Naming Esters - pesteresters
advertisement

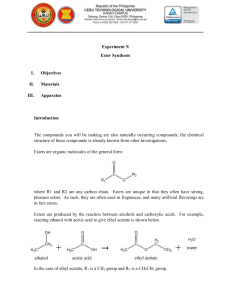
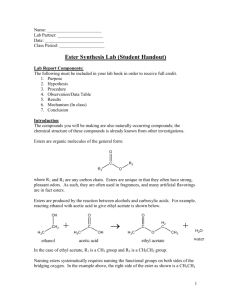
Naming Esters Esters (R-CO-O-R') are named as alkyl derivatives of carboxylic acids. The alkyl (R') group is named first. The R-CO-O part is then named as a separate word based on the carboxylic acid name, with the ending changed from -oic acid to -oate. Alcohol component the root name is based on the longest chain containing the -OH group. The chain is numbered so the -OH has the lowest possible number. Carboxylic acid component the root name is based on the longest chain including the carbonyl group. Since the carboxylic acid group is at the end of the chain, it must be C1. The ester suffix for the acid component : -ane + -oate = -anoate etc. Example methyl propanoate An ester name has two parts - the part that comes from the acid (propanoate) and the part that shows the alkyl group (methyl). Propanoic Acid The hydrogen in the -COOH group is replaced by an alkyl group in this case, a methyl group. Ester names are confusing because the name is written backwards from the way the structure is drawn Example #2 Ethyl ethanoate This is probably the most commonly used example of an ester. It is based on ethanoic acid (hence, ethanoate), a 2 carbon acid. The hydrogen in the -COOH group is replaced by an ethyl group. Example of Acids HCOOH = methanoic acid CH3COOH = ethanoic acid CH3CH2COOH = propanoic acid C3H7COOH = butanoic acid Resources http://www.chemguide.co.uk/basicorg/conventions/names2.html http://www.chemguide.co.uk/organicprops/esters/background.html http://www.youtube.com/user/EducatorVids?v=oUMrNkiAKJ8&feature=pyv& ad=8587454348&kw=organic%20chemistry http://www.chem.ucalgary.ca/courses/351/orgnom/esters/esters-01.html