electrolysis of molten compounds
advertisement

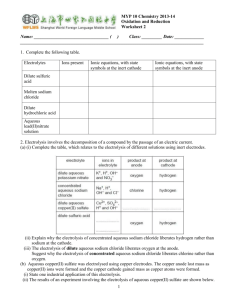
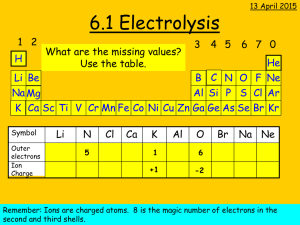
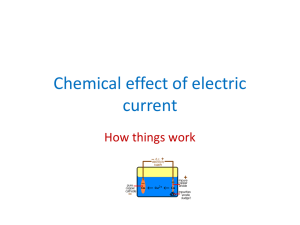
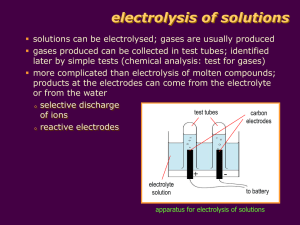
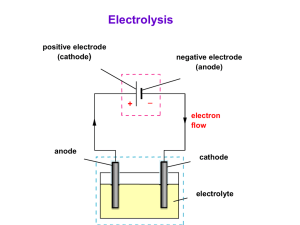
contents • Electrolysis of molten compounds • Electrolysis of solutions • Electroplating • Extraction of metals • Electric cells electrolysis of molten compounds an electrolyte is an ionic compound that conducts electricity; molten state or solution in water molten ionic compounds and solutions of ionic compounds can conduct electricity due to presence of mobile ions that can carry current electrolysis is the conduction of electricity by an electrolyte, leading to its decomposition example: electrolysis of molten sodium chloride inert electrodes (e.g. carbon electrodes) do not react in electrolysis electrolysis of molten compounds electrolysis of molten sodium chloride battery - + carbon anode; attracts anions; oxidation carbon cathode; attracts cations; reduction molten sodium chloride porcelain crucible pipeclay triangle HEAT STRONGLY tripod ammeter to show current flowing electrolysis of molten compounds electrolysis of molten sodium chloride molten sodium chloride contains Na+ and Cl- ions at the cathode, Na+ ions take in electrons to become Na atoms; Na+ ions are discharged Na+(l) + e Na(l) at the anode, Cl- ions give away electrons to become Cl2; Cl- ions are discharged 2Cl-(l) Cl2(g) + 2e- overall reaction 2NaCl(l) 2Na(l) + Cl2(g) electrolysis of molten compounds electrolysis of molten sodium chloride electrons flow from battery into cathode sodium metal produced electrons flow from anode into battery molecules of chlorine gas produced sodium atom sodium ion attracted to cathode sodium ion takes electron from cathode chlorine atom chloride ion gives electron to anode chloride ion attracted to anode cathode anode electrolysis of molten compounds electrolysis of other molten compounds when a molten ionic compound is electrolysed, metal is produced at the cathode; non-metal is produced at the anode Molten Electrolyte Product at Cathode Product at Anode calcium chloride, CaCl2 calcium, Ca chlorine, Cl2 sodium iodide, NaI sodium, Na iodine, I2 lead(II) oxide, PbO lead, Pb oxygen, O2