Anticonvulsant OD fact sheet

Carbamazepine
Na valproate
Phenytoin
Anticonvulsant OD
Pharmacology: blocks:
Na channel
, NMDA;
antimuscarinic / nicotinic
Increases: NE (decr re-uptake)
Peak: 2-8hrs usually (8-12hrs in OD; 24-96hrs if CR); serum concentrations correlate well with degree of toxicity
In paeds: children get toxicity at levels 30% lower than adults due to incr active metabolite production, so higher incidence of dystonia, choreoathetosis and seizures, but lower incidence of cardiotoxicity; 1x 400mg tablet can cause significant toxicity
In preg: teratogenic in 1 st trimester
Sx: onset within 4hrs, most severe at 8-12hrs; prolonged if severe mild: dizzy, ataxia, mild confusion
Mod (<50mg/kg): choreoathetoid movements, decr GCS (may be fluctuating with agitation), dystonic reaction,
nystagmus, dysarthria, ataxia, delirium, mydriasis/miosis, opthalmoplegia, myoclonus
incr HR
Severe (>50mg/kg): seizures, GCS 3-5 (may be
delayed 8-12hrs
; will last several days due to ongoing
absorption due to ileus from anticholinergic SE , slow elimination and active
metabolite); arreflexia
decr BP, wide QRS and QTc, arrhythmias (VT, VF, asystole)
anticholinergic Sx
evident at high doses
hypoNa, incr BSL usually needs ventilation
Ix: levels (confirm diagnosis as should be evident within 1hr, useful to do serials if coma but don’t correlate with severity ); ECG shows 1 st deg HB and prolonged QRS
Mng: if decr BP
IVF; if seizures, benzos
NaHCO3 if
: decr BP despite IVF, QRS widening, significant arrhythmias
Decontamination: charcoal yes <1hr
MDAC yes
(decr toxic levels by 20%; if ETT; but doesn’t change clinical outcome)
Elimination:
haemodialysis/filtration
if severe toxicity resistant to other trt
prolonged coma with rising levels at 48hrs or CV instability
need for inotropes / ongoing CV instability
Disposition: observe 8hrs, and if levels are decreasing can discharge
Pharmacology: increases: GABA
Decreases GHB; blocks NMDA
Peak: 4-17hrs; 400-1000mg/kg = significant CNS depression; >1g/kg potentially fatal
Sx: may be
delayed up to 12hrs
lethargy (70%), coma (>200mg/kg), seizures, resp dep (ventilation in 60% if >850mcg/ml), decr plt, AGMA (lactate), hyperNH, decr WBC (25% if >850mcg/ml); metHb, hyperNa, decr BSL , cerebral
oedema, hypoCa/phos , BM sup, incr LFT’s, incr lactate
decr BP, incr HR
Ix: levels correlate well with Sx (do urgently if comatose); do serial levels if decr LOC as will help determine risk of life-threatening OD and need for haemodialysis; serial FBC, U+E, ABG’s, BSL, NH3 if severe to detect MOF; always repeat level if there is decr LOC
Decontamination: charcoal yes (if >400mg/kg), consider ETT 1 st ; can do rpt dose at 3-4hrs
MDAC/WBI yes if CR
Elimination: haemodialysis/perfusion if life-threatening (>1g/kg with level >1g/L; level >1.5g/L; acidosis or CV instability)
Disposition: observe 8hrs, and if levels are decreasing can discharge
Pharmacology: blocks:
Na channels; K channels
at high doses ; may also affect Ca and GABA
Saturable metabolism (1 st
0 order kinetics); at more risk of toxicity if elderly, neonate, preg, uraemia, hypoAlb; greater risk of IV administration
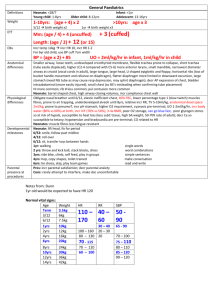
Peak: 24-48hrs (up to 230hrs in OD)
In paeds: 1-2 tablets OK
Sx: cerebellar (
ataxia
, dysarthria, horizontal nystagmus (vertical or bidirectional if severe; when >20mcg/ml,
disappears when >50mcg/ml), tremor, involuntary mvmts, opthalmoplegia as become more comatose, N+V,
choreoathetosis); coma and seizures are rare (potential if >100mg/kg, >50mcg/ml); seizures are brief and
generalised
mild GI Sx; maybe hyperNa and incr BSL in massive
ORAL DOES NOT CAUSE CARDIAC PROBLEMS
If IV: decr HR, hypotension
asystole, V arrhythmia, AVN depression, incr PR, wide QRS, altered ST and T
lactic acidosis
– due to parenteral vehicle (propylene glycol); more rare with fosphenytoin; IV can also cause skin necrosis
and compartment syndrome
Ix: levels (useful to confirm diagnosis; correlate with toxicity; coma >50mg/L; nystagmus >20mg/L; serial levels in severe intoxication); no need for cardiac monitoring after PO OD
Mng: supportive; falls are greatest risk; charcoal if <4hrs (MDAC may be useful); benzos for seizures; if IV, may need atropine / pacing; do serial levels and discharge once levels falling
Ethosuximide, phenobarb, primidone Other older agents
Newer agents Eg. Gabapentin, lamotrigine, levetiracetam, pregabalin, topiramate
Less toxic (mild decr LOC, ataxia, N+V); Sx within 2hrs; resolve in 24hrs; topiramate can cause metabolic acidosis and seizures; lamotrigine can cause cardiotoxicity; can give charcoal if ETT, otherwise usually not severe enough to warrant; observe 6hrs
Pharmacology: incr GABA (by incr release or decr reuptake); lamotrigine and topiramate also block Na channel
Ix: serum levels less helpful