Organic Chem Notes
advertisement
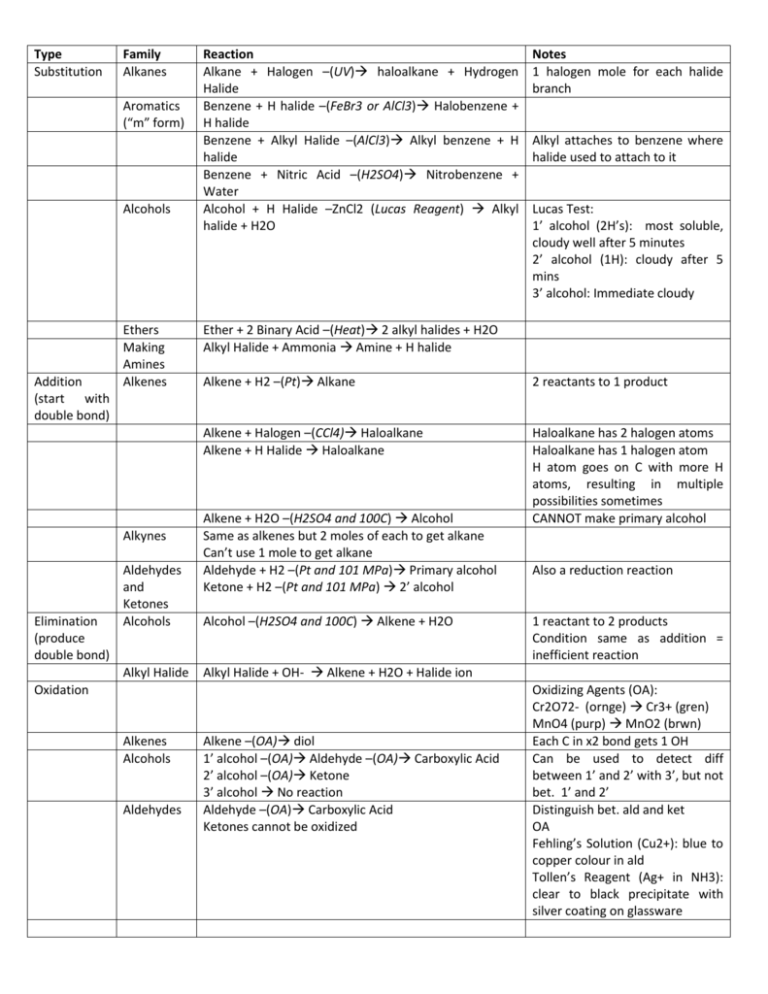
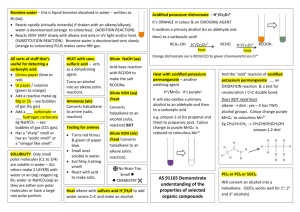
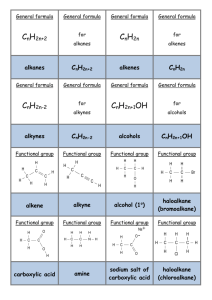
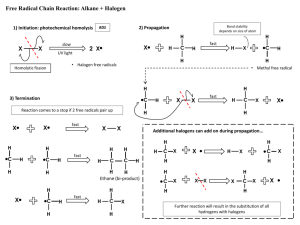
Type Substitution Family Alkanes Aromatics (“m” form) Alcohols Addition (start with double bond) Ethers Making Amines Alkenes Alkynes Elimination (produce double bond) Aldehydes and Ketones Alcohols Alkyl Halide Reaction Alkane + Halogen –(UV) haloalkane + Hydrogen Halide Benzene + H halide –(FeBr3 or AlCl3) Halobenzene + H halide Benzene + Alkyl Halide –(AlCl3) Alkyl benzene + H halide Benzene + Nitric Acid –(H2SO4) Nitrobenzene + Water Alcohol + H Halide –ZnCl2 (Lucas Reagent) Alkyl halide + H2O Aldehydes Alkyl attaches to benzene where halide used to attach to it Lucas Test: 1’ alcohol (2H’s): most soluble, cloudy well after 5 minutes 2’ alcohol (1H): cloudy after 5 mins 3’ alcohol: Immediate cloudy Ether + 2 Binary Acid –(Heat) 2 alkyl halides + H2O Alkyl Halide + Ammonia Amine + H halide Alkene + H2 –(Pt) Alkane 2 reactants to 1 product Alkene + Halogen –(CCl4) Haloalkane Alkene + H Halide Haloalkane Haloalkane has 2 halogen atoms Haloalkane has 1 halogen atom H atom goes on C with more H atoms, resulting in multiple possibilities sometimes CANNOT make primary alcohol Alkene + H2O –(H2SO4 and 100C) Alcohol Same as alkenes but 2 moles of each to get alkane Can’t use 1 mole to get alkane Aldehyde + H2 –(Pt and 101 MPa) Primary alcohol Ketone + H2 –(Pt and 101 MPa) 2’ alcohol Alcohol –(H2SO4 and 100C) Alkene + H2O Also a reduction reaction 1 reactant to 2 products Condition same as addition = inefficient reaction Alkyl Halide + OH- Alkene + H2O + Halide ion Oxidation Alkenes Alcohols Notes 1 halogen mole for each halide branch Alkene –(OA) diol 1’ alcohol –(OA) Aldehyde –(OA) Carboxylic Acid 2’ alcohol –(OA) Ketone 3’ alcohol No reaction Aldehyde –(OA) Carboxylic Acid Ketones cannot be oxidized Oxidizing Agents (OA): Cr2O72- (ornge) Cr3+ (gren) MnO4 (purp) MnO2 (brwn) Each C in x2 bond gets 1 OH Can be used to detect diff between 1’ and 2’ with 3’, but not bet. 1’ and 2’ Distinguish bet. ald and ket OA Fehling’s Solution (Cu2+): blue to copper colour in ald Tollen’s Reagent (Ag+ in NH3): clear to black precipitate with silver coating on glassware Condensatio n Alcohols Alcohol + Alcohol –(H2SO4 and 140C) Ether + H2O Amines Amine + Carboxylic Acid –(H2SO4 and Heat) Amide + Only 1’ and 2’ amines H2O H from N, OH from carboxylic acid Amides + H2O –(H2SO4 and Heat) Amine + Carboxylic Acid Amides VS Elimination: H and OH of water come from different molecules Alcohol + Carboxylic Acid –(H2SO4 and Heat) Ester + Esterification H2O H from hydroxide, OH from carboxylic acid