Hydrocarbon Derivatives
advertisement

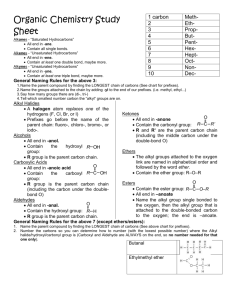
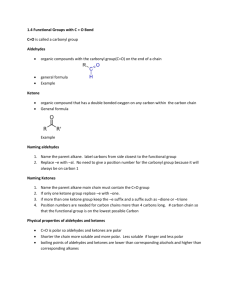
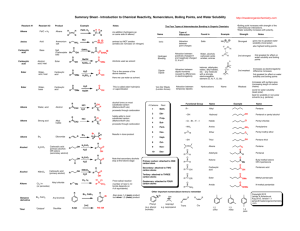
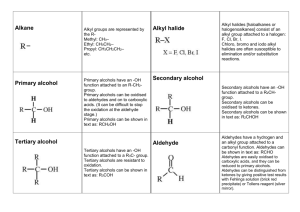
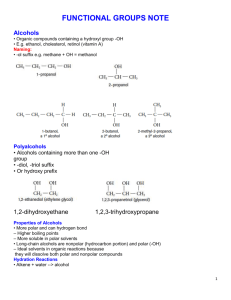
Hydrocarbon Derivatives molecular compounds of carbon and hydrogen that contain at least one other element. ex) alkyl halide, alcohol, carboxylic acid, ester Alkyl Halides one or more hydrogen atoms are replaced with a halogen (F, Cl, Br, I). Many of these are carcinogenic or toxic. Compounds include CFC’s, Teflon coatings and insecticides. Naming Organic Halides number parent chain from end closest to halogen, for a cycloalkane, start numbering at halogen use shortened names, put in alphabetical order and use prefixes as needed: bromo, chloro, fluoro, and iodo. name and number alkyl groups Ex. 1,2-dichloroethane Alcohols contain an hydroxyl (-OH) functional group-is polar higher boiling point than alkanes because of hydrogen bonds. Chains up to 12 C are liquid. short chain alcohols (methanol,ethanol) are very soluble in water due to polarity Longer chains become more non polar and do not dissolve in water but with non polar compounds Naming Alcohols name alkanes but replace the ending –e with the ending –ol unless there is a prefix then leave the –e and add –ol after prefix number closest to the OH the position of the OH group(s) is indicated with a number(s) before the –ol. use prefixes to indicate the number of OH groups name and number alkyl groups Examples ethanol 2-methylpropan-2-ol propane-1,2,3-triol rubbing alcohol propan-2-ol Carboxylic Acids contain a carboxyl (- COOH) carboxyl is polar, easily form hydrogen bonds. higher boiling points than other hydrocarbons and derivatives short chains are liquids and soluble in water, longer chains are waxy solids and not soluble hydrogen on the hydroxyl is acidic. found in sour fruits and vinegar Ex. Ethanoic acid = vinegar Naming Carboxylic Acids Replace the alkane ending, –e, with the ending -oic acid. Carboxyl is position 1 Name and number alkyl chains Ex. butanoic acid Some carboxylic acids have more than one carboxylic acid group, so they are given common names Ex) oxalic acid and citric acid. Esters functional group is similar to carboxyl except that the hydrogen on the hydroxyl is replaced with a carbon chain. responsible for the smells of many fruits and vegetables (volatile so create aromas) without an –OH group, can not make hydrogen bonds so boiling points are lower than carboxylic acids Small esters are liquids, larger are waxy solids 4 carbons or fewer are soluble, larger are not soluble in water formed when a carboxylic acid reacts with an alcohol Naming Esters Two parts: The name from the acid (contains C=O) is changed from –oic acid to –oate and is the main chain (name last) The name of the alkyl group from the alcohol ends in –yl and is given first. Example: ethyl ethanoate