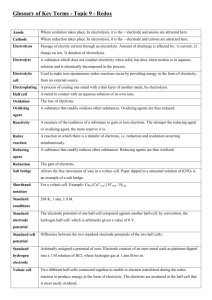
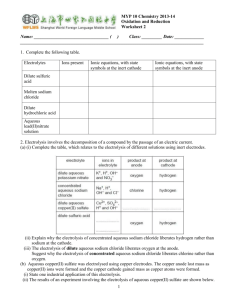
14 Electrochemistry Report Sheet Part I. A Galvanic Cell Observing the direct reaction: Temperature of the coupper(II) sulfate Temperature of the copper(II) sulfate & zinc powder after the reaction. Evidence of a reaction Galvanic cell Evidence of a reaction: This reaction took 2 hours, so you might not have seen the copper plate on the inert electrode, but you should have the voltage of the cell Voltmeter reading Report sheet Exp. 14 Page 1 On the diagram above, clearly label: The anode The cathode Show the direction of e– flow on the diagram. Show the movement of the Cu2+ ions, Zn2+ ions, and K+ ions on the diagram. Show the movement of the Cl– ions and SO42– ions on the diagram. Half reaction for zinc Half reaction for copper YOU CAN ANSWER ALL THREE QUESTIONS IN THIS AREA AND SHOW SUPPORT FOR YOUR ANALYSIS. SUPORT YOUR ANSWER WITH VALID ASSUMPTIONS ABOUT THE PROCESS OF A SPONTANEOUS CELL. Which way are the electrons moving through the wire, toward the cathode or the anode? . Report sheet Exp. 14 Page 2 Which way are the positive ions moving through the solution? Why? Which way are negative ions moving through the solution? Why? Part II. Quantitative Measurement: Determination of the Faraday Write the molecular equation for the reaction of lead(II) oxide with acid Write the net ionic equation for lead (II) oxide with acid Write the molecular equation for the reaction of lead metal with acid Write the molecular equation for the reaction of lead metal with acid PLEASE SHOW YOUR SET UP & CALCULATIONS CLEARLY Mass of the lead electrode before reaction Mass of the lead electrode after the reaction Mass of the lead used for the reaction Moles of lead used for the reaction Report sheet Exp. 14 Page 3 Average amps used Initial time (min) Final time (min) Time of the reaction (min) Time of the reaction in sec Coulombs Faraday Percent error Part III. Electrolysis Reactions Part III, section 1. Experimental Procedure for Electrolysis of Potassium Iodide Solution Experimental Procedure for Electrolysis of Potassium Iodide Solution http://ch302.cm.utexas.edu/images302/electrolytic-cell.jpg Report sheet Exp. 14 Page 4 http://biochemreview.weebly.com/uploads/1/0/4/0/10409756/4057155.jpg?352 Analysis for Electrolysis of Potassium Iodide Solution Which of the possible half reactions should affect the acid / base balance of the solution? Add an acid-base indicator by the appropriate electrode. Record your observations. Is an acid or a base being formed in the reaction? At which electrode does the reaction occur? Support your answer. Which of the oxidation and reduction reactions that you listed in the pre-lab question is actually occurring Look up the E° values for each half reaction. Is the reaction that you observed the one that requires the smallest voltage to make it happen? Report sheet Exp. 14 Page 5 Part III, section 1. Experimental Procedure for Electrolysis of Potassium Iodide Solution Experimental Procedure for Electrolysis of Potassium Nitrate Solution Which of the possible half reactions should affect the acid / base balance of the solution? Add an acid-base indicator by the appropriate electrode. Record your observations. Is an acid or a base being formed in the reaction? At which electrode does the reaction occur? Support your answer. Is elemental iodine (I2) being formed? At which electrode does the reaction occur? Support your answer. Which of the oxidation and reduction reactions that you listed in the pre-lab question is actually occurring Look up the E° values for each half reaction. Is the reaction that you observed the one that requires the smallest voltage to make it happen? Want 1 pt extra credit? Tell me how to improve this handout, or solve this problem: Calculate the potential required to initiate deposition of copper from a solution that is 0.010 M in CuSO4 and contains sufficient H2SO4 to give a hydrogen ion concentration of 1.00 X10—4 MH+. You might need to set up a cell. Report sheet Exp. 14 Page 6