Alkane Alkyl groups are represented by the R
advertisement

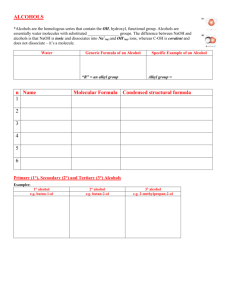
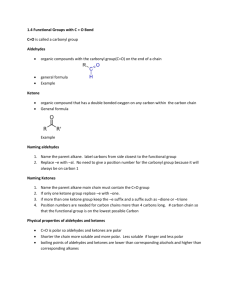
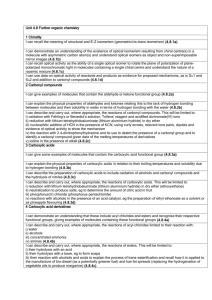
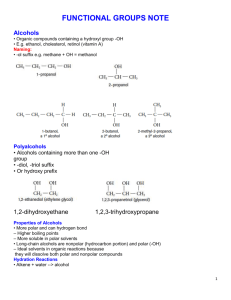
Alkane _ Primary alcohol Alkyl groups are represented by the RMethyl: CH3– Ethyl: CH3CH2– Propyl: CH3CH2CH2– etc. Primary alcohols have an -OH function attached to an R-CH2group. Primary alcohols can be oxidised to aldehydes and on to carboxylic acids. (It can be difficult to stop the oxidation at the aldehyde stage.) Primary alcohols can be shown in text as: RCH2OH Tertiary alcohol Alkyl halide Secondary alcohol Secondary alcohols have an -OH function attached to a R2CHgroup. Secondary alcohols can be oxidised to ketones. Secondary alcohols can be shown in text as: R2CHOH Aldehyde Tertiary alcohols have an -OH function attached to a R3C- group. Tertiary alcohols are resistant to oxidation. Tertiary alcohols can be shown in text as: R3COH Alkyl halides [haloalkanes or halogenoalkanes] consist of an alkyl group attached to a halogen: F, Cl, Br, I. Chloro, bromo and iodo alkyl halides are often susceptible to elimination and/or substitution reactions. Aldehydes have a hydrogen and an alkyl group attached to a carbonyl function. Aldehydes can be shown in text as: RCHO Aldehydes are easily oxidised to carboxylic acids, and they can be reduced to primary alcohols. Aldehydes can be distinguished from ketones by giving positive test results with Fehlings solution (brick red precipitate) or Tollens reagent (silver mirror). Ketone Ketones have a pair of alkyl groups attached to a carbonyl function. Ketones can be shown in text as: RCOR Ketones can be distinguished from aldehydes by giving negative test results with Fehling’s solution (brick red precipitate) or Tollens reagent (silver mirror). Carboxylic acid Carboxylic acids have an alkyl groups attached to a hydroxycarbonyl function. Carboxylic acids can be shown in text as: RCOOH Carboxylic acids are weak Bronsted acids and they liberate CO2 from carbonates and hydrogen carbonates. Ester The carbonyl group is a common functional groups in many compounds including: aldehydes, ketones, carboxylic acids, esters, amides, acyl (acid) chlorides Esters have a pair of alkyl groups attached to a carbonyl + linking oxygen function. Esters can be shown in text as: RCOOR. carboxylic acid + alcohol ester + water This is an acid catalysed equilibrium. Primary amides have an alkyl group attached to an aminocarbonyl function. Primary amides can be shown in text as: RCONH2 Secondary amides have an alkyl group attached to the nitrogen: RCONHR Tertiary amides have two alkyl or aryl group attached to the nitrogen: RCONR2 Primary amines have an alkyl group and two hydrogens attached to a nitrogen atom. Primary amines can be shown in text as: RNH2 Primary amines are basic functions that can be protonated to the corresponding ammonium ion. Carbonyl function Amide Primary amine Secondary amine Tertiary amine Acid chloride Acid chlorides, or acyl chlorides, have an alkyl group attached to a carbonyl function plus an easily displaced chlorine. Acid chlorides highly reactive chemicals. Acid chlorides can be shown in text as: ROCl Amino acid Tertiary amines have three alkyl groups attached to a nitrogen atom. Tertiary amines can be shown in text as: R3N Tertiary amines are basic functions that can be protonated. Secondary amines have a pair of alkyl groups, and a hydrogen, attached to a nitrogen atom. Secondary amines can be shown in text as: R2NH Secondary amines are basic functions that can be protonated. Amino acids have a carboxylic acid, an amino function and a hydrogen attached to a the same carbon atom. There are 20 naturally occurring amino acids. All except glycine (R = H) are chiral and only the L enantiomer is found in nature. Amino acids can be shown in text as: R-CH(NH2)COOH Carboxylate ion or salt Na+ Carboxylate ions are the conjugate bases of carboxylic acids, ie. the deprotonated carboxylic acid. Carboxylate ions can be shown in text as: RCOO– Their salts can be shown in text as: RCOONa Alkene Alkenes consist of a C=C double bond function. Alkanes are planar as there is no rotation about the C=C bond. Alkenes are susceptible to addition reactions. trans-alkene trans-alkenes are 1,2disubstituted functions with the two R, X or other groups on opposite sides of the C=C function. Due to the non-rotation of the C=C bond, cis and trans isomers occur. cis-alkene cis-Alkenes are 1,2-disubstituted functions with the two R, X or other groups on the same side of the C=C function. Due to the non-rotation of the C=C bond, cis and trans isomers occur. Polymer (addition) Ether Ethers have a pair of alkyl groups attached to a linking oxygen atom. Ethers can be shown in text as: ROR Diol or polyol Diols and polyols are alcohols with two or more -OH functions. Diols and polyols are very soluble in water. Polymers consist of small monomer molecules that have reacted together so as to form a large covalently bonded structure. There are two general types of polymerisation: addition and condensation.