File - Thomas Tallis Science
advertisement

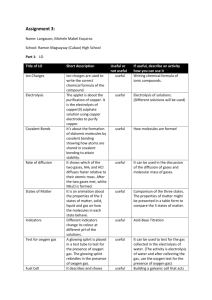
C2 REVISION – CHAPTER 1 – STRUCTURE & BONDING Fill in the gaps: When two elements react together they make a _________ substance called a_________. It is _________ to separate the elements after the reaction. Some atoms react by sharing electrons. We call this _________ bonding. Other atoms react by _________ or _________ electrons. We call this _________ bonding. When atoms react in this way they get the electronic structure of a _________ gas. Use pictures and words to describe each type of bonding: Ionic Fill in this table: Ionic Compound Ratio of ions in compound Sodium chloride Na+ : Cl1:1 Magnesium oxide Formula of compound Covalent MgO Ca2+: Cl1:2 CaCl2 Metallic Fill in this table of more complicated ions: Name of ion Formula of ion Calcium hydroxide, Ca(OH)2 hydroxide NO3CO32Suphate Example of compound Mg(NO3)2 Sodium carbonate CaSO4 KEY WORDS: Electronic structure Covalent bonding Ionic bonding Proton Electron Ion Giant structure (lattice) Metallic bonding ASSESSMENT: C2 REVISION – CHAPTER 2 – STRUCTURE & PROPERTIES IONIC COMPOUNDS What type of force holds the ions together? SIMPLE COVALENT MOLECULES GIANT METALLIC SUBSTANCES How strong are the forces between covalent molecules? [intermolecular forces] Why can metals be bent and shaped? What are delocalised electrons? Draw a giant ionic lattice: How does this affect their melting and boiling point How strong are the forces between atoms in a covalent bond? [intramolecular bonds] Why do ionic compounds have high melting and boiling points? Why do metals conduct electricity? How are polymers classified: What is nanoscience? Thermosetting: Thermosoftening: Why can ionic compounds conduct electricity when molten or dissolved in water? GIANT COVALENT SUBSTANCES Why is graphite slippery and conduct electricity? KEY WORDS: Giant ionic structures Intermolecular forces Macromolecules Fullerenes Shape memory alloys Polymers Thermosetting / Thermosoftening Nanoscience ASSESSMENT: C2 REVISION – CHAPTER 3 – HOW MUCH? Complete the table Relative Charge Relative Mass Write how many there are in: 23 Na11 Electrons: Proton Protons: Neutron Neutrons: What is an isotope? Electron What is percentage yield and what is the equation to calculate it? What is atom economy and what is the equation to calculate it? Calculate the percentage yield of calcium carbonate when 200tonnes of limestone is used and 98tonnes of carbon dioxide is produced: How do we identify food additives? What is gas chromatography? What is Ar? What is mass spectrometry? What is Mr? What is the Mr of C2H5OH? What is a mole? Balance the equation and say how many moles of each substance there are: H 2 + O2 H2O What is the symbol for a reversible reaction? Explain what happens after we add just reactants to a reversible reaction? KEY WORDS: Empirical Atomic number formula Mass number Molecular Isotope formula Relative atomic Yield mass Relative formula Percentage yield Reversible mass reaction Mole ASSESSMENT: C2 REVISION – CHAPTER 4 – RATES & ENERGY What do we mean by ‘rate of reaction’? Explain the effect of concentration on the rate of reaction Explain the effect of temperature on the rate of reaction [think about: kinetic energy & number of collisions] Draw diagrams to represent it? Draw diagrams to represent it: What 4 factors affect the rate of a reaction? What must happen for a reaction to occur? What is the smallest amount of energy that must be overcome for a reaction to occur? Low concn High concn Low temp High temp How does surface area affect the rate of reaction? What do catalysts do? Explain exothermic reactions: Explain endothermic reactions: What happens to them during a reaction? What energy changes are involved in a reversible reaction? KEY WORDS: Collision theory Activation energy Catalyst Exothermic Endothermic Thermal decomposition ASSESSMENT: C2 REVISION – CHAPTER 5 – SALTS & ELECTROLYSIS What is a base? What is produced when an acid and a metal react? What is electrolysis? What is an alkali Acid + Metal What do we call the substance that is broken down during electrolysis What ions make something acidic? Give a specific example: What is the negative electrode called? What is another name for an acid? P__________ D__________ What is the positive electrode called? What is produced when an acid and a base react? What ions make something alkali? Label a diagram showing the electrolysis of copper bromide Acid + Base What is the pH scale? How is electrolysis used to extract aluminium? Give a specific example: Why to we electrolyse brine? What is electroplating? What are the half equations? How is it work? What ions are formed? KEY WORDS: Alkalis Salt Bases Neutralisation Acids Precipitate Neutral Electrolysis State symbol Reduction Indicator Half equation pH scale Electroplating ASSESSMENT: