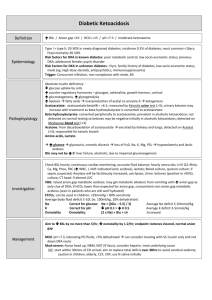
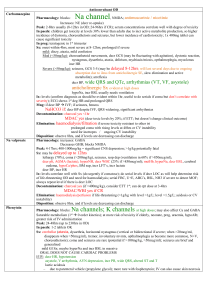
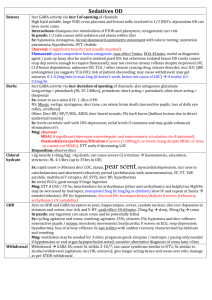
Diabetic Ketoacidosis Use N saline by default until BSL
advertisement

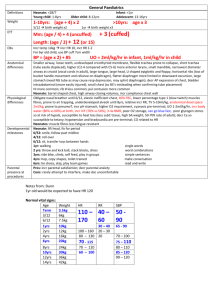
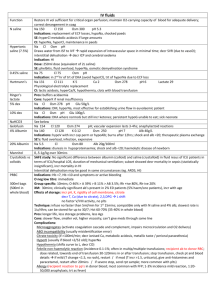
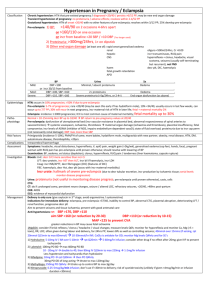
Use N saline by default until BSL <15 0.45% saline + 5% dex Diabetic Ketoacidosis Definition Epidemiology Pathophysiology Investigations Management Incr BSL / AG >10 / Bic <15 / pH <7.3 / mod ketonaemia Fetal mortality 30-50% Type I > type II; 20-30% in newly diagnosed DM; incidence 0.5% of DM; most common <18yrs; RF for DKA in known DM: poor metabolic control; low SE status; prev DKA; adolescent female; psych disorder RF for DKA in unknown DM: <5yrs, FH DM, low SE status, meds (eg. High dose steroids, antipsychotics, immunosuppressants) Trigger: Concurrent infection, non-compliance with meds, MI Absolute insulin deficiency Decr glu uptake by cells Incr counter-regulatory hormones – glucagon, adrenaline, GH, cortisol Incr gluconeogenesis, incr glycogenolysis Incr lipolysis f.a. overproduction of ACoA ketogenesis Acetoacetate: acetoacetate:betaHB = >6:1; measured by Ketostix urine test (>3); urinary ketones may increase with trt as beta-HB converted to acetoacetate Beta hydroxybutyrate: converted peripherally to acetoacetate; prevalent in alcoholic ketoacidosis; not detected on normal testing so ketones may be negative initially in alcoholic KA; detected on Medisense blood test (>3) Acetone: from decarboxylation of acetoacetate excreted by kidneys and lungs; detected on Acetest (>5); responsible for ketotic breath Amino acids, Lactate Incr glu glycosuria, osmotic diuresis loss of H20, Na, K, Mg, PO4 hypoV and lactic acidosis BSL may not be incr if: liver failure, alcoholic; due to impaired gluconeogenesis Check BSL hourly; continuous cardiac monitoring; accurate fluid balance; hourly neuro obs; U+E Q2-4hrly; Ca, Mg, Phos, FBC (incr WBC, L shift indicated lactic acidosis), lactate; Blood culture, sputum culture: if sepsis suspected; Amylase will be factitiously increased, use lipase; Urine: ketones (positive in >95%); culture; CT head: if altered LOC VBG: AGMA; may get met alk from vomiting with incr AG as only clue of DKA; if HCO3 lower than expected for AG, concomitant NAGMA (seen in patients who are still well hydrated) ETCO2: can be used in children; <29mmHg = 80% sens average body fluid deficit 5-10L (ie. 100ml/kg, 10% dehydration); Na correct for glu: Na + ((Glu – 5.5) / 3) average Na deficit 5-10mmol/kg K correct for pH: decr pH 0.1 = incr K 0.5 average K deficit 3-5mmol/kg Osmolality osm: (2 x Na) + Glu + Ur increased Aim decr BSL by no more than 5/hr, decr osm by 1-2/hr; endpoint: ketones cleared, normal AG Mild = pH >7.3, tolerating PO fluids, <5% dehydrated can consider treating with SC insulin only and not down DKA route Mod-severe: Nurse head up, NBM, NGT (if ileus), consider heparin, treat underlying cause IVF: start within 30mins ED arrival; aim to replace total deficit over 48hrs to avoid cerebral oedema; caution in children, elderly, CCF, CRF; use N saline initially Adults: 1L stat (if dehydrated ++) Children: Adults: 10-20ml/kg bolus N saline 1L over 1hr if shocked, until haemodynamically stable 1L over 2hrs 1L over 4hrs 1L over 10hrs use N saline Add K to fluids in 2nd hour and once UO established and K <5 Children: replace deficit over 48hrs If K >5 = none K 4-5 = 10mmol/hr K 3-4 = 30mmol/hr K <3 = 40mmol/hr Na <150 / osm <320 use N saline Na >150 / osm >320 use 0.45% saline and correct over 72hrs Deficit = %dehydration X weight X 10 (remember to subtract any bolus given Both: ) When BSL <15 / if BSL decreasing by >5/hr use 0.45% saline + 5% dex, aiming BSL 12-15 If BSL <10 but ongoing ketones use 0.45% saline + 10% dex Once K <5.5, patient PU’ing, insulin infusion started, add 40mmol KCl per 1L bag Insulin: start 1hr after initial fluids; only start if K >3.4, otherwise replace K first 0.1 iu/kg/hr (max 6iu/hr) actrapid decr to 0.05 iu/kg/hr when BSL <12 and acidosis improving, aiming BSL 9-14; if BSL still too low despite this, can stop infusion for 10-15mins only Use 0.05iu/kg/hr if new onset DM in child or young child, as will be sensitive to insulin Decr to 0.05iu/kg/hr for 4hrs if K <3 Criteria for change to SC: BSL <11, HCO3 >16-18, pH >7.3, AG <15, E+D, normal LOC, ketones cleared When stopping, give mixed short and long acting SC dose @ least 1hr before stopping infusion Phosphate / Mg: only if severe / symptomatic decr phos / Mg K2PO4 5mmol/hr MgSO4 2.5g over 1hr HCO3: only if pH <7, HCO3 <5, life-threatening hyperK, coma, and haemodynamic compromise unresponsive to fluid resus May cause rapid decr K, worsened intracellular acidosis, impaired offloading of O2, Na overload, hypertonicity, cerebral oedema (4x incr risk), vol overload, paradoxical CNS acidosis HCO3 mmol = 0.15 x base deficit x kg / 0.5-2mmol/kg over 1-2hrs Endpoint: pH >7.1, HCO3 >10 Discharge Prognosis Admit ICU if: In children: <2yrs, pH <7.1, altered LOC, need for arterial line, severe hyperosmolar dehydration Patient education (incr insulin by 4iu or more when intercurrent illness, even if not eating) Mortality 5-15% (0.3-1% in children) - due to underlying disease, cerebral oedema, thromboembolism Poor prognostic factors: ARF, altered LOC, hypotension Complications Cerebral oedema DD Other crises Decr BSL, decr K, decr phos, ARDS, recurrence, thrombosis Leading cause of mortality from DKA; 70% mortality; 10% survivors have permanent neuro sequelae; more common in children (1% incidence) Risk factors: 1st presentation; long history poor control; <5yrs; initial corrected Na >160; severe incr osm; persistent hypoNa; severe acidosis; ??related to overaggressive fluid resus Sx: onset 4-12hrs after starting trt; headache, decr Na, altered LOC, decr HR, HTN, decr RR, incontinence, pupil changes, seizures, papilloedema Trt: 0.5-1g/kg mannitol IV bolus / 5-10ml/kg 3% saline IV over 30mins; give half maintenance fluids; admit PICU; neurosurg review; CT; hyperventilate if ETT DD: cerebral venous sinus thrombosis (may require contrast CT / MRI for detection if initial CT normal) Ethylene glycol, isopropyl alcohol, salicylates New onset hyperG but no DKA: give 0.1iu/kg SC regular insulin; admit HyperG, known DM, no DKA: give additional 10% of normal daily insulin dose as regular insulin SC Notes from: Dunn, Cameron (adult and child), TinTin, Starship Guidelines