Carboxylic Acid Derivatives note guide
advertisement

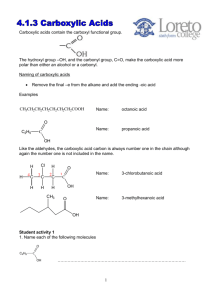
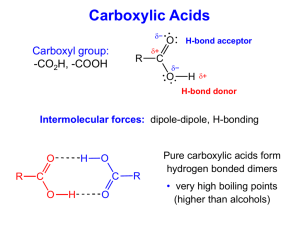
Carboxylic Acid Derivatives Esters: Esters are ____________________________________________________ that are formed from the reaction of a carboxylic acid with an ___________________. General Reaction: H+, heat Example: Ethanoic acid + ethanol + water Properties of Esters: • Mildly _______________ • Have pleasant _______________________________ • Found in _____________________________________________________________ • Boil at approximately the same temperature as ____________________________________ of similar molecular weights • _____________________________ ones are somewhat soluble in water Naming Esters: • Use the _____________________ portion of the ________________________ as the first name. • Remove the __________________________________ ending of the carboxylic acid and replace it with ______________________. • The same naming rules apply if the _______________________________________ of the carboxylic acid is used. Examples: YOU TRY THESE! Esterification Reactions (making esters): 1) Ethanoic acid + ethanol 2) Butanoic acid + methanol 3) How would you make ethyl propanoate from only alcohols??? • Fats and oils are ____________ of the alcohol _________________ • Carboxylic acid + alcohol ester + water O H2C 3 CH3(CH2)14COOH + H2C OH HC OH C(CH2)14CH3 O HC 3 Palmitic acid H2C O O O OH Glycerol C(CH2)14CH3 H2C O C(CH2)14CH3 Triglyceride Tripalmitoylglyceride Formation of Soap (__________________________________________________): • When ______________ are hydrolyzed by ______________________________________, the products are _____________. • ____________ -catalyzed hydrolysis of esters • General Reaction: Ester + water OH C.A. salt + alcohol • __________ is a salt of long-chain carboxylic acids • Lower molecular weight salts (<12 carbons) have _______ water _____________ and large ______________ • __________ salts are more water soluble than _________ salts • Saponification Reaction: • Ester + water • Ex: methyl ethanoate + water base C.A. salt + alcohol (AKA: ___________________) Acid Chlorides: IUPAC name - Replace the ____________ ending of the IUPAC name with _____________ Common name – Replace the ___________ ending of the common name with _____________ Examples: Properties of Acid Chlorides: • ________________________, _______________________________ chemicals • Slightly ____________________________ • Boil at approximately the same temperature as _____________________________________ of similar molecular weights • React violently with _____________ Formation of Acid Chloride: Example: Ethanoic acid Ethanoyl chloride Hydrolysis of Acid Chloride: Example: Ethanoyl chloride Ethanoic acid Acid Anhydride: • An acid anhydride is _________carboxylic acids with a _____________ molecule removed. • “Anhydride” means ________________________________________________. Formation of Acid Anhydride: