6.1 Electrolysis
advertisement

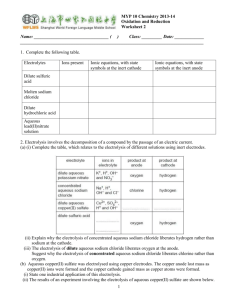
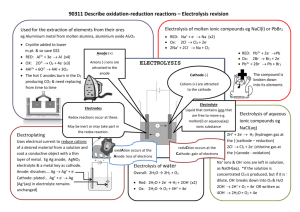
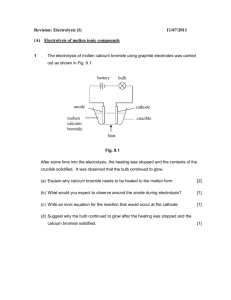
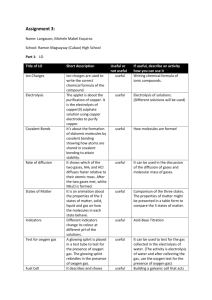
6.1 Electrolysis 1 2 H What are the missing values? Use the table. Li Be Na Mg 3 4 5 13 April 2015 6 7 0 He B C N O F Ne Al Si P S Cl Ar K Ca Sc Ti V Cr Mn Fe Co Ni Cu Zn Ga Ge As Se Br Kr Symbol Outer electrons Ion Charge Li N 5 Cl Ca K Al O 1 6 +1 -2 Br Na Ne Remember: Ions are charged atoms. 8 is the magic number of electrons in the second and third shells. 6.1 Electrolysis 13 April 2015 Key words Electrolysis electrolyte ions Anode cathode inert • Ionic compounds can undergo electrolysis. • Which substances can be electrolysed? • The products of electrolysis. Electroplating uses electricity to cover objects in metal. This can be any metal but is normally copper, silver or gold. Ionic compounds • Ionic compounds are made from charged ions e.g. Sodium Chloride. Na+ ClThe ions can move in solution or when the substance is melted (molten). Electrolysis of Copper Sulfate - + Cu2+ SO4 Anode Cathode • Copper sulfate is an ionic substance. Copper forms positive ions, sulfate forms negative ions. Opposites attract. What charge does the sulfate have? Electrolysis of copper chloride Write the captions for every slide to explain what is happening. Negative – + Positive One electrode is negative, the other is positive. Cathode – + Anode The negative electrode is called the cathode, the positive electrode is called the anode. – + Copper chloride Copper chloride is added to the electrolytic cell. – + CuCl2 Copper chloride has the formula CuCl2. Cathode – + Anode Copper chloride solution CuCl2 Copper chloride solution is bright blue in colour. Cathode – + Anode Cl Cu2+ Cl It is made of a copper ion with a 2+ charge, and two chlorine ions with a charge of 1– on each. Cathode – Cu + Anode Cl Cl The copper ion is attracted to the cathode, where it gains two electrons and becomes a copper atom. Cathode – + Cu Cl Anode Cl The chlorine ions are attracted to the anode, where they lose an electron each and become chlorine atoms and then chlorine molecules. The products of electrolysis • What is produced on the electrodes? – Metal forms on the cathode (-) – Sulfate forms on the anode (+) 13 April 2015 6.1 Electrolysis • Electrolysis involves splitting up a substance using electricity. • Ionic substances can be electrolysed when they are molten or in solution. • In electrolysis positive ions move to the negative electrode (cathode) and negative ions move to the positive electrode (anode). Key words Electrolysis electrolyte ions Anode cathode inert